Many people have a stereotype that the goal of any psychologist is to reveal the insides of the soul, get to the bottom of problems, find out the root causes of suffering that goes back to childhood, and work with them. In fact, this is far from the case. For example, one of the directions - behaviorism - studies primarily behavior. In their opinion, the most important things are reflexes, acquired skills, reactions to external stimuli and motivation. This is what determines the essence of a person’s mental organization. Based on this concept, behavioral psychotherapy was created and successfully applied in practice.
What it is
Behavioral psychotherapy is one of the most effective and popular areas in psychology and psychotherapy. Considers some mental illnesses as a consequence of incorrectly formed skills during life.
The scientific basis for it was behaviorism, so its alternative names are behavioral-behavioral therapy or simply behavioral therapy. It is considered one of the newest methods, although in fact it has been used for a long time: its features can be seen in the combination-reflex therapy of Bekhterev, the practical application of Pavlov’s conditioned and unconditioned reflexes, the systematic desensitization of M. K. Jones - all this was actively introduced already in the 20s gg. XX century. Even the term itself was born in 1911 (it was first used by Thorndike in his writings).
The goal of behavioral therapy is to eliminate incorrect behavior strategies and instill useful skills in the patient. Typically, treatment follows a well-established scheme:
Behavior analysis → Identification of an incorrectly formed way of activity → Step-by-step correction by instilling a new skill → Practicing, training → Checking how successfully it can be applied in real life
Everyone is so accustomed to the fact that the root of any evil (be it physical or mental illness) lies in the causes and without eliminating them, recovery is impossible, that the behavioral direction in psychotherapy at first was often criticized and even ridiculed. However, soon his opponents and ill-wishers were defeated, since this method has no equal when working with phobias, eating disorders, autism and alcohol addiction. Patients are completely freed from them. Other concepts cannot boast of such results.
Through the pages of history. Despite the fact that behavioral psychotherapy took shape as an independent direction only in the 50s of the 20th century, its methods have been used in the USSR since the 20s. In the Soviet scientific literature of those times it was referred to as “conditioned reflex psychotherapy.”
Cognitive behavioral therapy course
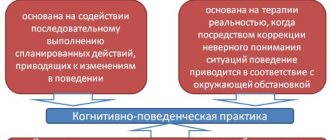
Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on current problems - the here and now. In treatment, most often, they do not turn to the past, although there are exceptional situations when this is inevitable.
The duration of therapy is about twenty sessions, once or twice a week. The session itself usually does not last more than one hour.
One of the most important elements of successful treatment is the collaboration between the therapist and the patient.
Thanks to cognitive behavioral therapy, it is possible to identify factors and situations that give the effect of distorted perception. In this process it is necessary to highlight:
- stimulus, that is, a specific situation that causes the patient to act
- a patient's specific way of thinking in a particular situation
- feelings and physical sensations that result from specific thinking
- behavior (actions) that essentially represent the patient.
In cognitive behavioral therapy, the therapist tries to find connections between the patient's thoughts, emotions, and actions. He must analyze complex situations and find thoughts that lead to an incorrect interpretation of reality. At the same time, it is necessary to instill in the patient the irrationality of his reactions and give hope for the possibility of changing the perception of the world.
Basic principles
The principles on which behavioral therapy works are constantly being updated and improved.
Patterns play a major role in disease
These are the very skills and patterns of behavior that are formed throughout a person’s life. They are the source and essence of a mental disorder, play a decisive role in its development and even cause reactions from the endocrine and autonomic systems.
Treatment methods are only proven
In behavioral psychotherapy, only those treatment methods are used that have been tested more than once in laboratory conditions and bring only positive results. No experiments on patients.
"Here and now"
As in Gestalt therapy, behavioral therapy does not use hypnosis with the goal of looking into childhood and finding there the psychological trauma that becomes the cause of all troubles in the present. The work is aimed at what is bothering a person at the moment and how to cope with this problem “here and now.”
Minimal Intrusion
The specialist does not meticulously delve into the soul, does not ask to bring out hidden thoughts and desires, does not look into the corners of the past. Maximum patient comfort and respect for his personal boundaries are one of the main principles of this direction.
Everything is relative
An alcoholic for society is a patient who requires long-term and compulsory treatment. For a psychotherapist working in the behavioral direction, this is the same person as everyone else, but he has formed an incorrect attitude towards alcohol, which can be corrected.
The opposite situation. Most members of society live the rest of their days with phobias and do not find it necessary to get rid of them (unless they take a pathological form). Nobody considers them sick. And in behavioral psychotherapy these are the main patients. So here they emphasize the relativity of such concepts as “norm-deviation” and “health-illness”.
Psychotherapist - dominant
When you come to see a psychotherapist, you don’t need to try to explain your experiences and formulate the problem. The “speaking out” technique is practically not used here. The main tool is dialogue, and the leading role in it is played by the specialist. He asks questions according to a certain pattern, and after making a diagnosis he gives tasks and exercises. So, if you want to cry into your vest, this is definitely not the place.
Using outside help
This cannot be called family psychotherapy, since it does not work with common problems. Sometimes people close to the patient can be invited to classes, but only for the purpose of helping him consolidate (or, conversely, “unfasten”) a skill.
Types of Behavior Therapy
There are several different types of behavior therapy:
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy is extremely popular. It combines behavioral therapy with cognitive therapy. Treatment centers around how someone's thoughts and beliefs influence their actions and moods. It often focuses on a person's current problems and how to solve them. The long-term goal is to change a person's thinking and behavior patterns to healthier ones.
Cognitive behavioral play therapy
Cognitive behavioral play therapy is commonly used with children. By observing children play, therapists can gain insight into the discomfort the child is expressing or unable to express. Children can choose their toys and play freely. They can be asked to draw a picture or use toys to create scenes in the sandbox. Therapists can teach parents how to use play to improve communication with their children.
Systemic desensitization
Systemic desensitization is largely dependent on classical conditioning. It is often used to treat phobias. People are taught to replace the fear response to a phobia with relaxation responses. The person first teaches relaxation and breathing techniques. Once mastered, the therapist slowly exposes them to fear in increased doses while they practice these techniques.
Aversion therapy
Aspiration therapy is often used to treat problems such as substance abuse and alcoholism. It works by training people to associate a desirable but unhealthy stimulus with an extremely unpleasant stimulus. An unpleasant stimulus can be something that causes discomfort. For example, a therapist might teach you to associate alcohol with an unpleasant memory.
Indications
Behavioral psychotherapy does not treat all mental disorders, but only those that are based on a clear and persistent violation of acquired skills and incorrectly developed methods of action. Indications for contacting such a specialist:
- panic attacks;
- phobias;
- obsessive-compulsive disorder;
- depression, dysthymia, bipolar affective disorder, cyclothymia, manic syndrome;
- eating disorders: bulimia, anorexia, psychogenic overeating, allotriophagia;
- sexual psychogenic problems based on psychopathy, endogenous psychoses and character accentuations;
- schizophrenia;
- antisocial, deviant behavior;
- insomnia, nightmares;
- hyperactivity;
- autism;
- poor performance at school, speech therapy problems in children.
As practice shows, therapy is effective in the treatment of many physiological diseases: hypertension, migraine, bronchial asthma, stomach problems.
Contraindications
Behavioral psychotherapy is contraindicated in some cases. This applies to those patients who have a persistent impairment of consciousness if they cannot understand what is required of them. This entails the inability to perform exercises and tasks aimed at treatment.
Absolute contraindications:
- worsened psychoses;
- prolonged depression in severe form;
- deep UO.
Relative contraindications:
- personality disorders - a course of treatment will be effective only if the psychotherapist manages to establish trusting contact with the patient;
- mild form of mental retardation - treatment is possible, but only with the selection of simple tasks and exercises that the patient can cope with.
Each specific case of contacting a psychotherapist is considered individually.
Behavioral therapy for children
Applied behavior therapy and play therapy are used for children. Treatment involves teaching children different ways to respond to situations more positively.
A central part of this therapy rewards positive behavior and punishes negative behavior. Parents should help reinforce this in the child's daily life.
It may take some time to trust your advisor. This is fine.
They will warm up eventually if they feel like they can express themselves without consequences.
Children with autism and ADHD often benefit from behavioral therapy.
Methods
Imitative (observational, vicarious) learning through observation (modeled)
Basis: A. Bandura's theory of social learning.
Essence: The patient is taught a new skill through the process of imitating another person (a psychotherapist, a movie or book character).
Example: Diagnosis - Aichmophobia. During the sessions, the specialist gradually accustoms the person to the idea that nothing bad will happen to him if he uses a needle, knife, fork, razor, or nails in everyday life, demonstrating his skillful use of them.
Basic techniques: self-modeling (replaying successful moments in the patient’s behavior), prompting (encouragement), fading (reducing rewards as the desired form of behavior is consolidated).
Role-playing training (role play)
Basis: imagotherapy, play therapy.
Essence: Playing out a problematic situation for the patient. Moreover, he can play himself, or a psychotherapist can take on his role so that he can see how his behavior looks from the outside.
Example: Diagnosis - alcohol addiction. A romantic dinner situation is being played out. First, the therapist demonstrates the incorrect (true) behavior of his client, how he gets drunk and ruins the date. Then it shows the successful outcome of the event - if you abstain from alcohol. The patient himself participates in the third act.
Basic techniques: group training, confrontation, systematic desensitization.
Biofeedback (BFB procedure)
Basis: theories of conditioned reflexes of Sechenov and Pavlov, cortico-visceral connections of Bykov, functional systems of Anokhin, stable pathological conditions of Bekhterev.
Essence: Equipment is connected to the patient, with the help of which his physical condition is monitored. Along the way, a session is carried out with exercises and tasks. For every successful decision there is a “reward” in the form of relaxing and pleasant sensations that are created by the same equipment.
Example: Diagnosis - depression. The devices record high blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, heavy breathing, hand tremors and other reactions from the autonomic system. The psychotherapist gives the patient the task of relaxation and peace, liberation from heavy, obsessive thoughts. As soon as he succeeds, he hears pleasant music, sees a beautiful clip on the computer monitor, and is treated to something tasty.
Basic technique: physiological mirror.
These are the main treatment methods used in behavioral psychotherapy. Other techniques may also be used:
- aversive therapy (weaning off addictions);
- systematic desensitization (reducing sensitivity to what causes anxiety and phobias);
- implosion therapy (reintegration of suppressed emotions through immersion in traumatic memories);
- shaping (a multi-step process, practicing a new skill through positive and negative reinforcements);
- method of auto-instructions / self-instruction training (use of inner speech to regulate behavior);
- stress vaccination therapy / stress vaccination / stress vaccination training (learning self-control techniques to help cope with traumatic and stressful situations);
- applied behavior analysis;
- “thought stopping” method.
Treatment methods are selected depending on the diagnosis.
Treatment
Despite the variety of methods, treatment in behavioral psychotherapy is carried out primarily according to one scheme:
Behavioral therapy is often used for children who are struggling in school. For example, the shaping method for speech therapy correction, when the main task is divided into a small chain of correct behavioral acts:
Repeat the syllable after the teacher → Read it correctly yourself → Read the whole word correctly → Read an unfamiliar word correctly → Read the whole phrase correctly
At each stage, a method of systematic desensitization is used.
Behavioral therapy is incredibly effective for autistic people. She breaks down all the skills that are difficult for them into separate blocks: speech, contact, play, listening and looking into the eyes. Each of these actions is mastered gradually.
An example of one of the very first exercises in behavioral psychotherapy for autism, “Language - Understanding”:
- Assignment: Raise your hand when asked.
- Hint: the specialist himself takes the child by the hand and raises it, pronouncing the task.
- Stimulus: encouragement in the form of praise or sweets.
- Independent completion of the task.
Autistic children perform this exercise only 5 or even 10 times.
Features of the study
Anxiety disorders and social phobias limit the lives of at least one in 10 children. However, up to half of these children do not benefit from short-term psychotherapy treatment alone or medication alone. That's why researcher John Walkup, MD, and his colleagues cited several government-funded studies to determine whether the combination treatment would help.
Researchers observed 488 children and adolescents aged 7 to 17 years. They all suffered from separation anxiety disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, or social phobia.
There were four different treatment groups:
- 76 children received inactive placebo tablets.
- 133 children received Zoloft alone - starting at 25 mg per day and up to 200 milligrams per day for eight weeks, including eight 30- to 60-minute sessions to study drug response and side effects.
- 139 children received CBT only - 14 one-hour sessions.
- 140 children received a combination of cognitive behavioral therapy and Zoloft.
After 12 weeks:
- 24% of children in the placebo group experienced significant or moderate improvement.
- 55% of children in the Zoloft group experienced significant or moderate improvement.
- 60% of children in the CBT group experienced significant or moderate improvement.
- 81% of children in the CBT/Zoloft group experienced significant or moderate improvement.
Directions
Behavioral psychotherapy is evolving and has several branches.
Dialectical-behavioral psychotherapy
In 1987, the American psychologist M. Linehan gave birth to a new direction, which was called dialectical behavioral psychotherapy.
The goal is to treat borderline personality disorders.
Results:
- the risk of an emotional reaction to traumatic situations is reduced;
- the risk of suicide, aggression, and deviant behavior is reduced.
Dialectical psychotherapy received this name because the patient begins to realize that even the most hopeless situation has several ways of successful resolution. During the course of treatment, he learns to be calm, weigh the pros and cons, and choose the best outcome.
This is the eclectic movement of the “third wave”. Methods used: problem analysis, involvement in action, effective communication, non-judgment, meditative techniques, self-soothing, etc.
Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy is supported, first of all, by its high effectiveness, which has already been repeatedly confirmed by clinical studies.
The advantage of this type of treatment is the development of self-awareness of the patient, who after therapy achieves self-control over his behavior.
This potential remains in the patient even after the end of therapy, and allows him to prevent relapses of his disorder.
An additional benefit of therapy is the improvement of the patient's quality of life. He receives an incentive for activity and higher self-esteem.