To analyze the topic of the article in detail, it is necessary to find out the meaning of the word “agglutination”. This term in psychology defines a combination of properties, qualities or parts of objects that are at first glance incompatible in reality.
The human imagination is capable of actively creating new images. The incentive for this is both general life vicissitudes and serious personal motives. The process, or rather the way in which these images are created, is precisely the very agglutination that will be discussed below.
The concept of agglutination in psychology
By this definition, psychologists understand a certain play of the individual’s imagination, as a result of which completely new images, postulates and ideas are born, uniting qualities and characteristics of various phenomena and objects that are not comparable in real terms. The word “agglutination” itself, translated from Latin, literally means gluing, sticking together.
Agglutination in psychology is a special type of connection or fusion in the imagination of unconnected features and characteristics of different objects.
Agglutination is classified as an analytical-synthetic process. The result of the work of the imagination (or the process of agglutination) is the emergence in a person’s head of a collective image of several figures, characters and types that are incompatible in primary perception.
Vivid examples of how the imagination works are such famous images created by people as a centaur or a hut with chicken legs. It is agglutination that helps writers, poets, artists and screenwriters realize their creative ideas.
The creation of a new holistic image is possible thanks to the specifics of the functioning of the human brain - analysis and synthesis. By analyzing data, a person breaks down incoming information into its component parts, and by synthesizing them, he gets the opportunity to combine it into new ideas and concepts.
However, it is worth understanding that this process of “putting together a mosaic” is not chaotic. The combination of various details into a single whole is facilitated by a certain idea, design or other motives, which can sometimes manifest themselves in the context of a person’s subconscious.
In this case, the starting point for these transformations will be a person’s personal experience. The possibilities of his imagination will depend on how bright and varied he is.
Sometimes agglutination may indicate the presence of certain serious mental illnesses (schizophrenia), as well as speech disorders. The neologisms (new words) that arise will not have much meaning and, most often, will be incomprehensible not only to the doctor, but also to the patient himself. However, it is the appearance of such neologisms that makes it possible to diagnose these diseases.
Agglutination in psychology as a method of assessing the state of the individual – Psychological assistance
15.07.2019
Agglutination is the most important tool in psychology, with the help of which the state of the individual is assessed and how a person sees the surrounding reality. This phenomenon is quite common not only in human nature, but also in the whole world. In some cases, it can be found in people suffering from schizophrenia, as well as in those who have speech disorders.
In psychology, this concept is considered as an imagination created by combining objects that exist in reality. The term itself is represented by a description of a phenomenon that fuses together different elements in the form of images, thoughts and words.
This method in psychology is a special type of fusion, where a combination of completely incompatible features and characteristics belonging to objective reality occurs.
The essence of the human imagination seems to be a dialogue between the various parts of the “I” and the personality itself . Various motives related to the necessity of life are stimulants.
The imagination of a person himself is accomplished through human actions related to the mental, due to which images are formed.
Agglutination in psychology can be represented in the form of fairy-tale images
- sphinxes, in which the outlines of a human face are combined with lion characteristics;
- centaurs, in which human characteristics are combined with the characteristics of a horse;
- mermaids, in which the torso of a beautiful woman is connected to a fish tail.
Each of these images was created through the rich imagination of man.
Agglutination, as a phenomenon, is a process related to psychology, and can also be found in linguistics and medicine.
In linguistics, this method, as a process, is the merging of different words into one. In this case, the original meaning is preserved, but the morphological structure is reduced. Accordingly, in linguistics, agglutination is a process by which words are created using the morphological elements of language combined into a whole.
Causes of agglutination
Agglutination in psychology is a game of imagination, based on the previously acquired experience of an individual, as a result of which new images arise.
The reasons for the phenomenon are:
- features of human mental activity - it is human nature to analyze and synthesize information, which leads to its transformation and combination into unexpected forms in different individuals;
- existing experience – the acquired knowledge is not kept idle in people’s heads. The peculiarity of a thinking person, as mentioned above, is that he strives to use the accumulated experience, passing the information received through the prism of his own thinking;
- the desire to create something new - sometimes it happens that a person is fascinated by an idea, but for its concrete expression he needs to create something new, previously unknown, in his head;
- the dynamism of the development of the world - human consciousness knows that the world is not something immutable and static and that it can be changed by creating something new - discoveries, achievements and inventions, while improving one’s life.
Sometimes the causes of agglutination are mental illnesses and disorders in the development of speech, but these cases are extremely rare.
Combination, agglutination, accentuation, typification - imagination techniques according to S.L. Rubinstein
This article belongs to the Category: History of the study of the creative process itself
1. S. L. Rubinstein
“The transformation of reality in the imagination is not a purely arbitrary change; it has its own natural paths, which find expression in typical methods or techniques of transformation.
One such technique is combining
, a combination of elements given in experience in new, more or less unusual combinations. This is a very common way of transforming reality. It finds application in science, in technical invention; it is used in art, in artistic creativity.
Yes, Tolstoy
wrote that he created the image of Natasha by taking some features from his wife Sonya, others from her sister Tanya, “reshaping” them and thus getting the image of Natasha.
However, there is no doubt that the main work of creating the artistic image of Natasha was not in “combining” the features of Sonya and her sister Tanya, but in that very complex creative process, which deeply processed and essentially transformed some and other features, which Tolstoy mentions when he says, that he “remixed” the features of both sisters. Only as a result of deep synthesis and transformation could such an extremely holistic image of Natasha be obtained.
2. L. Pasternak, illustration for the novel “War and Peace” - “Natasha Rostova at the first ball”
A special case of transformation through combination or new combinations of data in the experience of elements is the so-called agglutination
, which has long been widely used by art. It is found, for example, in monuments of ancient Egyptian art and in the art of North American Indians.
An example of agglutination is the allegorical figure shown in the figure. Commenting on his composition, Leonardo da Vinci
explains that she depicts “pleasure together with displeasure, and they are depicted as twins, since sometimes one is inseparable from the other; they are made with their backs turned, since they are opposite to each other...”
From these words of the artist it is clearly seen that combination, or agglutination, is regulated and directed by a certain tendency that gives it meaning. Combination is usually not a random set, but a selection of certain features. The artist produces it consciously, guided by a certain idea, design, and general composition.
Sometimes the tendency which determines and regulates new combinations of elements in the imagination functions unconsciously; but, as always, it is there, contained in the motives that determine the activity of the imagination. Supporters of the associative, atomistic concept tended to put forward combination as the only method of transformative activity of the imagination.
The combination itself was reduced only to new combinations and rearrangements of unchanged elements given by experience.
3. Annunciation (1475–1480), Uffizi, is thought to be Leonardo's earliest complete work
There is no doubt that the starting point for the transformations carried out by the imagination is experience. Therefore, the wider, richer, more diverse a person’s experience, the richer his imagination will be, all other things being equal.
But the recognition of this dependence of the imagination on experience should in no case lead to the recognition of that widespread and deeply rooted, although erroneous, theory, according to which the transformation carried out by the imagination is reduced to combination, that is, to the movement or (rearrangement of elements) .
This purely mechanistic conception of the imagination, which assumes that the elements themselves must remain unchanged, is inextricably linked with associative psychology, and its importance declines with it. The perception of reality does not consist of bundles, bundles or mechanical aggregates of unchanging elements.
All his formations can be subject to transformation, which is carried out by the imagination. These transformations are extremely diverse; they include combination as one of the techniques, but are in no way reducible to it.
As a result of the transformative activity of the imagination, since we are talking about creative imagination, what is obtained is not just a new combination or combination of invariably given elements or features, but a single new image in which individual features are not simply summed up, but transformed and generalized.
4. Unfinished painting of Saint Jerome in the desert (c. 1480), Vatican
Combination is only a “mechanism”, the action of which is usually subject to some tendency that determines the selection of combined moments and gives it meaning. Another method of transformative activity of the imagination is emphasizing
certain aspects of the displayed phenomenon, which transforms its overall appearance.
Accentuation is emphasizing features. It is often achieved through a shift, a change in proportions.
Caricature uses this technique in a more or less sharp, rude form: the caricature reproduces the features of the original, otherwise it would not have hit the person it was aiming at; but she exaggerates one or another of his features, otherwise she would not be a caricature.
At the same time, accentuation, in order to be significant, must highlight the characteristic, essential, must in a visual image, in the particular and concrete, reveal the generally significant.
From here there are two lines. On the one hand, the quantitative aspect of changes in proportions in the sense of size finds a specific expression in changes in magnitude, in decrease and increase (litotes and hyperboles), which are widely used in the fantastic depiction of reality.
Thus, in fairy tales, in epics, in folk art, giant heroes of unprecedented size and unprecedented strength usually appear (Svyatogor puts Ilya of Muromets in his pocket, from his whistle leaves fall from the trees and the earth trembles; in F. Rabelais, little Gargantua, amused, removes the bells from Notre Dame Cathedral and hangs them around the neck of his horse, etc.
; in fairy tales there is a boy-thumb). These exaggerations and understatements, shifts in size and magnitude in the fantastic depiction of reality are always motivated by some semantic tendency.
The appearance of a giant, grandiose size, physical strength, majesty of appearance can serve to make visual and obvious the inner strength and significance of the hero portrayed in this way.
On the other hand, greatly underestimated in comparison with reality, fantastically small external dimensions can, by force of contrast, especially emphasize the great internal advantages of such a character.
Just as the performance of a child barely visible on the stage produces a greater impression than the objectively equal performance of an adult, the manifestation of intelligence, intelligence, and fearlessness on the part of a child is especially striking if he presents himself as a little boy. Thus, deviation from reality, fantastic larger or smaller dimensions serve to more clearly reveal and illuminate more clearly a certain phenomenon, property or side of reality.
5. Last Supper (1498), monastery of St. Maria delle Grazie, Milan, Italy
Finally, the transformation of reality in the activity of creative imagination follows the line of typification
, i.e., a specific generalization. Already accentuation emphasizes and thereby distinguishes something as significant.
This is just one of the ways in which a single image is transformed, giving a generalized meaning.
The emphasis on certain features or aspects of the image is combined with a number of other transformations: some features are completely omitted, as if dropped out, others are simplified, freed from a number of particulars, details, and their complicating aspects. […]
All means of expressiveness (tropes, figures, etc.) used by literary creativity serve as a manifestation of the transformative activity of the imagination.
Metaphors, personifications, hyperboles, antitheses, litotes - these are all techniques that so emphasize one or another aspect in the image that the whole of it is transformed.
All the main forms of creative transformation of reality that literature uses reflect in a processed, stylized form those transformations that the imagination uses.”
Rubinstein S.L., Fundamentals of general psychology, St. Petersburg, “Peter”, 2008, p. 304-307.
Source - portal VIKENT.RU
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/vikent_ru/kombinirovanie-aggliutinaciia-akcentuirovanie-tipizaciia—tehniki-voobrajeniia-po-sl-rubinshteinu-5db149b62beb4900ada0c8c3
Signs
Agglutination in psychology is a person’s imagination, with the help of which, by analyzing and synthesizing information obtained experimentally, he manages to recreate new objects as images and ideas.
If we talk about agglutination as a normal mechanism of the imagination, during which new ideas are generated, then we can highlight the following distinctive features of this process:
- the brightness of incoming images;
- their novelty and originality;
- varying degrees of realism and truthfulness of emerging theses;
- sustainability;
- arbitrariness and controllability - a person can control his mental activity.
If we are talking about agglutination associated with mental disorders or speech disorders, then some signs may have their own characteristics. Thus, the images that come to the minds of mentally ill people can be no less stable, vivid and new than those of a healthy person.
However, they arise involuntarily in such people and the sick person is not able to control the occurrence of obsessive ideas and scenarios in his head.
Hyperbolization as a mechanism of imagination
The term “hyperbolization” is understood as the process of exaggerating or minimizing an object or parts of an object. In other words, these are fantasies about an unusual creature that acquires qualitatively new properties. Hyperbole is often used in fairy tales. Examples of hyperbolization are giants, gnomes, Thumb, Gulliver, the many-armed Indian god, Cyclops, Serpent Gorynych, Dwarf Nose, Thumbelina. Some scientists consider the process of hyperbolization to be one of the types of emphasis.
Note 2
Also, some scientists share the concept of hyperbolization and litotes: hyperbolization is an exaggeration of an object, and litotes is an understatement.
Degrees of agglutination
Agglutination is a mental process in which the imagination plays a dominant role. In psychology, there are several degrees or stages of agglutination that a person goes through at each stage of his development and formation.
| Involuntary | Occupies a time period in early childhood from 2 to 4 years. At this age, the development of the baby’s mental activity allows him to reproduce previously acquired knowledge and impressions, but the child is not yet able to create and combine various images. |
| free | It develops after 4 years and is accompanied by the transition of mental activity into the active phase, when the child can not only reproduce some kind of drawing on paper, but also come up with something of his own. During this period, play activity is indicative, in which the process of agglutination is revealed to the maximum. |
When the process of agglutination occurs involuntarily, then pictures and images in a person’s head arise unintentionally and are based on previously gained experience. The most striking example of the involuntary work of the brain and imagination is dreams.
With the voluntary process of agglutination, mental activity is not limited only to the reproduction of previously received impressions. As a result of conscious voluntary processing of information, dreams appear, creative imagination develops, and new ideas and images are born.
Functions and connection with thinking
One of the important characteristics of imagination is its versatility. There are several such functions:
- Cognitive – from the name it is clear that it means the process of cognition and broadening one’s horizons, and also reflects a person’s ability to design his behavior depending on the situation.
- The forecasting function helps a person imagine the end result of an unfinished action and develops the ability to dream and achieve set goals, while simultaneously coming up with ways to solve problems and problems along the way to these goals.
- The understanding or empathy function gives a person the ability to empathize and understand the feelings of another person and, perhaps, figure out how to help.
- Protection function - a person can prevent expected difficulties by choosing a different way to resolve any issues.
- The self-development function will help you invent, fantasize and create for the benefit of your future.
- The function of memory is expressed in the ability to remember past events of any nature. It is expressed in the form of images and ideas.
Each individual personality is dominated by one or another function; this may depend on many factors: environment, upbringing, communication skills, habits and everything that a person encounters throughout his life. In accordance with the dominant function, a person’s character and style of behavior is developed, and it should also be noted that each way of creating images and ideas in the head is a complex multi-level mental process.
Imagination helps us solve mathematical and logical problems. By solving school assignments, the child learns to find the right solution, determine truth and lies. And the more he engages in brain training, the easier it will be for him in adulthood, and the more confident he will feel in confusing situations.
Imagination in psychology is closely related to thinking and therefore directly affects the knowledge of the world. Thanks to it, we can plan our actions, which teaches us to organize our lives and helps us draw images of objects in our thoughts. All this contributes to the development of analytical thinking.
Oddly enough, imagination or, as it is also called, the power of thought can regulate our physical state. That is, if a person feels sorry for himself, crying about how sick he is, how bad he is, then he provokes his body into weakness and illness. And if a person, even with a noticeable slight illness, realizes that he needs to lead an active lifestyle, helping his body overcome a temporary illness, then in this case the illness will pass faster and in a milder form.
As a result, we see that imagination is a powerful lever or engine of our consciousness.
Examples of agglutination
In fact, the process of agglutination is extremely important, because it is the main engine of the progressive development of all mankind. The wheel, bicycle and steam locomotive arose in their time precisely as a result of intense human brain activity, and therefore it is wrong to think that agglutination helps only people of creative professions.
The most common, familiar and understandable examples of agglutination are unprecedented fairy-tale characters:
- Phoenix;
- mermaid;
- a hut on chicken legs;
- centaur.
All these characters appeared as a result of the merger of several components; they do not actually exist, but the idea turned out to be so successful that it was remembered and appreciated by many people.
Literary authors also often create their heroes based on a certain collective image. Thus, the great Russian writer, Leo Tolstoy, more than once admitted that the image of Natalya Rostova from the work “War and Peace” was actually invented by him, thanks to women who really existed close to him - his sister and wife.
In addition to writers, agglutination also plays a huge role for artists who create paintings. It is known that Leonardo da Vinci taught his students the techniques of gluing together several images.
Using agglutination in creativity
In art, many imaginative techniques - agglutination, emphasis - are often used. For example, Leo Tolstoy admitted that the image of Natasha Rostova from the novel “War and Peace” was based on two real women – his wife Sophia and her sister, Tatyana Bers. The combination of two types of women - one impetuous, lively and enthusiastic, and the second feminine and gentle - helped to give birth to an integral and absolutely vital character.
Sharpening, or emphasizing attention, no less helps to achieve a memorable result. Cartoonists especially love this technique. The depiction of a chatterbox as a person with an excessively long tongue, or a beer drinker with a huge belly, allows us to emphasize the most significant in the appearance and habits of the people depicted in the picture.
In literary works, the emphasis is placed at the moment of describing the hero. Focusing the reader's attention on any of his qualities allows him to convey the essence of the character's nature without further ado and even determine the author's attitude towards him.
Ways to create images of the imagination
It is wrong to believe that creative activity, imagination and the process of agglutination itself are built chaotically and chaotically. In fact, the transformation of reality into new images is subject to its own laws and occurs in accordance with certain techniques and methods.
As mentioned earlier, thanks to analysis and synthesis, new ideas can arise, and therefore the very process of mental division of information into its component parts and its subsequent connection is of an analytical-synthetic nature.
In psychology, the following methods and techniques for creating images in the imagination are distinguished:
- Hyperbolization is a deliberate increase or, on the contrary, understatement of an object or its parts. The easiest way to trace this is through the example of folklore, in which all heroes were endowed with mighty strength, strength and height, or, on the contrary, individual heroes had diminutive characteristics that did not prevent them from demonstrating extraordinary mental abilities (Tom Thumb). This technique is used not only in Slavic folk art, but can also be seen in fairy tales and stories of other nationalities (Cyclops with one eye, Buddha with several arms).
- Agglutination - as a method of imagination, involves the mental connection of various parts of objects or elements together. Using this method, images of a mermaid and a centaur were created.
- Accentalization – involves highlighting any part or individual detail in a newly created image. This technique of emphasis or sharpening is often used by caricaturists, emphasizing some shortcomings in the image, for example, a talkative person can be depicted with an enlarged tongue, a lazy official can be depicted as fat and with a large belly.
- Typing - or typification, on the contrary, involves the creation of collective images inherent in many people or phenomena. These could be jealous heroes (Othello) or, for example, dishonest lovers of power and money.
- Schematization is a process as a result of which similar motifs or features are identified in dissimilar objects, and on the basis of this, something new is created, for example, an ornament or pattern characteristic of a particular nationality.
Mechanisms of imagination: agglutination, hyperbolization, accentuation, schematization and typification.
⇐ PreviousPage 9 of 15Next ⇒
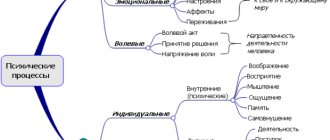
Along with perception, memory and thinking, imagination plays an important role in human activity. In the process of reflecting the surrounding world, a person, along with the perception of what is acting on him at the moment, or the visual representation of what influenced him before, creates new images. Imagination is the mental process of creating something new in the form of an image, idea or idea, consisting in the creation of ideas and mental situations that have never been generally perceived by a person in reality. The mechanisms of imagination have been studied very poorly, including its anatomical and physiological basis (where it is localized in the brain, etc.). The leading mechanism of imagination is the transfer of some property of an object. Imagination is always a certain departure from reality. But in any case, the source of imagination is objective reality. Being closely connected with thinking, imagination is characterized by greater uncertainty of the problem situation than with thinking. Imagination is the basis of visual-figurative thinking, which allows a person to navigate a situation and solve problems without the direct intervention of practical actions. Imagination differs from perception in that its images do not always correspond to reality; they contain elements of fantasy and fiction. The process of imagination is unique to man and is a necessary condition for his work activity. Imagination is always directed towards the practical activities of man. Before doing anything, a person imagines what needs to be done and how he will do it. Thus, he already creates in advance the image of a material thing that will be manufactured in the subsequent practical activity of man. This ability of a person to imagine in advance the final result of his work, as well as the process of creating a material thing, sharply distinguishes human activity from the “activity” of animals, sometimes very skillful. In psychology, we distinguish between active, passive, productive and reproductive imagination. Passive imagination arises spontaneously, in addition to the will and desire of a person and is subject to internal factors. In the images of passive imagination, the unsatisfied, mostly unconscious needs of the individual are “satisfied”. Passive, in turn, is divided into voluntary (daydreaming, daydreaming) and involuntary (hypnotic state, dream fantasy). Active imagination is characterized by the fact that a person, of his own free will, by an effort of will, evokes appropriate images in himself. Includes artistic, creative, critical, recreative and anticipatory. Active imagination is always aimed at solving a creative or personal problem. Recreating imagination is one of the types of active imagination, in which new images and ideas are constructed in people in accordance with stimulation received from the outside in the form of verbal messages, diagrams, conventional images, signs. Anticipatory imagination underlies a very important and necessary human ability - to anticipate future events, to foresee the results of one’s actions. In older and older people, the imagination is more focused on events of the past. Creative imagination is a type of imagination in which a person independently creates new images and ideas that are valuable to other people or society. (Ribault concluded: Dissociation is the first stage of creative imagination, the stage of preparing material. The impossibility of dissociation is a significant obstacle to creative imagination. Association is the creation of a holistic image from the elements of isolated units of images. Association gives rise to new combinations, new images).
Productive imagination - in it reality is consciously constructed by a person (but at the same time it is creatively transformed in the image).
Reproductive imagination - here reality is reproduced as it is (elements of fantasy).
There are also other types of imagination:
Dreams are classified as passive and involuntary forms of imagination. Fantasies are images of the imagination that have little or no correspondence with reality.
Hallucinations are fantastic visions that have almost no connection with the surrounding reality (as a rule, the result of certain disorders of the psyche or the functioning of the body).
Daydreaming is a completely normal mental state, representing a fantasy associated with a desire, most often a somewhat idealized future.
Dreams are not addressed to the sphere of a more or less distant future and do not imply the immediate achievement of a real result, as well as its complete coincidence with the image of the desired one. At the same time, a dream can become a strong motivating factor in creative search.
⇐ Previous9Next ⇒
Recommended pages:
How is the problem diagnosed?
Agglutination in psychology is a powerful mental practice of processing information, allowing you to divide it into separate parts and create completely new objects, both material and immaterial. Thanks to this process, humanity does not stand still, but is constantly evolving. However, sometimes this phenomenon can be associated with certain mental disorders.
Thus, during an exacerbation of schizophrenia, one of the most striking symptoms is agglutination. At the same time, the sick person loses the ability to distinguish between certain concepts, since due to disorders his brain perceives the new images that arise as true.
The same situation can also be observed with deviations in speech development, which, as a rule, are closely related to mental disorders. At the same time, such people come up with new words (neologisms), the meaning of which is unclear even to them.
Often, in people with schizophrenia, the normal perception of their own personality is disrupted due to agglutination. They may identify themselves so closely with other individuals or even phenomena that they become unable to distinguish between themselves and their imagination.
As a result, the events of the outside world are very closely intertwined with their lives, and they may claim that some phenomena are their expression (for example, it seems to them that the rain is their tears).
Diagnosing schizophrenia is a fairly long process, since to make this kind of diagnosis, specialists comprehensively study the patient’s life and symptoms:
- patient complaints are taken into account;
- a survey is conducted of people close to him who can characterize his behavior;
- attention is paid to the general state of health, existing chronic diseases, injuries;
- It is examined whether the patient has encountered:
- hallucinations;
- delusional obsessions;
- repetition (“echo”) of one’s own thoughts;
- the feeling that his thoughts are open to everyone.
At a minimum, the specialist observes the patient for a month before making a diagnosis. In addition to behavioral and cognitive deviations, attention is drawn to the presence of neologisms in speech, which may also indicate schizophrenia.
What is agglutination?
Agglutination in its direct meaning implies the fusion of individual elements into a single whole. Usually we are talking about elements that do not combine with each other. These can be words, images, thoughts, etc. Thus, thanks to agglutination, such fairy-tale creatures as mermaids, centaurs, etc. were invented. Human imagination united animals, fish, birds with human bodies, which is why they got such fairy-tale characters.
Psychology actively studies agglutination because it involves the thought process of each individual. Agglutination is common to all people. Most often it is observed in people with various mental disorders, in particular schizophrenics. However, it should be understood that agglutination does not mean a sick imagination. By combining individual elements from different areas, something new is created. This is how all those objects that people use today were created.
Psychology turns to agglutination as a way of understanding the inner world of an individual. His imagination is directed in a specific direction. If a psychologist has extensive experience working with the unreal world of people, then he can understand the nature of each client.
Agglutination is the combination of individual objects that exist in reality into a single whole, creating something new that does not yet exist in the real world.
We can call a kind of agglutination a set of personality traits in one person that are usually not common in their set. This can occur under the influence of the individual himself, who is engaged in self-improvement or self-change. External circumstances can create a personality that is similar to other individuals who have also encountered similar situations. However, each individual has a choice of how to react, how to be, what qualities to show. It is in such a situation that a person becomes unique. It reveals a set of qualities that can be considered incompatible, but these traits fit perfectly into the image of one person.
Psychology perceives imagination as a dialogue between a person and himself. There are many personalities living inside a person:
- Daughter/son, husband/wife, employee, boyfriend/girlfriend, etc.
- The ideal “I”, the desired “I” and the real “I”.
- Beliefs, worldview, thoughts, public opinion, rules and laws.
Everything in a person must be combined so that it can help him exist in the world of people. However, often a person is faced with contradictions between individual parts of his inner “I” or a discrepancy between the external and the internal. Then a dialogue arises. A person negotiates with himself, reasons, thinks from different angles, fantasizes, imagines, etc. As a result of the thought process, in which experience, knowledge, imagination, unrealistic ideas may participate, something new appears. Either a person uses what is already known and real, that is, resorts to existing experience, or begins to combine individual parts of what is already known and real to create something new.
In this way, a search for a solution to a problem occurs when a person is not satisfied with the already proposed options. For example, it is assumed that a person will choose between “either” - “or”, and the individual decides to combine everything - to do “and” - “and”.
Agglutination is considered a difficult phenomenon to study in psychology because it has no obvious external manifestations. You can only hear or see the result. But the process itself is not visible.
Agglutination is also used in medicine and linguistics.
- In linguistics, agglutination refers to the merging of words with a change in their morphological structure, but maintaining the meaning. In this way a new word is created.
- In medicine, agglutination refers to the union of cells into a new cell.
go to top
Treatment
If we are talking about agglutination, as a result of which new interesting, non-destructive ideas are born and useful ideas are realized, then this type of mental activity does not require any treatment.
On the contrary, this may indicate the harmonious development of the individual and her ability to comprehensively apply her experience and develop her imagination.
In the case when a person has speech disorders associated with mental disorders or is diagnosed with schizophrenia, then such a person should be provided with comprehensive assistance from specialists, otherwise the process of agglutination in such people can lead to sad consequences both for themselves and for their environment.
Until now, the concept of treating this type of deviation causes a lot of controversy among specialists, since there are no uniform approaches to the treatment of this condition. Most experts believe that schizophrenia can be treated on an outpatient basis, resorting to hospitalization only in severe forms. Treatment methods include drug therapy, as well as psychocorrective work with the patient.
Medication
The symptoms that accompany the process of agglutination in speech disorders and schizophrenia are, for the most part, amenable to medication adjustment.
American psychiatrists generally recommend using atypical neuroleptics for the treatment of such patients, which act specifically on the negative signs of the disease. At the same time, they note the importance of an individual approach and optimization of treatment regimens for each patient.
To treat such patients, medications such as:
- Clozapine;
- Risperidone;
- Olanzaline;
- Amisulpride.
Patients should continue to take these medications after the acute attack has stopped, in order to maintain remission and minimize the risks of exacerbation of the disease.
When using these medications, 40-50% of patients respond positively to therapy, 30-40% respond slightly worse, and only 20% of patients do not have the desired effect. Also, these medications reduce the negative phenomena characteristic of this disorder, reducing the tendency and craving in such patients for suicide, drug addiction, and alcoholism.
Psychotherapy
If agglutination is a symptom of a disorder, psychotherapy is often used to correct the condition, which is carried out in combination with drug therapy. Only medication relief of the symptoms of the disease will not be able to fully return the patient to full social and professional activities.
To work with such patients use:
- cognitive behavioral therapy – this technique has a solid evidence base and can reduce the number of relapses of the disease in patients. Its essence lies in working through the patient’s false destructive attitudes and reconfiguring his mental activity in the right direction;
- family therapy - when the patient interacts with the psychiatrist not alone, but together with his family. The specialist’s task is to identify problematic issues, resolve them and establish a normal healthy microclimate in the family, which will reduce the risk of exacerbation of the disease in the patient.
These techniques help patients better understand their condition and reduce episodes of delirium and hallucinations. The disadvantage of these approaches is their high cost, since such classes are conducted on an individual basis and are not cheap.
Forecast
In approximately every 3rd case, over time, all unpleasant symptoms are relieved and the patient feels like a full-fledged member of society.
Another significant proportion of such patients demonstrate moderate remission, with an almost complete absence of manifestations of the disease (including unhealthy agglutination). Success in treatment depends on the timeliness of identifying the problem and the complexity of the approach to treatment - a combination of psychocorrection with drug treatment.
If there is a favorable environment in the family and all the doctor’s recommendations are followed, it is possible to avoid acute manifestations of the disease (delusions, hallucinations), as well as to prevent the patient’s social degradation, which is expressed in an increased tendency in such patients to:
- taking drugs;
- drinking alcohol;
- suicide.
Agglutination is a unique form of thought process that allows a person to discover new things by processing previously received information.
In psychology, agglutination can be considered as a useful tool that allows a mentally healthy person to develop, as well as a symptom of serious mental disorders. As a rule, these deviations do not occur often, so agglutination largely helps people improve their experience and find new answers when solving various problems.