Auto-aggression in adults manifests itself in the form of destructive behavior. A person directs the negative impact only on himself. This can manifest itself in alcoholism, drug addiction, derogatory expressions, and self-flagellation. In the absence of help, everything can end in suicide.
Auto-aggression is not a mental illness, but it can be considered a behavioral deviation
What it is
In psychology, auto-aggression is a pathological reaction of an individual to stress. In a normal state, a living being does not attack itself, as this will lead to serious problems. Men are more prone to this disorder.
A pathological reaction only in extreme cases takes a dangerous form: alcoholism, drug addiction, suicide. In this case, the person already risks actually losing his life.
Important! In most cases, the individual engages in self-flagellation, self-cutting, and derogatory remarks about himself.
Auto-aggression is not the only definition in psychology. In psychoanalysis, it is literally understood as “turning against oneself.” In some situations, a person cannot express his anger at an object, so he has to direct it towards himself.
From the point of view of A.I. Ipatov, this term is understood as a personality anomaly that appears as a result of a violation of the socialization process. In psychology, there are several forms of auto-aggression, each of which has its own characteristics.
Correction of teenage self-aggression
To treat self-aggression and self-harmful behavior, psychotherapeutic techniques and medication are usually used. The first group includes:
- Family psychotherapy. Conversations and activities that are held with the entire family in which an auto-aggressive teenager lives. All participants learn to show each other empathy, kindness and care, and in practice practice safe ways to splash out negative emotions and adequate conflict resolution strategies.
- Cognitive behavioral psychotherapy. The technique is individual. Includes identifying negative attitudes in a teenager, for example, low self-esteem, increased responsibility, uncertainty, and discussing the inappropriateness of dealing with them using self-harming methods. There is also the development of techniques for stopping attacks of auto-aggression and their gradual replacement with more adequate ways to discharge negativity.
- Group training work. It is aimed at developing the ability to interact, resolve conflicts, and respect each other’s opinions. Observing feedback from other participants, the teenager begins to see his own importance and independently determines his positive and negative personal qualities.
The second group includes several types of drugs: antipsychotics, antidepressants and tranquilizers. They are prescribed by a psychiatrist or psychotherapist in severe cases, when there is a high probability of a teenager causing serious harm to his health.
Main reasons
Psychological trainings for adults
Experts do not have a consensus on why a person might develop such a deviation. Adults are more resistant to various stressful situations, children experience everything much more sensitively.
In a child, auto-aggression develops against the background of character traits: low self-esteem, a small number of social contacts. The reaction may occur against the background of a conflict with an adult or problems in the family.
Sometimes children use aggression to attract their parents' attention.
Self-harm is a form of punishment. A child may do this out of guilt. With an adult, everything is a little different. The term “auto-aggression” can appear in the life of any individual. People who grew up in an atmosphere of hatred are most prone to such behavior.
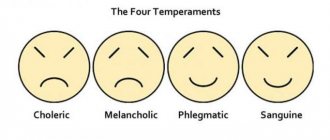
Individual psychological factors of auto-aggression include impulsiveness, immaturity, inflated demands, and inadequate self-esteem. Temperament also influences this; melancholic people are most prone to self-hatred.
Symptoms
It should be noted that an attack of auto-aggression can occur in a person both consciously and unconsciously, so it is not always possible for a person to explain the reason for such behavior.
The following factors may indicate that a person is having such attacks:
- the presence of scars, fresh wounds on the arms, legs and other accessible parts of the body (most often these are stripes, marks from nails or teeth);
- the habit of wearing long sleeves and overalls appears, even if it is out of season;
- detachment from loved ones and acquaintances;
- a person often talks about being accidentally injured;
- irritability, sudden mood swings;
- a person begins to use alcohol and drugs;
- becomes withdrawn, responds sharply to questions;
- traits appear in the psychotype that were previously unusual for him.
During the manifestation of autoregression, a person, consciously or not, can inflict cutting wounds on himself, both with his hands and with objects that are at hand. In some cases, he pulls out his hair, beats himself with his hands or improvised means, and tears his face. In other words, he causes himself physical or moral harm in every possible way.
How to avoid self-aggression
How to develop imagination in adults and children - recommendations
In order to cope with a problem, a person must first acknowledge its existence. After this, he will have to learn to cope with negative emotions. You can’t suppress them, you should express them in a safe way.
Important! The best way to do this is by speaking words.
Aggression directed at oneself only brings destruction of personality. Therefore, it needs to be warned and stopped. Such a violation does not appear in those who perceive themselves adequately and do not overestimate their capabilities.
Aggression towards oneself develops in a person at a time when he is in an unstable state. For example, experiencing emotional burnout, stress or nervous tension.
Aggression towards oneself appears when an individual gets used to perceiving himself ideally. Perfectionism makes him feel dissatisfied when it is impossible to please every person. The lower the number of internal conflicts, the lower the likelihood of auto-aggression.
Article “Auto-aggression in adolescents”
Auto-aggression as a personal problem in adolescents.
From the point of view of modern psychological theories, auto-aggressive behavior is aggression against one’s own personality. Auto-aggression - manifested in self-accusation, self-humiliation, self-harm, even suicide.
Auto-aggression manifests itself in various forms, including in the form of self-destructive behavior (drunkenness, alcoholism, drug addiction, suicidal behavior, risky sports, provocative behavior). Bad habits can be considered both as a cause and as a consequence of social maladaptation of adolescents, leading to various forms of auto-aggressive behavior.
Drunkenness and alcoholism. Dependence on alcohol in adolescence develops much faster than in adults. Alcohol destroys not only the physical health of a teenager, but also his mental health, and reduces intellectual capabilities. Characteristic symptoms of alcoholism at the behavioral level are: craving for alcohol, fears, inability to concentrate, memory loss, dysfunction of vital organs, as well as unmotivated and spontaneous aggression.
Teenagers who have been exposed to the influence of alcohol are developmentally delayed, are restless, lethargic, get tired quickly, suffer from headaches, and are unbalanced in communication; they constitute a risk group for the development of aggressive forms of behavior.
Drug addiction and substance abuse. Experts note that smoking and drinking alcohol in adolescence create the most favorable background for various types of drug addiction and substance abuse. At the same time, the boundaries between drunkenness, substance abuse and drug addiction quickly disappear, since all the drugs in this series (inducing addiction and dependence) belong to narcotic poisons, the effect of which leads to a harmful disease that is difficult to treat. The formation of addiction to various substances with intoxicating properties depends on the personal characteristics of the teenager. Persons who are emotionally unstable, prone to hysteria, anger, and aggression most often resort to such means.
The causes of addiction to drugs, alcohol, tobacco and other toxic substances are different. They are formed as a result of a number of general social, psychological and physiological factors that encourage a teenager to become addicted to drugs. These reasons include:
- a tribute to fashion in taking various dopings
- unsatisfactory physical and mental state of the body: poor health, presence of mental disorders, hereditary predisposition;
- lack of spiritual communication, moral microclimate, humanity in raising a teenager, frequent quarrels, conflicts;
- a teenager’s tendency to imitate (elders or peers from a disadvantaged social environment);
- the desire to obtain pleasure and pleasure;
-lack of ability to stand up for oneself due to weak will, hence submission to a stronger person or inability to say “no”.
Suicidal behavior. Suicidal behavior (intention or attempt to voluntarily die) is considered a consequence of socio-psychological maladaptation of the individual, arising under the influence of various types of traumatic and stress factors, including as a result of social insecurity and disruption of the mechanisms of interaction between the individual and the environment. Therefore, suicide is largely regarded as an inadequate means of resolving life conflicts (the social side of the problem) and an undesirable way out of a psychological crisis.
Based on this duality, two central groups are distinguished among suicidal motives: motives of trouble (loneliness, loss of meaning in life, loss of loved ones) and motives of conflict, in which, in addition to the suicide, other persons are involved.
Indicators of possible suicidal risk are:
- certain behavioral manifestations, such as suicidal threats, previous suicide attempts, significant changes in a person’s behavior or personality, complaints of “life fatigue” or “hopeless situation”, as well as preparations for a final expression of will;
- certain psycho-emotional states, such as depression, feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, despair, loneliness, uselessness and social isolation, etc.
Risky sexual behavior. Risky sexual behavior - relationships with casual partners, refusal to use condoms - poses a great personal danger in terms of contracting sexually transmitted diseases, the risk of unplanned pregnancy and unwanted paternity.
Bibliography
- Avdulova T. P. Aggressive teenager. A book for parents. - M.: Academy, 2008. - 128 p.
- Baron R., Richardson D. Aggression. – St. Petersburg: Peter, 2001. – 352 p.
- Lebedinskaya K.S., Raiskaya M.M., Gribanova G.V. Adolescents with disorders in the affective sphere. – M: VLADOS, 2002.-432 p.
- Lichko A. E. These difficult teenagers: Notes of a psychiatrist - St. Petersburg, 2006. - 126 p.
- Mozhginsky Yu. B. Aggression in children and adolescents. Recognition, treatment, prevention. – M.: Publishing House Cogito-Center, 2008. – 181 p.
- Nalchadzhyan A. Human aggressiveness. – St. Petersburg: Peter, 2007. – 736.: ill. – (“Masters of Psychology Series”).
- Obukhova L.F. Age-related psychology. Textbook. – M.: Pedagogical Society of Russia, 2001.- 442 p.
- Rogov E.I. Handbook of a practical psychologist in education: Textbook. – M.: Vlados, 1999. – 529 p.
- Semenyuk L. M. Psychological features of aggressive behavior of adolescents and conditions for its correction: Textbook - M.: Flinta, 1998. - 96 p.
- Furmanov I. A. Aggression and violence: diagnosis, prevention and correction. – St. Petersburg: Rech, 2007. – 480 p.
- Shipitsina L. M. Psychology of children's theft: Textbook. St. Petersburg: Rech, 2007. – 276 p.
Classification
Mnemonics for memory development for adults and children - methods and techniques
There are several types of self-destructive behavior. Experts identify different reasons for the appearance of auto-aggression, and they have also developed several classifications.
For example, according to the form of manifestation, suicidal behavior, food and chemical addiction, autistic traits and others are distinguished. The degree of manifestation is also distinguished: consciously or unconsciously.
Aggressive behavior in a person can develop gradually and affect only one area of life. This is what became the basis for another classification.
Mental
Mental auto-aggression consists of self-flagellation, humiliating statements addressed to oneself, and devaluation of one’s achievements. In every situation and every action, a person sees only negative aspects.
Often an individual with mental aggression seeks to punish himself for an offense
Constant self-humiliation leads to deterioration in communicative and professional activities. Depression may develop against the background of negative thoughts.
Physical
This group includes any damage: intentional scarring, tattooing, other wounds and piercings.
Important! A person does not seek to kill himself, only to express anger and other negative emotions.
Sometimes people with this form of auto-aggression engage in extreme sports, deliberately violate safety regulations and try to put themselves at risk.
Social
It consists of refusing contact with the outside world. A person withdraws into himself, he ceases to be interested in other people, and he avoids communicating with them. An individual may begin to behave destructively, violate social norms, this will lead to the fact that he will no longer be accepted.
Spiritual
In rare cases, a person becomes a member of sects, groups banned in Russia. He is instilled with false moral and ethical principles that he is forced to follow.
Often the inability to follow one’s ideal ideas results in drug addiction or alcoholism. Thus, a person is trying to punish himself, this may mean that he is trying to destroy his body, to cause harm. With spiritual self-aggression, the individual is malleable and easily falls under the influence of others.
Advice for parents and loved ones
If your loved one or your child expresses auto-aggressive tendencies, you need to do the following:
- Determine the need for outside help at the moment. That is, to understand auto-aggression, that is, his intention, impulsive or not - the person is going to carry out his plan right now or not. If yes, then outside help is needed at this point in time. If not, then there is time to evaluate and develop a plan for further action.
- Determine how realistic the existing plan is and the presence of protective factors (faith, fear, shame of suicide, concern for the family). Find out the essence of the situation that led to auto-aggression, namely, determine the criticality of the situation and the available alternatives. Identify a person’s place on the spectrum of suicidality (from thoughts of death to preparations for suicide).
- If possible, identify concomitant mental pathology.
- Seek help from a psychologist or psychiatrist, or a suicidologist.
- In a conversation with a person inclined to auto-aggression, it is necessary to rely on limiting factors (national and family traditions, religiosity, spiritual and moral values, feelings of loved ones - children, parents and spouses).
Signs of the disorder
Self-destructive behavior can manifest itself in different forms and may include several characteristic symptoms. With their help, it is easy to determine the presence of auto-aggression.
The first sign is self-harm. They can be inflicted consciously in the form of cuts or expressed indirectly through piercings or tattoos. Sometimes the person hits his head against walls, kicks furniture, and punches tables.
Since auto-aggression is condemned in society, an individual can direct his anger in another direction. In this case, he becomes a member of radical groups, joins a group of sports fans, and in short, tries to get into situations where there is a high probability of fights.
With auto-aggression, a person provokes people into a collision, behaves defiantly
The second sign, which does not appear in everyone, is a decrease in the level of social life. The person refuses to meet friends, does not meet new people, does not communicate with anyone. In severe cases, he may go into self-isolation.
The third sign is the appearance of any addiction. Not everyone can take their situation seriously, so the problem is hidden under alcohol or drugs. Eating too much of one type of food is also a warning sign. The difficulty of diagnosing auto-aggression lies in the fact that the condition can manifest itself in only two or three symptoms.
Advice for people who want to get rid of self-aggression
- In case of severe nervous shock, an irresistible desire to hurt oneself, psychologists recommend trying to express your emotions on paper. Experiences can be expressed in the form of text or drawing and then destroyed.
- To calm down, you can take a hot bath, get a massage, or interact with your pets. Listening to your favorite music also helps.
- When a person feels apathy and inner emptiness, you can eat something with a bright taste or chat with a stranger: for example, you can talk anonymously on a psychological help forum.
- Anger and anger also cannot be suppressed: to release emotions, you can beat a pillow, shout, express emotions on a piece of paper, and then tear it up.
The help of loved ones to a person who is struggling with manifestations of auto-aggression cannot be underestimated. People around him can help him a lot, showing sincere support and care: it is very important that there is someone close and understanding nearby, someone who will never blame or judge him for showing emotions, who will help and support him in a crisis situation. A person who has taken the path of fighting auto-aggression should be praised more often, without allowing humiliating negative statements addressed to him.
The problem of self-destructive behavior is of particular social significance, because often self-aggression becomes the cause of destructive phenomena in society, brutal murders and immoral behavior.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
The examination can only be carried out by a psychiatrist. To do this, he collects anamnesis, conducts a conversation and clarifies the symptoms. If necessary, MMPI, Eysenck questionnaires, a test to determine the level of aggression, etc. are carried out.
The specific set depends on the preferences of the psychiatrist. Some experts prefer to use projective techniques: for them you need to draw a picture or say what is shown in the picture. Analysis of the obtained data requires special knowledge from a specialist, so such techniques are not used everywhere.
The Rorscharch test reveals strong personality traits
A short list of treatment methods - psychotherapy, physical activity, medication support. All three components are aimed at eliminating symptoms and solving the causes of the development of auto-aggression. Treatment can take from a month to a year, it all depends on the form of the disease and its degree of development.
Auto-aggression can be called one of the most common problems in the modern world. If not treated promptly, a person can be seriously harmed. Therefore, if alarming signs appear, you should consult a doctor.
Models (theories) of auto-aggression
Why does auto-aggressive behavior occur in society? There are three models (theories) of their occurrence.
- Medical theory. According to this model, auto-aggression occurs as a result of diseases such as a mental or behavioral disorder. At the moment, followers of this theory are actively searching for a biological substrate. One of the most substantiated versions of the medical model is serotonin deficiency in individuals suffering from auto-aggressive behavior. As you know, serotonin is a hormone of joy that provides positive emotions. Thus, in fact, the level of serotonin correlates with the severity of suicide (the lowest levels of serotonin were observed in individuals who chose the most brutal methods of suicide). In addition, one cannot ignore the genetic factor - 6% of people with auto-aggression have a suicidal history (that is, one of their relatives has attempted suicide before).
- Sociocultural theory. Within the framework of this model, auto-aggressive behavior is a deviation, a social disease, which is determined by such socially significant factors as gender, age, nationality, marital status and employment (employment). This theory is divided into three subtypes: egoistic, altruistic and anomic. The egoistic subtype refers to auto-aggressive behavior that occurs when there is a loss of meaning in life; when personal motives are higher than the feelings and emotions of loved ones. Most often, this phenomenon is observed in people of the creative profession (artists, musicians, poets, writers). With the altruistic subtype, the authority of society or a certain group is stronger than individualism. This subtype is a certain trend of fashion or time among a small population (for example, a group on social networks promoting the cult of suicide among young people). The anomic subtype is the result of a loss of spiritual values and being in a state of unbelief and lack of norms. Most often occurs during revolutions.
- Ecological model. According to this theory, auto-aggression is considered as a series of independent but interrelated factors, personal and environmental circumstances that potentiate suicide. For example, the easy availability of firearms.
Auto-aggression psychotherapy. Content
Auto-aggression (auto- + lat. aggressio attack, attack) is a very ambiguous concept, most often manifested in self-destruction, punishing oneself both morally and physically, taking out anger, resentment, and hatred on oneself or others. Often at the heart of this phenomenon lies anger and self-dislike, which serve as a trigger for auto-aggression. Auto-aggression is destructive; it is aimed not at eliminating the cause of a stressful situation, but at destroying a person suffering in a stressful situation.
An anxious brain stops producing endorphins (happiness hormones). The biochemistry of the brain changes, stress hormones enter a person’s blood, which prompt him to action, to aggression.
In psychoanalysis, auto-aggression is considered a protective mechanism of the psyche - when a person for some reason cannot direct an aggressive impulse to the external object that caused it, he redirects it to himself.
Auto-aggression as a habit of experiencing one’s wrong, bad behavior is not inherent in a person by nature. In the first year of life, children do not make excuses and do not worry about their mistakes; they learn this later.
The problem of auto-aggression, aggressive, cruel, self-destructive behavior of a person in society is currently acute and relevant, discussed in the media due to the increasing frequency of cases of auto-aggression, unjustified brutal murders, antisocial, immoral behavior of people in society. The social significance of the problem comes to the fore.
Self-help for self-aggression:
• — Who do you forbid yourself to be angry with? • entertainment: music, films, walks, chatting with friends without alcohol; • relaxation and work on increasing self-esteem; • pay attention to what is going well and excellent in life; • creativity: literature, drawing, modeling, singing, dancing; • sports: wrestling, running, weightlifting; • harmless ways to vent anger: hitting a punching bag, screaming, making noise.
If self-aggression is typical of someone close to you, do not ignore alarm bells. Show concern, be interested, delve into it. Remember, love can literally heal and save lives. Be sure to devote time to your children, relatives, family, and friends. Listen, reassure and support.
Protecting your loved ones from self-destruction and helping them is in your interests. If you want to move from self-aggression to creativity, sign up for a consultation.
You have problems? Do you need a psychologist? Call, write right now!
Skype OlegVZobnin Phone +7(987) 955–49–56 WhatsApp +7(987) 955-49-56 Viber