What is communication
In general, if we consider the term “communication” itself, it came into Russian from the word communico (Latin), which means “joint” or “common”.
In connection with this definition, they began to say that communication is communication. In other words, communication is those situations in which two or more people talk to each other about topics that are familiar to them. At the same time, during communication, people can argue, give each other advice, express their own opinions or express their thoughts in other ways. During the communication process, the interlocutor will receive incoming information and provide his reaction in response.
Issues
Psychologists identify a number of problems that prevent people from building communication:
- Reluctance to feel the feelings of the interlocutor. If you don't take into account the other person's mood, it is impossible to establish effective communication.
- Lack of interest in the problem, inability to express true interest. Situations often occur when one of the interlocutors is interested in something and talks about it with enthusiasm and active gestures. The topic may be indifferent to another person, but according to the rule of etiquette, he must keep the conversation going.
- Lack of desire or ability to listen to the interlocutor. This problem interferes with productive communication. The inability to listen is manifested in constant interruption of the interlocutor, a sharp change of topic. A person who does not know how to listen to others often experiences serious problems in finding friends and moving up the career ladder.
- Closedness when communicating with others. This is the first barrier that appears when meeting someone. The problem actively develops with a negative attitude from others. A person begins to withdraw and finds it difficult to express feelings.
- High or low self-esteem. Only two people with approximately the same level of intelligence can communicate effectively. In this case, there will be no obstacles in understanding the interlocutor, common topics for conversation will appear.
For communication to be effective, you need to follow a number of rules:
- Learn to reject selfishness, think about the problems of your interlocutor.
- Every day learn to listen to others.
- Show interest in the topic of conversation.
When interacting with other people, you need to watch your words. It is unacceptable to insult the interlocutor, speak negatively about his point of view, or ridicule statements.
Classification and structure
Communication is a rather complex concept that has its own structure. All communication can be divided into two main groups - communication between several people (also known as interpersonal) and communication between companies (also known as organizational). Interpersonal communication is divided, in turn, into informal and formal.
From all these names of groups and subgroups, it becomes clear that there are types of communication conducted according to certain rules, with the necessary intonation, as well as with the formality inherent in certain events.
And there is also informal communication, in which people communicate with friends, family, or just acquaintances, without observing any regulations or rules. During informal communication (communication) with other people, a person behaves at ease and naturally.
Organizational communication is divided into external, which occurs between any organizations and the environment, and internal, in which communication is built between departments in a particular company.
But here too there is a division in communication – horizontal and vertical. With horizontal communication, communication occurs between departments located at the same level, and with vertical communication, communication occurs between subordinates and superiors.
From all this we can conclude that communication is a definition that exists in any area of human life and requires a certain understanding and approach.
Communication means
Communication means can be divided into two large groups:
- Nonverbal - non-verbal ways of interacting with society (gestures, touches, facial expressions, etc.).
- Verbal - speech skills.
The structure of verbal communication has 3 components:
- Speech sound phenomena. This is modulation of voice pitch, tempo and rhythm of speech, tone and timbre of voice, diction, intonation.
- The meaning, meaning of words, individual phrases. A person must be able to construct phrases from words so that they are understandable to the listener. You need to choose the right intonation.
- Expressive voice qualities. These are specific sounds that can occur during communication - whispering, laughing, crying, sighs, grunting, etc.
Scientists have proven that only 45% of a person’s daily communication consists of speech skills. Non-verbal skills occupy 55%.
Nonverbal means of communication can be divided into 2 large groups - paralinguistic and extralinguistic. They are divided into separate subgroups.
Paralinguistic:
- Graphics is the ability to write. Depending on the emotional background and personal experiences, the style of writing may change.
- Kinesics - movements used when communicating with other people (facial expressions, gestures).
- Prosody - components that complement speech (depth of voice, strength, timbre, stress placement, nature of pauses, length of words).
Paralinguistic means of communication must be tied to speech.
Extralinguistic:
- Sensory - with the help of the senses, a person perceives the interlocutor. He responds to any smells, touches, visual perception.
- Extralinguistics - emotions (sighs, dissatisfied rumbling, screams, coughing) are transmitted with the voice, but are not tied to speech.
- Proxemics - distance control. When interlocutors communicate with each other, they may be at different distances. Distance depends on trust.
- Takesika are intangible signals (kisses, pats, hugs, handshakes, stroking) that are transmitted between people when communicating.
- Chronemics - time distribution. For example, you can postpone a call or rush to a personal meeting. You can reduce the duration of the conversation or stubbornly wait for the moment when the interlocutor is free.
Psychologists divide gestures into several separate subgroups:
- Effectors: uneven gait, hunched figure, downcast face.
- Adapters - touching, twitching, scratching, stroking.
- The emblems are clenched hands raised above the head or crossed on the chest. Each such gesture has its own interpretation.
- Regulators - purposeful hand movements, nods, smiles, gaze direction.
- Illustrators - signals, body movements, pointing.
You can also identify microgestures that depend on the emotional state - an increase in the number of eye blinks per minute, reddening of the cheeks, eye movements, twitching of the lips.
Key concepts from the field of communication
The main definitions related to the field of communication include the following:
- Speech culture is the correct and correct use of the basic linguistic elements of communication in all respects. Any person who knows the rules of the Russian language and Russian speech knows how to use words correctly and how to behave depending on the situation.
- Speech communication is the purposeful or accidental use of speech structures to voice one’s own opinion, as well as to maintain the topic of conversation.
- Speech behavior is the use of certain verbal expressions depending on a specific situation (at school, in the family, among friends, etc.).
- A speech event, consisting of two elements, is a certain life situation or setting within which the dialogue takes place, as well as the language itself, through which the conversation takes place.
- Speech activity is a purposeful, isolated impact on one or more citizens through language.
From all this we can conclude that communication is a definition consisting of a large number of language structures that take part in the exchange of information data.
How to develop communication skills?
Even the most unsociable person who loves solitude can develop sociability. Due to his character, he may not achieve leadership in the team (he usually does not need this), but it is quite possible to become a pleasant interlocutor.
To do this, you need to take note of a number of tips:
- Expand your social circle
. Often people are used to communicating only with certain acquaintances who are close to their interests. But this is not enough to become sociable. You should be able to establish contact even with someone who is completely opposite to you in character and worldview; - Take advantage of convenient opportunities to communicate
. Often unsociable people don’t even notice how many wonderful opportunities there are to start a conversation and get to know a work colleague or friend better. For example, a person was asked about how his weekend was. In this case, instead of a simple and meaningless answer, you can tell a funny story that happened on vacation or turn the dialogue into a discussion of common hobbies; - Learn to enjoy the conversation
and focus on positive topics. Some perceive communication only as a formal obligation to maintain social connections. But as soon as you add sincere interest and an optimistic attitude to your daily communication, people immediately begin to gravitate towards such a person.
In this video, psychologist Dmitry Samarin will talk about ways you can improve your communication skills and communication skills in general:
Verbal and nonverbal communication
Communication (communication) is a complex and diverse process of establishing and subsequently developing contacts between several people. Communication is generated by the need for activity and exchange of information data.
There are two main types of communication:
- Verbal. Verbal communication refers to communication in which people exchange information using sentences and words. Such communication takes place in written or oral form, and the output is words and sounds.
- Nonverbal. Nonverbal communication between people is the expression of emotions and nonverbal actions - facial expressions, gestures, as well as intonation, body position and other data.
An important point: the types and concepts of means of nonverbal communication are an interesting topic for research, because it is nonverbal communication that allows you to significantly feel the interlocutor and gain his favor.
Communicative communication in psychology - how information is exchanged
Communication allows people to exchange information with each other, share experiences and emotions. The individual must be ready to receive new data, since the effectiveness of communication will depend on this. Therefore, the conditions or information expressed by the partner cannot always be assimilated by the interlocutor correctly and fully. The possibility of losing the original meaning is allowed.
If both subjects are at too different levels of intellectual, emotional and spiritual development, then the information during their communication will be practically not absorbed. In some cases, this is also due to differences in value systems.
In communicative communication the following styles can be distinguished:
- Imperative. Authoritarian style, in which the subject has a significant influence on the object, which is in a subordinate state. Used in organizations with a strict hierarchy, such as the army.
- Ritual. Highly dependent on the cultural environment. Expressed in maintaining the customs of society. An example is the greeting phrase “How are you?”, to which it is customary to respond “Everything is fine.” Also included in the ritual style are apologies, congratulations, condolences, farewells, and hospitality.
- Manipulative. The goal of this style is to gain control over the subject. In this case, the influence is masked. In this case, personal motives become the main goal, and the exchange of information fades into the background.
- Humanistic. It is distinguished by equal rights for all parties, due to which effective perception of information can be achieved.
The communicative style of communication has the following features:
- correct speech, without an abundance of filler words;
- softness of tone;
- brevity, correctness and tact in relation to the interlocutor;
- absence of criticism, reproaches and accusations;
- unobtrusive compliments, praise.
In a conversation, both parties should demonstrate a desire to discuss positive topics and avoid all kinds of disputes, objections and interruptions of the interlocutor. In this way, good mutual understanding can be achieved, which will greatly facilitate the transfer of even very complex information.
If you devote enough time to developing your own speech, its thoughtfulness and logic, as well as the delicacy of presenting information, you can acquire enough skills for full-fledged communicative communication.
How partners influence each other during communication
When communicating between interlocutors, subconscious dominance of one of the interlocutors occurs. A dominant person is able to convince someone of something or, conversely, dissuade another. He can also give advice or condemn for wrongdoing. Based on all this, we can distinguish 4 scientific ways of influencing one person on another:
- Infection. These are situations in which a person is involuntarily, unconsciously exposed to a certain mental state. That is, these are those cases in which the partner directly infects the other person with certain ideas that fill everything else.
- Suggestion. Suggestion refers to the purposeful and unjustified influence of one person on another. Very often you can find a similar method of communication in stores - some sellers are able to literally stick it in and force you to buy certain goods.
- Belief. This method is based, first of all, on using arguments and arguments to achieve a positive or negative action about the person receiving the information. That is, one person tells another person reasonable information so that the interlocutor draws the necessary conclusions and takes certain actions.
- Imitation. When compared with infection and suggestion, imitation differs from both of these actions not by simply adopting the interlocutor's traits, but by reproducing behavior. That is, a person tries to behave and speak the same way as his interlocutor. Practical benefit – persuasion and liberation of the interlocutor during communication.
Knowing all these techniques, a person can, during communication, if not manipulate the interlocutor, then at least find a common language with him, regardless of the topic.
An important point: regardless of the method of communication, its main goal is to convey the necessary and important information data in such a way that the other person (interlocutor) understands what exactly is being discussed in the dialogue. However, the use of some speech patterns and elements of nonverbal communication will not provide any guarantee that the person has accepted and understood the information.
Communication skills and abilities
There are certain abilities that together provide an individual with communicative competence:
- the ability to predict the socio-psychological characteristics of a communication situation;
- communication programming, which implies that a person knows how to direct a conversation in the direction he needs, depending on the purpose of the conversation, as well as personal preferences;
- communication management, which allows you to get answers to questions that the interlocutor does not want to talk about;
- the ability to accept and give signs of attention;
- ability to respond to criticism;
- the ability to respond to provoking behavior of an interlocutor;
- ability to ask;
- the ability to refuse someone else's request;
- the ability to provide empathy and support;
- correctly accept sympathy and support from people around you;
- contact;
- respond correctly to attempts to make contact.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
Basic elements of communication
In total there are 4 important links in communication processes:
- recipient - the one who listens and perceives the information received;
- communication flow – means, methods and means of transmitting information;
- message – information conveyed to the interlocutor;
- sender – a person who sends and communicates the necessary information to another person (recipient).
It follows from this that the definition of communication and communicative processes indicates their complementarity.
History of the study and researchers
It is easier to understand the history of the study by the main researchers of communication if we consider the main models of information transfer between people:
- Socio-psychological - founder T. Newcomb.
- The linear model of communication was created by G. Lasswell.
- Noise model - founders K. Shannon, W. Weaver.
- The factor model was created by G. Malecki.
- Text model - founder A. Pyatigorsky.
In addition to these models, there are two well-known theories - communicative acts (creator T. M. Newcomb) and means of communication (founder Marshall McLuhan).
What is the difference between communication and communication?
Communication and communication, related to social processes of information exchange, yet there are some differences between them:
- 1. In the process of communication, in contrast to communication, an important point is not only the receipt of data and its analysis, but also such points as the general emotional background and the content of the transmitted information.
- 2. The main, main function of communication is the establishment of maximum contact between interlocutors, and the main function of communication is the establishment and selection of means of communication, that is, the choice (depending on the situation) of non-verbal and verbal means of expressing the own opinions of each interlocutor.
- 3. Communication – a general definition that also includes “communication”.
Communication is a multifaceted concept that requires more careful study and consideration to convey the necessary information. A person, knowing all the features and subtleties of communication processes, will be able to receive all the information he needs about his interlocutors
.
Using speech patterns and non-verbal communication methods, you can create an excellent environment for further communication processes. However, it is important to know the rules of communication and observe censorship depending on the situation. Knowing and following simple rules will be an excellent guarantee of good communication.
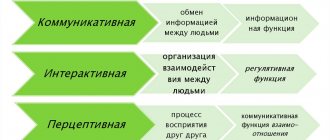
Functions and theories
The psychology of communication identifies a number of communication functions:
- Cognitive - people learn new information through contact with others. The obtained data can be used in practical activities.
- Normative - consolidation, transmission of norms that are gradually preserved in consciousness.
- Interactive - organization of joint activities, achievement of assigned tasks.
- Information and communication - exchange of information.
- Social-practical - exchange of skills, abilities, abilities.
- Psychotherapeutic - creating relationships with others. Without communication, a person will gradually develop psychological disorders.
Communication problems
Uncommunicative people are often afraid of being judged for their words. Therefore, you should overcome the fear of offending your interlocutor or seeming stupid.
It should be understood that there are no ideal people in communication. Sometimes even an intelligent and reasonable interlocutor can blurt out something stupid, for which they will get angry or laugh at him. In this case, a healthy reaction would be to calmly accept failure, take into account your mistake and continue communication without tormenting yourself for the stupidity you have done.
An anxious person should keep these three simple steps in mind if they are avoiding social contacts out of fear of getting things wrong.
How are abilities manifested?
They manifest themselves in a special psychological make-up of the individual , on which the effectiveness of information exchange with other people depends.
A person's success in life is determined not only by his character, temperament and destiny.
The type of interaction with people around you and the ability to build contact with them .
Often individuals who have a large number of positive character traits and a high level of intelligence do not achieve success in society, at work or in their personal lives due to the low level of development of communication skills.
They simply do not know how to convey information to others so that it is perceived in the right way. In this case, they speak of a low level of communication abilities.
If a person always finds an approach to his interlocutor or audience, knows how to adapt to the proposed situation and easily influences, then in his case his communication skills are highly developed.
the influence of close people and the environment is essential
The more time parents devote to communicating with their child and instilling in him the skills of interacting with others, the easier it is for him to establish interpersonal and business contacts in the future.
Self-improvement also plays a significant role, since communication skills can be developed through experience. Reading specialized literature, self-control, consultations with specialists, and participation in trainings help.
Communication skills include the following components:
- Informational . The ability to attract the opponent’s attention, to interest him in the topic of discussion, as well as the possession of verbal and non-verbal communication skills.
- Affective . The ability to recognize the emotional state of the interlocutor and competently adapt to it, showing understanding, participation, and sympathy when necessary.
- Regulatory . The ability to accept and show support. This allows you to interact with people in the most productive way, minimizing the likelihood of conflicts.