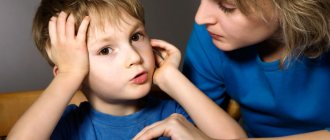
The crisis of 7 years in a child is associated, first of all, with a new stage of development and life - entering school. A feeling of adulthood, cognitive interest and a new type of interaction with adults and peers appears, aimed at acquiring knowledge.
At the same time, the first-grader begins to feel new pressures and new responsibilities, and therefore, by his behavior, he demonstrates to adults that he is still a child. Grimaces, grimaces, capricious. The main task of parents is not to burden the child with many new responsibilities at once, but also to use gentle methods to show that there is no longer any possibility of returning to kindergarten.
Characteristic age features
Role-playing games are replacing manipulative games. Parents become role models and transmitters of social norms. A preschooler’s knowledge of the world of relationships between people occurs through role-playing games and communication.
A play environment is a necessary component for the proper psycho-emotional development of a little person. During the game, the baby ceases to be afraid and gets rid of the effects of traumatic moments (for example, nightmares).
For a preschooler:
- there is an active development of imagination;
- visual thinking is being formed;
- the formation of thinking with the help of concepts begins;
- your own vision of the world is being rebuilt;
- the motivational system changes;
- there is greater freedom of behavior.
The basis of the new position is the child’s readiness for school. In addition, one should understand the degree of formation of the personality, its characteristic features, and prospects. The psychology of a 7-year-old child consists of the following factors:
- The degree of pretentiousness shows how confident the child is in his abilities. The formation of this feeling occurs thanks to “ups” and “downs”. The more successful results a child gets, the more confident he is. The goal of parents is to encourage the child’s success and guide him in the right direction.
- Perspective implies a goal in life. If a child, looking at adults, realizes that studying is important for achieving future success, he will have a positive attitude towards school. If a child does not understand the meaning of the educational process, he will resist learning with all his might.
- The concept of one's own "I" contains 3 parts: evaluative, emotional and cognitive. A child of preschool age has almost no self-esteem; external criteria are the guideline. For his perception, such qualities as kindness and responsiveness are incomprehensible, but at the level of feelings he understands them. The cognitive part refers to the extent to which a child can describe himself. Emotions characterize the specificity of perception - a child at this age evaluates and remembers everything on an emotional level. Therefore, you can communicate with preschoolers through drawings.
- The motivational and incentive hierarchy is formed by the age of 5–6 years. The baby is able to meaningfully perform actions, he can make choices, analyze the meaning of the action.
Rules of conduct for parents
Panic is a bad adviser in matters of education. Adults need to calm down and adhere to a number of rules:
- Explain the prohibitions, otherwise the children will not understand them. Any restrictions should be presented as advice or wishes. There will be no obvious negative reaction. Parents are afraid of losing their authority, but at this stage it is more important to build a trusting relationship. Moreover, children instinctively always reach out to their elders and listen to their advice.
- Listen to your child, watch movies together, read. Establish friendly relations, discard harsh criticism, do not cut off the little one’s story mid-sentence. The absence of ridicule of the little man’s experiences will subsequently eliminate the fear of public speaking.
- Consult with your seven-year-old to make him feel like an important part of the family. Discuss purchases, tell the baby about the financial state of the family. This will allow you to ensure that your child does not steal money from you or demand large purchases. Follow the rule of the golden mean - consult superficially, without focusing on the economic side of life. Don’t transfer difficulties to a little person. Suffice it to say that temporarily there is money only for necessary things.
- The use of violence for educational purposes is prohibited. Physical punishment will leave resentment for life, and moral torture will lead to the inability to refuse (even in dangerous situations) and will reduce self-esteem.
It’s not worth nurturing a seven-year-old all the time. The crisis period of 7 years for a child is the time when he begins to grow up. He needs to spend time with friends, without parents, read alone, do homework on his own, design, draw.
By the age of 6, the baby should have his own room or place where other family members will leave him alone for a while.
Distinctive features of the crisis
The main cause of behavioral problems in the preschool period is growing up. The baby’s living conditions completely change, the child is worried and worried. He will need to learn a lot, adapt to a new schedule, and understand his responsibility.
The age-related psychology of a crisis in a 7-year-old child is such that this period is difficult, the child needs to get used to communicating with peers who are also experiencing difficulties, and learn to cope with the school load.
Experts say that the seven-year crisis manifests itself at approximately 6–8 years of age. It is impossible to say an exact figure; each baby is individual. Distinctive features of the period are:
- inappropriate behavior of the child, frequent manifestations of harmfulness;
- fake conversation when communicating;
- decreased perseverance and concentration;
- attempts to imitate adults;
- attempts to attract attention.
Some children try to tell adults. Such changes are unconscious; the child temporarily loses control over his actions. The preschooler reacts negatively to criticism; the mind blocks all negative information coming from the outside.
The main impetus of the crisis is the gradual departure from childish spontaneity, the maturation of the intellect, and the emergence of anxiety for the actions taken. In addition, the child is worried about his success at school and tries to resist changing his usual conditions.
Self-diagnosis
Symptoms of the crisis:
- often rude;
- does his homework poorly;
- refuses to go to school or kindergarten;
- he stands on his point of view until the last moment; clowning, antics, and posing begin;
- I'm not happy with everything in the family.
Also the child becomes:
- irritable and hot-tempered;
- get tired easily;
- absent-minded;
- withdrawn and timid.
If at least two points coincide and are observed in a child, he is experiencing a 7-year-old crisis. But don't worry too much. In the near future, parents need to adjust their behavior so as not to hurt their child’s feelings. Because inaction and ignoring manifestations, both active and passive, will affect the child’s behavior in the future.
It is also possible that the 7-year-old crisis has not yet begun, and all of the above behavior patterns found in the child are the result of improper upbringing. Then, mom and dad need to pay attention to this moment and adjust their parenting methods.
Symptoms
Parents themselves can identify the psychological characteristics of this period. Each has its own logic.
The child stops obeying subconsciously, tries to insist on his opinion, refusal to follow parental orders helps development. Punishment is undesirable; even a calm explanation rarely helps. It's better to try to step away temporarily.
Stubbornness is also a symptom of a crisis period. The baby denies refusals, becomes demanding and persistent. In this way he asserts himself. The goal itself is not important, the main thing is the process of demand.
The consequence of the first symptoms is self-will. The child wants to do everything on his own. The best way out is to try to direct energy in the desired direction: provide limited freedom of choice, give simple tasks. For example, choosing clothes, food from several proposed options.
Initial signs may be noted by the age of six. Closer to eight years of age, symptoms become more smoothed out.
Main symptoms
Developmental psychology of this period highlights symptoms of crisis that parents can notice on their own. There is an explanation for each of them:
- Disobedience, which is unusual for a child, manifests itself subconsciously. The seven-year-old begins to defend his position, and refusals to carry out the will of his parents help him develop his personality. You cannot punish for such behavior; thorough explanations will not have a positive effect. Lack of pressure on the baby will help smooth the situation.
- Every parent of a 7-year-old child faces stubbornness. This is the second symptom of the beginning of the crisis. The child begins to insist on his own, demand, and resist refusals. He does not want to possess any thing, but asserts himself. At the same time, the goal he is achieving fades into the background, and the process of demand itself comes to the fore.
- The biggest problems are caused by obstinacy, which causes problems with studies. The child refuses to obey the rules, attend kindergarten or school, or sit quietly in class.
- Self-will arises in conjunction with the previous symptoms. The child wants to fully serve himself independently and help his parents. The best way to cope with this situation is to direct the baby’s energy in the right direction: offering him alternative tasks that he can cope with, giving him limited freedom of choice. Independence can be shown in different ways: choose clothes from the suggested options, offer a book to read.
- It is not possible to come to an agreement with your child in all cases. The crisis of 6-7 years is characterized by a state of protest and quarrels that exhaust all family members. This behavior is associated with internal conflicts that the child feels. They appear due to the difficulties of adaptation within the class, and the child splashes them out on everyone around him.
- Another characteristic symptom is the devaluation of ideals. What previously seemed good becomes unpleasant for the baby. He may break previously beloved and dear toys and loses attachment to things. Children take special pleasure in demonstrating unacceptable behavior, repeating swear words, showing despotism, and subjugating the entire family to their will.
Another important symptom is a passion for playing “school.” A little person strives to become more mature and enjoy beautiful things. At the same time, the baby does not fully understand what will be required of him.
The first symptoms can be noticed at six years of age. By the age of 8, the effect of the crisis weakens. It is important for parents to act correctly when the first signs of a difficult period appear. Excessive guardianship and the use of unconscious prohibitions will only aggravate the situation.
How to behave as parents
In raising a child, panic is the worst advisor. You should get together and follow the recommendations of experts.
When prohibiting, it is necessary to provide justification. Each limitation should be presented in the form of advice or wishes. Then there will be no sharp refusal.
Listen to your baby, spend more time together. Let the child trust you. Always listen to his fears and worries. You can't mock his worries. In the future, this will help the child cope with the fear of speaking in public.
Ask your child for advice often. He will feel the importance of his opinion for adults. Discuss shopping, daily chores, school, work. But at the same time, you don’t need to burden your baby too much with your difficulties.
Violence for educational purposes contributes to the aggravation of the situation and can leave an imprint on the child’s entire life and reduce his self-esteem.
At the age of 7, the child begins to grow up, you need to perceive him as an adult, full-fledged person. The child should communicate with peers more often and try to fulfill his responsibilities independently. It is advisable that the baby has his own place of solitude.
Manifestations
Negativism
- this is a refusal of everything that the parent asks the child to do. This sign should be distinguished from ordinary disobedience, characteristic of all children. In the case of negativism, the baby almost always refuses. It is not recommended to punish a child at such moments. Even a heart-to-heart conversation or a demand for an explanation will not help in this case. But if, at the moment of refusal, the child is engaged in something that completely captivates him, then disobedience in this case is natural.
Stubbornness
- when a child demands something from his parents. It could be a toy, candy or any other thing. But the child doesn't need it. The main thing that a child wants is self-affirmation, and not possession of a thing.
Obstinacy
- the child tries in every possible way to violate discipline, the daily routine that they are trying to impose on him. This may be a reluctance to get up early in the morning, go to school, eat, or do homework.
Self-will
- the child wants to be independent, so he tries to do everything on his own, overcome difficulties, without asking permission or advice from his parents. The wishes and instructions of adults are not important to him. The needs of the child himself come first.
Protest
- when a baby adapts to a new way of life and the conditions of society, he accumulates internal denial, protest, which he splashes out on almost every person. Quarrels in the family and at school are becoming commonplace. This occurs because the child experiences an internal conflict in adapting to society.
Depreciation
- the child develops new ideals. What he previously considered interesting now has no meaning to him. The child breaks his favorite toys, says bad words that are prohibited in society. He is a hooligan and does all sorts of mischief to all the children around him, sometimes treating them with cruelty.
In families where children are under strong guardianship, despotism
: the child changes the family’s lifestyle to suit his needs.
Duration of the crisis period
The beginning of the crisis period is associated with obtaining the status of a schoolchild, which implies significant changes in the child’s living conditions: a new team, obligations, skills. Based on the research, it has been revealed that this period usually lasts several months, depending on the characteristics of the particular child and the behavior of the parents.
Several stages of the crisis can be distinguished:
- the child realizes the need to go to school, therefore he will grow up and become more important;
- the baby tries to master his emotional state and begins to communicate more calmly;
- full awareness of the new status.
When should you see a doctor?
It’s better not to see a doctor at all. This period is temporary and will soon pass. You just need to accept that the child is forming his own new inner life, into which he is still allowing his parents. But they already need to ask him for permission to enter it. Therefore, the natural course of the baby’s mental development should not be treated by a doctor.
Causes of a child's crisis state
Age crises are normal stages in the development of a person’s personality. During their course, a transformation of a person’s thinking occurs, which leads to his preparation for new stages of life.
The 7-year crisis is noted by psychologists as one of the most turbulent. At this time, children's spontaneity is lost and the baby's position in society is formed.
During this period, a complete restructuring of the behavior of the little person is carried out. He goes to school, which implies a number of innovations: the child must maintain discipline and a certain order.
In the process of communicating with classmates, the baby learns to communicate. Moreover, it does not happen just like that, but for a reason.
The student realizes two truths. The first is that he needs to take into account the opinions of others and sometimes restrain his needs for a while. The second is that the baby grows up and gets his place in the world of adults, which, in his opinion, gives him the right to own “adult” things.
The child attends school for various reasons:
- Game. In this case, the child perceives school as a game, but he is not ready to fulfill the requirements.
- Demonstrative. Kids are excited about new things; they are perceived as a stage of growing up. But even in this case, the child does not want to obey, do homework, or read.
- Educational. By the age of seven, very few people have such motivation. But such children are happy to attend school to gain knowledge. This approach causes the least amount of trauma to the child’s mental state and allows him to quickly adapt to a change in environment.
Consultation for parents “Signs of a 7-year-old child’s crisis. What should parents do?
Oksana Martynova
Consultation for parents “Signs of a 7-year-old child’s crisis. What should parents do?
Consultation for parents.
“ Signs of a crisis in a 7-year-old child . What should parents do ?
a child's transition from childhood to 7-year-old preschool is usually accompanied by certain changes in his character and a crisis in his upbringing . Long observed and studied by psychologists, this critical period of childhood has been conventionally called “ 7-year-old crisis. ”
.
An age crisis is usually associated with a restructuring of a child's - with the transition from preschool to seven-year school status. The main characteristics of a 7-year-old child’s crisis are issues of discipline and difficulty in observing social rules.
Age crises in children : crisis 7 years
of a child's growth and development are accompanied by certain crises throughout the entire period of his growing up. Psychology has recorded a number of critical ages of a child , each of which has its own characteristics and timing, including the seven-year crisis .
• crisis of infancy;
• 3-year crisis : the period of first adaptation, change of environment to a nursery and kindergarten;
• crisis 6 – 7 years : manifests itself during the period of change in the environment of the kindergarten and school;
• crisis of 13 – 14 years : associated with the well-known period of adolescence – the period of puberty.
There is no panacea in the timing of the beginning and end of psychologically designated age stages. This division is influenced by individual development, upbringing and the nature of the child’s with his immediate and distant social environments. So, for example, a three-year crisis can begin at 2.5 years and end at about 4.5 years; and the first signs of a crisis at 7 years old can appear at 6 years old - when the child first goes to school.
There is no need to perceive the 7-year crisis as inevitable suffering for parents and their children . But it is also possible to think that this can be avoided by protecting the child from the natural external factors of growing up. You see, age-related crises are a normal and natural process of a child’s to changing external factors. And, no matter what you do , together you will have to go through every one, including the crisis of 7 years . The only thing that parents, for their part, can influence after noticing the first symptoms crisis is the duration and severity of its course. This is very important, since a child may not outgrow the negative manifestations of a 7-year-old crisis , then they will become firmly entrenched in his character. All further attempts to change his personality and raise him correctly will be problematic, if not futile.
Signs of a crisis in a 7 year old child
When a child says goodbye to kindergarten and stands on the threshold of school, he has to overcome a lot of emotional difficulties in order to harmoniously fit into the new environment and become a full member of it. To some extent, becoming a little adult, your child will have to overcome one of the first steps - the 7-year-old crisis in order to be ready to study at school. Features crisis include the need for the child to overcome school stress , communication with peers of different levels who are also experiencing a similar period in their own way, as well as changes in relationships with parents . Psychologists have proven that crisis affects your child’s .
You may encounter the following signs of a 7 year crisis :
• ridiculous harmful behavior;
• artificial pretense;
• poor perseverance and agility;
• during the crisis of 7 years, children begin to clown around and imitate their parents ;
• one of the signs of a 7-year-old crisis is attracting attention to oneself through clownery.
During 7-year crisis symptoms are accompanied by the following emotional and behavioral characteristics:
• fast fatiguability;
• hot temper and irritability;
• absent-mindedness and, as a result, poor academic performance;
• isolation and shyness or, conversely, aggressiveness;
• search for authority – it is during crisis that your children make older friends, mostly bullies and hooligans;
• in search of their place, many children during the crisis of 7 years begin to curry favor with their elders and slander their peers;
• During their formative years, many children tend to underestimate themselves and compare themselves with others.
Symptoms of crisis 7 years
In psychology, there are 7 main signs of crisis in a child .
Crisis of 7 years : negativism
This manifestation of a 7-year-old child’s crisis must be distinguished from his characteristic disobedience. A characteristic of a 7-year-old child’s crisis is his negative attitude towards his parents’ - a groundless and widespread refusal of what an adult asks him to do. Do not resort to punishment in such a situation, because even a thorough conversation and explanations are unlikely to help in this case. But if at the time of the request your child is passionate about something, this is ordinary disobedience and you can deal with it.
Crisis 7 years : stubbornness
In this case, the child categorically demands something from the adult. The motive for such behavior of a child in a crisis of 7 years is the reluctance to possess a thing, but the process of self-affirmation in one’s own eyes and the eyes of adults. Most likely, the thing itself is not particularly important for him at this moment; the purpose of such persistence is the need to achieve what he requires.
Crisis 7 years : obstinacy
This manifestation of the age crisis of 7 years is aimed , rather, at denying the routine and way of life that they are trying to impose on him: going to school, getting up early, sitting in class, learning lessons, etc.
Crisis 7 years : self-will
During the crisis of 7 years, such a characteristic of behavior as self-will is manifested in the desire to do everything independently , that is, to be independent of the desires, instructions and help of adults.
Crisis 7 years : protest
In the process of adaptation to new social conditions, lifestyle, rules of behavior and order of life, the child experiences widespread denial. Therefore, the crisis at the age of 7 takes place under the sign of quarrels. It seems that your child is in an insurmountable conflict with everyone. In fact, in psychology, crisis the child’s internal conflicts regarding adaptation to the environment, which he splashes out on everyone and everything.
Crisis 7 years : depreciation
At the time of the formation of new values in a seven-year period, a peculiarity is the crisis of ideals . At this time, the child speaks of what he previously considered white as black and vice versa, and also breaks things that were once very dear to him. He gladly repeats bad words and rude phrases, because his parents , and treats other children with particular cruelty. In addition, children overly cared for by their parents begin to show despotism towards the rest of the family, practically subordinating the way of life of all its members to their will.
How do you know if a child is having a 7-year-old crisis ?
Questionnaire for parents
In the questionnaire below, answer the questions as honestly as possible:
0 – if your child ;
1 – you noticed something like this, but you’re not sure;
2 - this is exactly what is happening to my child .
Questions to determine the signs of a crisis in a 7-year-old child
1. I began to notice big changes, it seems that my child has become completely different.
2. My child often does not listen to me and is rude when I ask him not to interrupt adults.
3. The child has stopped learning his homework on his own, is not interested in games that until recently aroused wild interest, and only spends hours walking with friends.
4. I began to find it difficult to take my child to kindergarten/or primary school - he completely refuses to go there.
5. We often play school with him/her.
6. My child began to be mischievous and insist on his point of view until he is blue in the face.
7. Grimaces, posing, talking in a squeaky voice - his constant behavior.
8. All his relatives are constantly in conflict with him. It seems that he is not satisfied with absolutely everything.
Analysis of responses
By summing up all the answers, you get a number from 0 to 20.
• If your final number is from 11 to 20, then your child is now in the crisis stage of 6–7 years . Therefore, you need to fundamentally reconsider your behavior. Because your active action or passive inaction can greatly affect the direction of his upbringing.
•If your number was from 6 to 10 points: most likely, these are the consequences of improper upbringing of a child and the age crisis of 7 years has not yet begun. But pay attention to this and in the near future try to correct the situation with proper upbringing.
• For parents with a score from 0 to 5, it is recommended to observe the child's . Your child is too calm . Perhaps the crisis of 7 years is passing deep inside, which is clearly not good for your child.
Crisis in a 7-year-old child : ambulance!
1. Don’t panic, this is just another difficulty that you will definitely overcome. Like any illness, crises are only temporary in your life. Just behave correctly, and soon everything will be back to normal.
2. One of the reasons for the acute manifestation of conflicts crisis is the inconsistency of your attitude towards the child . Maybe give the child a little freedom - let him figure it out on his own. Don't restrict it so much - just control and guide it carefully.
3. Your baby has already grown up - you don’t need to take care of him like that. Give him the opportunity to spread his wings, and when he himself comes for advice, then you too will show your parental care .
Crisis of 7 years , recommendations for parents !
1. All negative symptoms of the 7-year-old child’s crisis are associated with internal protest regarding the increasing demands at home and at school. Too much suddenly becomes a “need to do ”
, and
the child immediately has an endless “I don’t want to, I won’t
.
Recommendations 7 year crisis : correctly veil your “shoulds”
so that
the child himself wants to do it.
Tell an instructive story where an authoritative hero shows him an example of such behavior. 2. At the crisis age of 7 years, the child can already make decisions based on personal experience. During the period of another refusal, do not force him with your authority - remind him how cold he was when he didn’t dress well enough or how his tummy hurt last time from so much sweets.
3. Give your child the opportunity to argue with you. If in a crisis of 7 years he has his own opinion, let him argue for it. In this case, he will learn not to demand anything unreasonably, and you will learn to hear and take into account his opinion.
4. At the transitional stage of the crisis of 7 years, it is recommended not to immediately switch the child from toys to books and writing. Introduce school subjects gradually, even playfully. Allow your child to relax while playing his favorite game, while repeating the words assigned for homework. Or draw the letters together with colored markers. the child's daily routine .
5. A feature of crisis is disobedience. If your child refuses to stick to the usual daily routine, don’t force him. Find out how long it will take him to finish all his work - let him feel like an adult. During crisis, psychologists recommend communicating with the child as an equal : asking adult questions, giving the child the opportunity to make independent decisions and take responsibility for them.
6. In the crisis of seven years, the child, although he grows up , still deeply remains a child . Take fairy-tale characters as an example, fortunately there are now a lot of instructive cartoons with deep meaning. This is how you shift the authoritarian position from yourself and smooth out to do something ”
with the help of other factors.
7. An important recommendation during a child’s crisis at 7 years old : do not treat the child as your own thing . Yes, you gave birth to him and raised him , but he is a separate person and does not have to be absolutely like you. The strongest manifestations of the symptoms crisis occur precisely because of the behavior of the parents . When things start, don't feel like the situation is out of your control, and don't think that your "toy"
broke.
Don't try your best to fix it. You must cope with your parental feelings and understand that child now. crisis together for 7 years, hand in hand . Your main task, as a parent , is to support and guide your child during this important and difficult period for both of you.
Possible changes
Undoubtedly, a child’s crisis is a difficult period not only for him, but also for all other family members. It is accompanied by disputes and stress. But, nevertheless, there are also beneficial consequences of this phenomenon:
- Gradually, a readiness to attend school lessons develops: the child tries to complete all tasks in order to be praised. He tries to please his classmates and teachers.
- The baby shows his “I” - he accepts the obligations that have appeared, adapts to the restrictions.
- The kid tries to comprehend his condition. He can explain his feelings: anger, resentment, joy. This is a huge leap in development, which is very important in the development of personality.
Unwanted actions from parents
How easily the crisis will pass depends on the behavior of the parents and other adults around the child. Below are recommendations for parents:
- Take your child to school no earlier than 7 years old.
- Make adequate demands. Excessive school load leads to serious negative consequences.
- No attempts to control the child’s actions or overprotectiveness. You need to give your baby space to do his own thing.
- Aggression is unacceptable.
- If your performance is poor, you need to show maximum calm and try to find out the reasons.
Signs
Parents will be helped by knowledge about the manifestations of an age-related crisis, so that they can make sure that it has arrived and not mistake other, contextual personal difficulties for signs of a crisis.
Symptoms:
- does not want to obey and does not respond to requests, allows self-will;
- shows stubbornness and obstinacy, demonstrates whims;
- exhibits a painful reaction to any criticism;
- demonstrates a negative perception of everything;
- changes mood abruptly;
- reveals his actions and words (calls names consciously), can openly express his protest;
- allows himself to devalue previous ideals: he can break a toy that is dear to him, uses forbidden vocabulary, and shows cruelty and despotism.
wants to be considered an adult (does not play with younger ones, tries to imitate older ones);
The set should include at least three or four symptoms of the seven-year-old crisis. Otherwise, they will not illustrate an age crisis, but only a contextual case. For example, after a hard day, overwork and fatigue, a child may become capricious in the evening and refuse to go to bed at the usual time. But this is not a sign that the seven-year-old crisis has arrived.
Often at the age of 7, when parents have the wrong attitude towards this stage of the child’s life or the child is not prepared for the school stage, the latter may develop a certain symptom complex. If it is not detected in a timely manner, it will subsequently result in numerous troubles.
In the conditions of the crisis, at first there is a protest (against the fact that social roles have changed, the behavior of parents has become different, a new regime, school, and teacher have come into life). Suffering needs a way out, and it manifests itself in protest (the child does not do his homework, refuses to go to class, does not do what the teacher demands). This is also expressed in somatic manifestations (pressure rises, cold sweat appears, the heart beats faster, the ability to work decreases, attention weakens). Neurotization is the final point in this chain; it requires a visit to a specialist.
Recommended Actions
In order to get through this difficult period faster, experts recommend adhering to the following rules:
- It is better to show the child the school, its attributes in advance and tell about the order that the child will need to follow. You can take a walk around the school, look into the future class, introduce him to the teacher. Regular stories about school will allow him to adapt much faster, because he will already be ready for what awaits him.
- Try to listen to the baby’s opinion and his arguments.
- Lift some restrictions. Let the baby show independence
- Give your baby more freedom of action.
- Do not point out, but convince by giving arguments.
- Praise for any achievements.
- Reward for good deeds and grades.
- Give your child some responsibilities. For example, cleaning the room, washing dishes.