All people experience feelings of anxiety and fear in different situations. A mother is worried about her sick child, a child is afraid of the neighbor’s dog, a grandmother is afraid of falling into ice, a novice motorist is afraid of getting into an accident... Why does the state of fear and increased anxiety in certain cases become the subject of study by psychiatry?
In all the examples given, there is a specific reason for anxiety and fear. Experiencing fear and anxiety in the face of real danger is the norm for a healthy person, the inclusion of protective mechanisms that help maintain health and life.
This kind of anxiety is called physiological. But if a person, as a result of the influence of mental disorders or psychological factors, including as a result of short-term intense stress or long-term mental overstrain, begins to constantly experience a feeling of fear or anxiety without any specific reason, we are talking about pathological anxiety.
You need to know that anxiety is a universal means that the human psyche uses as a warning about trouble. It may also indicate the emergence of a number and even most mental disorders. Experts speak of it as the cornerstone of psychiatry.
At the same time, when it comes to the neurotic level of anxiety, the following diagnostic names are usually used: anxiety neurosis, neurosis of fear and anxiety, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). The latter name is given in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), developed by WHO, but traditional terminology is still used in popular science literature and textbooks. Anxiety neurosis should be differentiated from phobias, since, despite the commonality - the irrational nature of fear - in phobias the object of fear itself is present. A characteristic feature of fear neurosis is to generalize an initially limited process into a widespread one, which in development has not only increasing mental, but also somatic, as well as vegetative manifestations.
What is anxiety neurosis?
Anxiety neurosis is a disorder that occurs due to prolonged anxiety, prolonged chronic stressful situations, or a single experience of severe stress. In the initial stages, the patient often does not realize that there is a problem, but later, when the symptoms become more pronounced, he often consults a doctor on his own.
Due to pathology, the quality of life deteriorates:
- Performance decreases, the number of contacts with other people decreases;
- It becomes more difficult to focus on any tasks or matters.
Often the cause of the condition is first attributed to cardiac problems. The patient may first note vegetative manifestations, not paying attention to psychological ones.
Hypochondriacal phobias
We are talking about the fear of some serious disease. In another way, this phenomenon is often called nosophobia.
The most common are speedophobia, cardiophobia, cancerophobia (fear of cancer), stroke phobia, and syphilophobia. Such conditions may also be a consequence of hypochondriacal depression.
People with such phobias do everything possible to avoid all kinds of situations that provoke fear. So, if they are afraid of transport, they do not use the elevator and move only on their own. Those who are afraid of cancer defects systematically undergo appropriate examinations. But even after receiving good test results, such people cannot calm down for long.
Why is anxiety neurosis so common?
Neurotic anxiety can arise due to many factors. For this reason, a large number of people are at risk.
Neurotic fears in children
In minors, anxiety-phobic neurosis may appear due to attempts at intimidation. Sometimes adults deliberately come up with scary characters in order to force a child to do something he doesn’t want. Scary films, books, and horror stories told by older brothers and sisters have a negative impact.
In addition, children may experience significant stress after psychological trauma due to:
- Divorce of parents or their constant quarrels;
- Attempts of harassment by any adult;
- Dog bites;
- Serious diseases for which painful methods were used.
Anxiety disorder in adults
Adults often face pathology due to heavy workload. Constant nagging from your boss, unfriendly colleagues, high competition for a possible promotion, the threat of dismissal or difficult conditions can cause chronic stress and constant anxiety.
An exacerbation of neurosis is possible when problems arise in the family: illness of parents, difficulties in relationships with a spouse, communication of a child with a company that has a bad influence on him.
This diagnosis is more often diagnosed during wars, mass layoffs, financial crises, after various disasters, tragedies, and disasters. Suspicious people with a family history are susceptible to the development of pathology: if one of the parents suffered from this disorder, the likelihood of its occurrence in children is high.
Reasons for appearance
Phobic disorder, like any other neuroses, most often occurs against the background of mental trauma in combination with too strenuous activity, severe lack of rest, and constant lack of sleep. In addition, various infections, endocrine pathologies, unhealthy diet, addictions and alcohol abuse are factors contributing to this phenomenon. All these conditions entail a significant weakening of the entire organism, and this, in turn, can lead to the development of neurosis.
Often this disorder appears against the background of another illness: psychasthenia, schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Symptoms
Symptoms develop gradually. At first it may be mild, making early detection of the disorder difficult.
A characteristic symptom is constant anxiety. A person tends to think for a long time about disturbing, frightening thoughts. Fear of the future appears. Often such thoughts have no basis, so they seem unreasonable and irrational to other people.
With pathology, vegetative manifestations also develop. There is constant muscle tension caused by emotional stress. A person constantly experiences fatigue that does not disappear even after a long rest.
Anxiety neurosis is also manifested by motor symptoms. The patient develops nervous tics and obsessive movements: the habit of constantly adjusting clothes or glasses, twirling earrings, a pendant or a cross in his fingers. Some patients begin to bite their nails. Such people become fussy, have difficulty staying in one place, feel a constant need to do something, move, even if their actions are ineffective and useless.
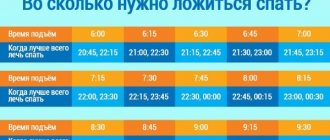
Sleep disturbances and insomnia are sometimes observed. It becomes difficult to wake up in the morning. People become more fearful and experience fear even because of familiar everyday situations (for example, they avoid using household appliances for fear of their breakdown, fire, short circuit). A panic attack may occur.
In advanced stages, characteristic symptoms include headaches, pain in the heart area, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath in the absence of physical activity.
Social phobias
Phobic neurosis can be accompanied by a huge number of such fears.
Social phobias involve a fear of being the center of attention, as well as of criticism. People experiencing such fear try to avoid public places.
The first symptoms of social phobias usually appear in adolescence or young adulthood. Often these fears are caused by negative psychological or social factors. At first, the fear of being in the center of everyone's attention concerns only certain situations or communication with specific people. But contact with relatives and family members does not cause discomfort.
Gradually, social phobia begins to manifest itself in the form of some restrictions regarding social activities. At the same time, a person, finding himself in undesirable situations, suffers from internal stiffness, shyness, sweating and trembling.
In some people, social phobia progresses to a generalized form. Such persons completely avoid public places, thinking that they seem funny and ridiculous.
Phobic neurosis can also manifest itself in the form of specific phobias - obsessive fears relating only to certain situations. These include fear of heights, animals, dentists and other doctors.
Treatment
For treatment, you should consult a specialist: a psychotherapist or psychiatrist. If the pathology is advanced, you also need to get rid of vegetative symptoms, for which you will have to make an appointment with a pulmonologist or cardiologist.
Hospitalization is rarely required; treatment at home is most often possible. Therapy can continue for many years; However, improvements can be observed after 1-2 months.
Medicines and tablets are used to relieve symptoms. They do not eliminate the cause, but help alleviate the condition. The most commonly prescribed tranquilizers are Atarax, Grandaxin. Antidepressants are used less frequently; they are necessary only in cases of severe condition, concomitant mental disorders, or an advanced form of pathology. All medications and their dosages must be selected by a doctor.
Average prices for drugs
Atarax
260₽
Grandaxin
400₽
The main method of treatment is psychotherapy. Individual sessions with a specialist, anti-stress therapy, and relaxation are recommended. In addition, it is recommended to get more rest, give up bad habits, eat natural foods, and add moderate physical activity.
A special massage, taking warm baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs, and electrophoresis will help. Additionally, traditional medicine can be used; Before selecting methods, you should consult with a specialist.
Symptoms
It is quite difficult for a person to understand what exactly is happening to him, because the symptoms resemble various diseases. That is why, when anxiety neurosis appears, you must immediately consult a doctor.
He will conduct a series of examinations and tests, based on the results of which it will be possible to understand what exactly is happening to the patient. A person should not let the disease go on and hope that it will go away on its own, because the condition tends to worsen.
A person often experiences intense and uncontrollable fear. He feels as if a real catastrophe is approaching, although there is no good reason for this. People can significantly exaggerate the existing danger, and also suffer from unreasonable anxiety. The attacks themselves last mostly up to 20 minutes. After this, the patient feels better, but the negative state tends to recur.
The main symptoms of anxiety neurosis include the following:
- Constant change of mood, and this happens without good reason.
- The emergence of obsessive thoughts and ideas that are extremely difficult to get rid of.
- Loss of orientation in space. As a rule, this symptom is temporary.
- Increased sensitivity to loud noises and bright lights.
- Depressed state. The person's mood deteriorates significantly, and depression may even occur.
If a person has a fear neurosis, then he will suffer from increased fatigue. As with other forms of mental disorders, in this situation the attacks will be accompanied by additional phenomena.
Often there is blurred vision, tachycardia, significant nausea and dizziness. The person becomes more sweaty, and there is tremors in the hands. Often there may be chest pain and a feeling as if there is not enough air. Patients often complain about neurotic shortness of breath.
All of the above symptoms can occur at the same time or alternate. When they appear, a person should definitely consult a doctor, because a medical specialist will be able to confirm anxiety neurosis.
You will need to start the right treatment so that you can significantly improve your well-being. It is also important to understand why the disease appeared. In most cases, it will be necessary to eliminate the provoking factor so that the health condition can be normalized.
Prognosis and prevention
Treatment of fear neurosis can result in a complete cure. The disorder is reversible. Therapy, however, is often lengthy and can take several years.
To prevent it, you should adhere to a healthy lifestyle. Adequate rest is important. Sports will be beneficial. Live communication is useful (correspondence on the Internet will not be effective).
For prevention, you can regularly visit a psychologist and listen to auto-training sessions that help reduce anxiety.
Why is it dangerous?
If a person has only a superficial knowledge of the systems and functioning of his body, he may consider that anxiety neurosis is not dangerous to health. The rapid end of an attack without visible consequences misleads the patient. At the same time, internal anxiety does not leave him, and this is the main danger of the disorder.
Despite the fact that many effective methods of treating the disease have been developed, it is impossible to completely get rid of the disorder. Anxiety neurosis is considered a chronic disease, but this does not mean that it does not need to be treated. Anxiety neurosis is reversible - every patient should adhere to this attitude.