Prerequisites
Team - what is it in psychology
There are factors influencing the formation of personality conformity:
- The closeness of the individual to group members;
- A person's willingness to make decisions independently. This means whether a person can make decisions at all, i.e. whether he has a pronounced tendency to conformism or not. There are people who in any group will follow the majority opinion. Some people with a tendency to conformity have a selective attitude: they will adapt only to the people they “need”.
- Social status in the group;
- Age;
- Physical and mental state of a person;
- Situation.
Interesting. The most common example of conformism in life is when a person joins a new team. The individual strives to impress others. Also, everything depends on the formation of the individual.
Sometimes it happens that circumstances force you to accept the demands of others. In this case, the internal position will differ from the majority opinion. The duration of such a situation depends on the circumstances and character of the individual.
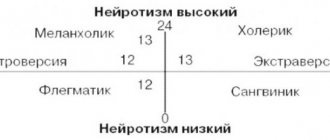
Conformity, conformism
Film "Me and Others"
Conformism.
Film “Me and Others”
Is the porridge sweet? Like everyone else, so am I.
Film “That Munchausen”
Can I trust my own eyes?
Conformism is following what is accepted by others or the authorities, the attitude (desire and habit) to be like everyone else (There is a certain relationship between conformity and the external locus of control. See Locus of control and conformity).
Like everyone else - think, talk, dress, live... Everyone wears jeans - and I will wear them, everyone has posters of their favorite bands at home - and I should have them.
Conformity is a tendency to conformism, to change one’s views and positions following those that prevail in a given society, group, or simply significant others. Conformal behavior is behavior where a person follows the expectations of others, ignoring his own opinions, goals and interests. A conformist is a person for whom conformism or conformity is characteristic. If conformity becomes a defining feature, they speak of a conformist personality type.
Conformity can be external and internal, passive and active, conscious and thoughtless... Although, as a rule, mindless agreement is called conformism, see Types of conformism
In one of the kindergartens they conducted an experiment and filmed it. Children aged about five years old were given porridge, or rather, they were offered to try porridge from one large plate. None of the children knew that some of the porridge was flavored with salt instead of sugar, and when they were offered normal porridge, all the children answered with pleasure that the porridge was very tasty. After most of the children said that the porridge was sweet, the experimenter gave the girl a heavily salted, almost bitter porridge to try. From the very first spoon, the girl’s face grimaced, tears flowed from her eyes, but when asked “Is the porridge sweet?” the girl replied: “Sweetie.” Since everyone said that the porridge was sweet, then she will say like everyone else.
What is the nature of conformity? Conformist behavior is usually based on the fear “if you stick your head out, it will be worse!”: As a rule, the group reacts negatively to those who oppose it. People who actively go beyond the mold are usually subject to pressure and aggression from conformists - the “silent majority”. Conformal behavior and agreement can sometimes be a manifestation of conscious loyalty to external demands: “As they tell me, that’s what I’ll think, and that’s right. Those from above know better.” Such conscious loyalty is sometimes wisdom, but more often it is cowardice and laziness to think for oneself, turning into a habitual standard of behavior in groups in which responsibility is dispersed. Fear and laziness to think for yourself are the two main reasons for conformist behavior.
Is conformity more likely to be innate or acquired? And so and so. There are children who are born with an attitude towards conformity, there are those who are rebels from birth, there are those who are neither conformists nor rebels, but simply those who look at everything with common sense. See→
The level of personality conformity depends on many factors. The larger the group and the higher the unanimity in it, the more difficult it is to resist. If a group is prone to aggression towards those who oppose it, conformity also increases: no one wants trouble for themselves... In this case, personal characteristics play a large role: usually women, children and adolescents, people with low status and low intelligence, anxious and suggestible. The more a person is attached to or dependent on a group, the higher the level of conformity. On the other hand, the conformity of almost any person manifests itself where the person understands little and does not care about what is being discussed. In this case, most people prefer to agree with the majority.
The most widely known are the following experimental studies of conformity (Kondratiev M. Yu., Ilyin V. A. Conformism // ABC of a social psychologist-practitioner. - Moscow: Per Se, 2007. - 464 pp. - 2000 copies - ISBN 978-5- 9292-0162-2);
1935 - Muzafer Sherif's experiment, 1951 - "Asch Experiment", 1963 - "Milgram Experiment", also known as the "Eichmann Test". See→
What to do with conformity? It's easier to say what not to do. For example, it is stupid to denounce such behavior “eye to eye.” If you observe pronounced conformist behavior in a person, think twice before telling him about it, especially - and God forbid - in a harsh form. The result will not be “wiser” of this person, but resentment and quarrel. If you want there to be less conformity in the world, do not touch those who have already formed, but take up the education of those who are still growing, still receiving an education, still looking for themselves and still thinking. This is definitely more promising.
I don't want to be a conformist!
If not to be a conformist, then what to be? You don't have to go with the flow, you have to go where you need to go. It is stupid to be “like everyone else,” just as there is no task to be “not like everyone else.” You need to think, listen to smart people - and develop your own values, live in a way that seems worthy to you. Your immediate choice is a self-determined individual. See→
Classification
Social perception - what is it in psychology
Scientific presentations also include classifications of this phenomenon. Conformity is of the following types:
- Interior. The individual agrees with the opinion of the group, but does not share it himself. A personal conflict occurs, a person stops striving to achieve his goals. He supports the aspirations of other group members and is forced to adapt to his environment.
- External or compliant. The individual tries to meet group requirements, while personal beliefs remain unchanged. He does not express his disagreement openly. Usually short and one-dimensional.
- Negative or non-conformist. A person clearly expresses his disagreement with the opinion of the majority and does not make concessions or constructive dialogue.
There is a classification according to the degree of attitude towards others:
- passive – the person is pressured by group members;
- active - actions are directed by a specific person who has a position in society.
Psychologists and sociologists divide conformism according to the degree of awareness:
- Conscious is the rarest variety. The individual understands that he is doing wrong, but accepts conformity;
- Unconscious - the individual does not notice that someone is influencing his decision.
A person’s behavior depends on the type of social conformity. This trait is not constant, its appearance depends on certain factors.
Manifestation of conformity
What influences conformist attitudes?
Some people are more willing to obey authority.
They are called authoritarian personalities or uncontrollable personalities. Their opposite is internal nonconformists who are not easily influenced by other people. Conformist behavior is influenced by:
- a person’s personality, formed in the process of socialization,
- the type of social relationships in which the individual participates,
- group structure,
- other members of the group (as evidenced by Solomon Asch's research),
- the type of task performed by a person in a group,
- a method of authorizing action or a form of social control.
There are also circumstances that favor the subordination of a person to a group.
This happens when:
- the person has low self-esteem and a strong sense of insecurity,
- the group consists of specialists
- a person seeks to participate in a group,
- the group is unanimous,
- the unit has no allies,
- the person has a weak position in the group.
Assertiveness in Psychology - What is it?
Conformism in psychology and sociology
Perception - what is it in psychology, definition
Conformity in psychology is a distinctive feature of a person’s character. Conformity is a behavior model in psychology when an individual accepts the opinion of the majority. A person takes it in order to be accepted in society. He believes that everyone should think the same and begins to make excessive demands on himself and others.
In sociology, conformity is a character trait that cannot be assessed unambiguously. This is due to the fact that it is an important component for the socialization of the individual and the preservation of self-esteem.
Levels of depth of conformity
There are many levels of depth of conformity.
This:
- Submission
, which only occurs when the pressure group is physically present. When it disappears, the person returns to his beliefs or behavior. The motive for action is most often the fear of punishment or rejection from the group. - Identification
is a deeper form of conformity. He appears even when the group is not physically present. This is said when an individual identifies with a group, resulting in his behavior adapting to the ideas of the individual. - Introjection
(or internalization) is the deepest form of conformity, which involves recognizing certain norms and values as one’s own. This is one of the tasks of socialization.
Psychologically unstable character: should you be afraid?
Basic theories
Among psychologists and sociologists, there are several theories about the emergence of conformism:
- Information theory. Its author is Leon Festinger. The basis is the impossibility of checking all the data that comes to a person. Because of this, he has to rely on the opinions of other people, but only if it is supported by the majority.
- The theory of normative influence. Its essence lies in the desire of a particular individual to have the advantages that can be obtained by becoming a member of the group.
For your information. Social conformity is usually assessed negatively. But you shouldn’t be unambiguous - it all depends on the specific situation. Sometimes you need to agree with established rules, for example, in extreme situations, when success depends on the coherence of the participants’ actions.
The concept and essence of conformism
Definition 1
Conformity is an individual’s acceptance of the norms and requirements of society or adherence to the principles of the social community in which the individual is included.
The essence of this term was studied by scientists from different scientific fields in different time periods. At the same time, it was given different meaning and content, as well as the reasons for its formation and development.
Conformity has been studied as:
- The relationship between the independence of the human soul and the need to belong to something, be identical to something, fulfill someone’s demands and be like someone. This is how conformism was viewed by ancient Greek thinkers - Aristotle, Socrates, Democritus;
- The phenomenon of development of large social groups. G. Lebon, G. Tarde, D.V. worked in this direction. Olshansky;
- Personal drama, caused by its destruction under social influence, when adapting to its structure. Conducted the following research: E. Fromm, K. Horney;
- Development of personal problems arising from social influences on its development. The researchers of these theories were: Z. Bauman, J. Erman, S.E. Krapivensky;
- Ability to adapt and adapt. Such views were held by S. Freud and G. Jung;
- A necessary component of personal socialization and the development of moral qualities. This issue was studied by scientists: I.S. Kon, Chudnovsky and others;
- Values through which it is possible to create sustainability in society, its stability. This view was held by R. Merton.
- It should be noted that all researchers considered conformity as following certain norms of behavior, in the absence of one’s own opinion and being subject to someone else’s, namely social, influence.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Coursework Conformity in psychology 490 rub.
- Abstract Conformism in psychology 230 rub.
- Test paper Conformity in psychology 210 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Personality conformity as a psychological personality trait was discovered by psychologist Solomon Asch.
Definition 2
Conformity is a conscious desire to agree with the opinion of the social group in which the individual or society as a whole is included.
This quality of personality reflects its involvement in society, the desire to be part of it. Traditions and customs that an individual adheres to are a manifestation of his conformity, since they characterize actions, the implementation of which occurs from generation to generation, i.e. their implementation is influenced by following social trends, the opinion of a social group - a nation, a nationality.
With the emergence of the term conformity, the social element in personal development was first approved, namely its significance and influence on personal formation and development.
Scientists studied various social groups and representatives of different genders. The results of the study were the identification of a large percentage of individuals who are susceptible to the development of conformism, i.e. can subordinate their behavior to the requirements of a social group, change principles and opinions based on social requirements.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
Manifestations of conformism
Most managers want this character trait in their employees because such people:
- Adapt faster. It's easier for them to make new acquaintances. They try to follow established rules, so they manage to avoid conflict situations;
- They are not independent. If an individual has agreed with others for a long time, then gradually he loses the ability to make decisions;
- Agree with almost everything that the leader or influential members of the group propose;
- Negative attitudes towards minorities. Such people have a negative attitude towards those who do not agree with the opinion of the majority. Competition disappears, individuals with different views are not given opportunities for development;
- They do not have creative thinking. Individuals prone to conformism try not to stand out from the crowd, so you should not expect ideas for new ways of development from them.
In the course of social research and experiments, it was concluded that such people are good performers, but cannot occupy leadership positions, where the ability to defend one’s point of view and offer ideas for solving problems is valued.
New team
Current test. Group cohesion. social studies test (grade 10) on the topic
Current test. Group cohesion. Option #1.
1. The possibility of conflict-free communication and coordination of actions in conditions of joint activity is the basis -
1) cooperation 2) coordination 3) compromise 4) compatibility
2. Are the following statements true?
A. Interpersonal compatibility is the mutual acceptance of partners in communication and joint activities.
B. Interpersonal compatibility is the effect of a combination of people that gives the maximum result of activity with minimal psychological “costs” of the interacting persons.
1) only A is true 2) only B is true 3) both statements are true 4) both statements are false
3. Interpersonal compatibility is studied -
1) psychology 2) sociology 3) cultural studies 4) philosophy
4. Specify factors that do not influence psychological incompatibility -
1) rejection of each other 2) asynchrony of mental and motor reactions 3) differences in attention 4) temperament 5) working conditions
5. Are the following statements true?
A. Low levels of group compatibility are determined by the psychophysiological compatibility of the temperaments and characters of group members.
B. At higher levels, group compatibility is the intensity of communicative intragroup connections.
1) only A is true 2) only B is true 3) both statements are true 4) both statements are false
6. The criterion for interpersonal compatibility is -
1) satisfaction of the needs of the individual 2) satisfaction with the result of the activity 3) satisfaction of the interests of the group 4) all of the above
7. A person strives to be with those with whose attitudes and positions he agrees - this leads to
1) interpersonal integration 2) personal individualization 3) group cohesion
4) interpersonal disconnection
8. Value-orientation unity is
1) high degree of consistency of views, positions, attitudes, opinions, assessments
2) a high degree of coordination of the actions of group members in connection with the immediate goals of its main activities
3) there is no correct answer
4) answers 1 and 2 are correct.
9. Who owns this statement: “Cohesion is the feeling of “We”, the degree of connection of group members with each other, for example, due to mutual sympathy”?
1) G. Andreeva 2) P. Sorokin 3) O. Kont 4) D. Myers
10. The conflict between the opinion of the individual and the opinion of the group, which is overcome in favor of the group, is
1) conflict 2) compromise 3) dialogue 4) conformity
11. Conformity associated with the subordination of an individual to the influence of a group due to the desire to remain a member of it is
1) internal conformity 2) external conformity 3) internal and external conformity
4) there is no correct answer
12. Are the following statements true?
A. Conformal behavior helps correct a person’s erroneous opinion or behavior if the opinion or actions of the majority are more correct.
B. Conforming behavior interferes with the assertion of one's own independent behavior or opinions.
1) only A is true 2) only B is true 3) both statements are true 4) both statements are false
13. Insert the missing words into the text.
“Depending on the reaction to group pressure, a group member can act: 1) as (1)__, i.e., agree with the opinion of the group and change behavior in the direction of group pressure; 2) how to (2)__, i.e. resist group pressure, think and act contrary to it; 3) as (3)__— selectively
respond to the group’s influences by agreeing with its opinion or not accepting it, depending on the specific situation.”
1)____________________________ 2)_____________________ 3)_____________________
Current test. Group cohesion. Option number 2.
1. Compatibility based on likes and dislikes is
1) interpersonal 2) emotional 3) business 4) friendly
2. “Workability” of group members is formed and manifested in activities -
1) emotional 2) interpersonal 3) professional 4) business
3. Indicate the factors influencing the compatibility of people -
1) personality type 2) operating conditions 3) combination of value orientations
4) social attitudes 5) temperament 6) living environment
Answer:______________________
4. Are the following statements true?
A. Interpersonal compatibility can be absolute.
B. There are higher and lower levels of compatibility.
1) only A is true 2) only B is true 3) both statements are true 4) both statements are false
5. Are the following statements true?
A. The highest level of group compatibility is expressed in the mutual reference of group members.
B. High levels of compatibility cannot affect low ones.
1) only A is true 2) only B is true 3) both statements are true 4) both statements are false
6. Interpersonal compatibility, as a rule, is accompanied by the emergence of -1) a feeling of satisfaction 2) antipathy 3) indignation 4) sympathy
7. Motivational cohesion is
1) level of mutual sympathy in interpersonal relationships
2) the degree of attractiveness of the group for its members
3) the degree to which the various needs of the individual are satisfied in the group
4) all of the above
8. Indicate factors that can influence the development of cohesion in a group
1) the activity being carried out 2) the incentive system 3) the temperament of the participants
4) perception of the surrounding world
9. Are the following statements true?
A. Group cohesion is also reflected in group opinion.
B. In a cohesive group, simultaneously with group opinion, there can be a diverse and even contradictory picture of individual tastes, preferences, interests that are not related to the content of the main activity and do not interfere with it.
1) only A is true 2) only B is true 3) both statements are true 4) both statements are false
10. The phenomenon of conformity has been established -
1) G. Andreeva 2) P. Sorokin 3) S. Ash 4) D. Myers
11. Conformity associated with real approval, a person’s agreement with the opinion of the group, its requirements is
1) internal conformity 2) external conformity 3) internal and external conformity
4) there is no correct answer
12. The category of people characterized by the “spirit of contradiction” is called -
1) conformists 2) nonconformists 3) nihilists 4) conflicting
13. Insert the missing words into the text.
“Depending on the reaction to group pressure, a group member can act: 1) as (1)_, i.e., agree with the opinion of the group and change behavior in the direction of group pressure; 2) how to (2)_, i.e., resist group pressure, think and act contrary to it; 3) as (3)_—selectively
respond to the group’s influences by agreeing with its opinion or not accepting it, depending on the specific situation.”
1)____________________________ 2)_____________________ 3)_____________________
Advantages and disadvantages
In social psychology, conformity is an issue due to the difficulty of assessing such behavior because it has its own advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include:
- Fast adaptation. It is easier for a person to make acquaintances; he does not have problems in a new team.
- Cooperation with other group members in difficult situations increases the chances of success.
- Clear distribution of responsibilities.
In addition to the listed advantages, the phenomenon of conformity has disadvantages, so this model of behavior cannot be given an unambiguous assessment:
- Loss of individuality. A person begins to think like everyone else, he has no choice. Over time, he forgets about his needs, his mind is occupied with the interests of other people, and not his own.
- Negative attitude towards people who have a different opinion from the generally accepted one. A conformist demands from those around him complete submission to established norms, not allowing that people may have a different view of things.
- Lack of development. The individual follows exclusively established norms. He does not make decisions on his own and does not generate ideas. Therefore, he has no need for self-development.
The phenomenon of conformity is a common psychological phenomenon, especially when a person wants to make a good impression on society. Sometimes people focus only on the merits of this model of behavior. However, if you adhere to such a pattern for a long time, personality regression occurs. Therefore, you need to find a balance between conformism and your opinion.
Test with answers on the topic “Preventing burnout and conflicts”
The unethical nature of the conflict between medical staff and the patient is due to the special role of the patient as someone in need of help.
1. Conflicts are possible within the framework of a nurse’s work in a health care facility.
1) with doctors;+ 2) with colleagues;+ 3) with the government; 4) with representatives of pharmaceutical companies; 5) with the patient’s relatives.+
2. What are the features of the conflict between the nurse and the patient?
1) the fault in such a conflict lies with the attending physician; 2) the fault always lies with the nurse; 3) the conflict can be caused by the patient’s personal characteristics;+ 4) the conflict is caused by professional burnout;+ 5) the nurse should always avoid conflict, regardless of the degree of her guilt.+
3. What is the specific feature of human conflicts that is not inherent in animals?
1) biological background; 2) conditioning of the symbolic world; + 3) the special role of mass media; + 4) social construction; + 5) purely psychological nature.
4. The main reason for patient aggression
1) malicious intent; 2) altered state of consciousness; 3) psychopathy; 4) fear, worry.+
5. The main quality of a professional in the social sphere
1) impeccable adherence to formal instructions; 2) suggestibility; 3) general intelligence; 4) reflection.+
6. The main aspect of reality in which a person exists
1) biological; 2) cultural; + 3) physical; 4) chemical.
7. Which factors play a role in the emergence of a conflict between a patient and medical staff?
1) influence of mass media; + 2) prohibitions in the medical environment; + 3) positive attitude of medical staff; 4) the condition of the patients; + 5) the economic activities of the administration.
8. What is the role of mass media in the relationship between staff and patients?
1) reporting only truthful information; 2) construction of ideas about the hospital and the formation of an information space; + 3) indirect induction of mistrust and aggression; + 4) insignificant compared to the patient’s own ideas; 5) creating a negative image of the doctor.+
9. What are constructive ways for health care providers to mitigate patient aggression?
1) retaliatory aggression; 2) lack of a symmetrical response; + 3) positive attitude; + 4) understanding the root causes of the patient’s aggression; + 5) use of physical force.
10. What are the conflict-prone features of the medical environment?
1) power of staff over patients; + 2) friendliness of staff; 3) the presence of many prohibitions; + 4) the irremovable inequality of staff and patients in the hospital space; + 5) the natural hostility of patients.
11. What are the grounds for effective communication in a conflict situation?
1) ignoring; 2) insistence on one’s own rightness; 3) awareness of one’s own state;+ 4) awareness of the state of another.+
12. What are the consequences of professional burnout?
1) loss of interest in the profession; + 2) mental well-being; 3) psychological dissociation; + 4) psychosomatic illnesses; + 5) increase in income.
13. What are the causes of professional burnout?
1) exhausting work; + 2) interesting and varied activities; 3) violation of self-identity in the profession; + 4) only physical fatigue.
14. What method of interaction between staff and conflict-ridden patients is constructive?
1) ignoring; 2) retaliatory aggression; 3) acceptance; + 4) physical suppression.
15. The key mechanism of human existence in the cultural world
1) biological struggle for survival; 2) psychological processes; 3) symbolic ideas about what should be; + 4) economic processes.
16. The key elements of the correct behavior of a nurse in relation to a patient are
1) aggression; 2) indifference; 3) care;+ 4) acceptance;+ 5) empathy.+
17. Conflict with the patient in nursing practice
1) absolutely unacceptable; + 2) desirable; 3) sometimes acceptable; 4) acceptable.
18. Conflict is a process
1) two-sided; + 2) not based on empathy; 3) one-sided; 4) based on empathy;+ 5) self-inducing.+
19. Our attitude to social reality is determined
1) sensory data; 2) introspection; 3) exclusively objective reality; 4) our culturally determined interpretations.+
20. The unethical nature of the conflict between medical staff and patients is due to
1) exclusively by tradition; 2) the special role of the patient as someone in need of help; + 3) the social status of the medical staff; 4) the criminal code.
21. Features of conflicts in the human environment
1) conditioned by biological instincts; 2) conditioning by both psychology and culture; + 3) purely cultural conditioning; 4) purely psychological conditioning.
22. Feeling tired when burned out
1) objectively reflects the fatigue of a professional; 2) usually does not appear; 3) is a psychological phenomenon; + 4) is a consequence only of hard physical labor.
23. The concept of reflection includes
1) external control; 2) suggestibility; 3) thinking about your actions;+ 4) self-control;+ 5) introspection.+
24. Causes of aggression in patients
1) hopelessness;+ 2) pressure of the hospital atmosphere;+ 3) hope for a speedy recovery; 4) mental well-being; 5) fear.+
25. Rational strategies for interacting with a conflict patient
1) aggression; 2) goodwill; + 3) complaints to the administration; 4) ignoring; 5) acceptance.+
26. Reflection in psychology is
1) type of empathy; 2) reflection of oneself in one’s own consciousness; + 3) ability to judge; 4) ethical actions.
27. Reflection is a property
1) basically innate; + 2) individual; 3) exclusively acquired; 4) socially determined.
28. Reflection is a competence
1) universal; + 2) political; 3) social; 4) economic.
29. What is included in the concept of professional burnout?
1) exhaustion by hard work; + 2) interest in work; 3) increasing work productivity; 4) getting used to the activity;+ 5) psychological fatigue.+
30. Which of the following could be the root cause of the conflict?
1) hyper-reflexivity; 2) lack of reflection; + 3) mental well-being; 4) satisfaction with your job.
31. What are the root causes of burnout?
1) lack of reflexivity; + 2) comfortable working conditions; 3) meaningful work; 4) difficult psychological working conditions;+ 5) hard work “for wear and tear.”+
32. Empathy is fundamentally a process.
1) verbal; 2) socially determined; 3) formalized; 4) emotional.+
If you want to thank the author, say thank you, or order a test, you can simply send a DONATION for the development of the project (for PCs on the right, for mobiles at the bottom of the site). This way we will see your support and feedback and will be motivated to do even more! Thank you.