VSD and neurosis are two interrelated pathologies. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a complex of functional disorders that arise against the background of impaired tone of blood vessels. This pathology often occurs with neuroses (dysfunction of the nervous system of a psychogenic nature). Neuroses are depressive, phobic, hypochondriacal, hysterical and obsessive. VSD and neurotic disorders, if not properly treated, can cause dyspeptic disorders, hypertension, cardiac dysfunction and other complications.
VSD disease and neurosis
VSD is a disease of the autonomic system, which is provoked by a disturbance in the functioning of the central nervous system, which leads to an imbalance of the entire body. Vegetovascular dystonia is not included in the international classification of diseases; abroad this disorder is considered as a generalized anxiety state.
Neurosis occurs against the background of a malfunction in the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the central nervous system.
It is very common among the adult population: citizens over 20 years of age account for about 45% of those suffering from nervous system dysfunction.
Often the disease is accompanied by nervous conditions, which are divided into 4 forms.
- Asthenic (neurasthenia) - frequent surges in blood pressure, mood swings, and the appearance of tachycardia.
- The hysterical form of neurosis with VSD is accompanied by panic attacks. It is provoked by self-hypnosis and can lead to convulsions and hallucinations.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder is a strong fixation on negative thoughts that puts a person into a trance. The patient is able to perform many of the same actions, for example, combing his hair, making movements with his hands, or shifting from one foot to another.
- Depressive – occurs due to the inability to cope with problems on one’s own. Apathy appears, a person in this state thinks about suicide.
Possible reasons
Constant stress contributes to the occurrence of VSD. Nervous breakdowns, everyday worries and poor nutrition are the main causes of exacerbation.
Various injuries and infections that affect the psychophysical state of a person also become provocateurs. The most common causes of exacerbation of VSD include:
- trauma to the cervical spine;
- protrusion of intervertebral discs;
- enlargement of the thyroid gland;
- gastritis and enterocolitis;
- allergies in an advanced stage;
- hypertension;
- stress and overwork;
- head injuries.
The causes of vegetative-vascular neurosis can be various factors:
- mental trauma;
- exhaustion of the body, lack of vitamins;
- genetic predisposition;
- overload during mental activity;
- alcohol, drug addiction;
- caffeine abuse;
- a sharp decrease in immunity due to an infectious disease.
The causes of neurosis in VSD can be various psycho-emotional shocks, most of which happened in childhood. If a child is often stressed due to quarrels in the family, he is offended by peers, the nervous system may not withstand the load and fail, which will inevitably lead to dysfunction of the central nervous system.
In adulthood, a common cause of the development of neurosis with VSD is:
- death of someone close;
- lack of financial fulfillment - if a person is not able to achieve success in his work, he becomes sad and depressed;
- sociopathy - the inability to be in a crowd, fear of communication leads to constant nervous exhaustion;
- poor rest or lack thereof;
- pregnancy and childbirth - young mothers are very susceptible to stress; after childbirth, overprotection syndrome may develop, which leads to constant fear for the life of the child.
It is useful to know which doctors treat VSD
The body suffers when the autonomic nervous system is disrupted. A list of symptoms appears, different in each individual case, which is commonly called vegetative-vascular dystonia.
The well-being of patients worsens, the quality of life decreases, so people try to find a way out of a difficult situation and improve their health. Below is information about which doctor treats VSD and what are the principles of the development of the disease?
General information about autonomic regulation
The nervous system is responsible for the functioning of all organs, ensures normal interaction of the human body with the environment, and is divided into 2 types:
- Somatic. Responsible for body movements and muscle activity.
- Vegetative regulates the functioning of internal organs, circulatory and endocrine systems.
In the vegetative department, homeostasis is maintained, the structure of the body remains unchanged and its viability is maintained. The autonomic nervous system is not controlled by consciousness, so it autonomously regulates the functioning of organs and the body’s reactions to the changing influence of the environment.
The sympathetic component controls the internal resources of the body and ensures high-quality work. The parasympathetic branch improves the process of restoring one’s own strength, promotes the transition of systems and organs to economical expenditure of energy. The interaction of body structures is corrected during rest, when consciousness is turned off.
Let's figure out what happens when the autonomic nervous system is disrupted:
- Change in emotional background.
- Changes in blood pressure and temperature.
- A person feels sick and has a headache.
- The quality of sleep deteriorates, and you feel tired during the day.
- The patient has trouble eating.
- Difficulty with concentration and memory.
- Vomiting, panic attacks, fear of death, the patient is afraid to be in a crowd or to be alone, suspiciousness appears.
- There is not enough air, breathing is frequent, shallow, when panic begins, the heartbeat rhythm is lost.
- Digestive problems.
- My heart hurts, my chest feels tight.
- Cold feet and hands.
- Intense sweating.
- The face turns pale or red.
- My head is spinning.
- The person may lose consciousness.
Taking into account the prevailing symptoms, the following categories of VSD are distinguished:
- In the hypertensive form, tachycardia, fatigue, headaches, poor sleep, fear for no obvious reason develop, and blood pressure increases.
- VSD of the hypotonic type is characterized by weakness, apathy, low performance, drowsiness, bad mood, low blood pressure, and frequent fainting.
- The mixed species is characterized by all of the above signs; they can alternate.
Who to contact
Signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia are varied, since they can relate to different body systems. Therefore, people are interested in which doctor treats VSD.
Everything is determined by the prevailing signs from the internal organs. It is preferable to seek advice from a general practitioner or family doctor.
He will recommend a highly specialized specialist who can provide assistance:
- A cardiologist will help if problems with the heart and blood vessels arise.
- A neurologist is responsible for the nervous system.
- A gastroenterologist treats gastrointestinal disorders.
- The psychologist examines the problem of psycho-vegetative crises, panic attacks, and neuroses.
Therapeutic specialists are accepted in city hospitals. Often specialists try to contact paid centers. In some large settlements, special centers are being developed that are responsible for the diagnosis and treatment of autonomic dysfunction syndrome. Vegetologists specializing separately in autonomic disorders are responsible for the reception.
The patient will have to collect all tests, documents from inpatient departments, and the results of examinations performed. It is preferable to arrange the documents in chronological order so that it is more convenient for the doctor to determine the dynamics of the patient’s condition.
There is no need to perform any other tests before going to the doctor, since the specialist will determine before therapy what data he lacks for diagnosis. This makes it possible to save your time and funds.
When patients return to cardiologists, they need to prepare for an ECG . Therefore, you should dress in such a way that you can easily expose your ankles and wrists to apply the electrodes.
A gastroenterologist writes a referral for an ultrasound of the peritoneal organs. Not every medical institution provides disposable napkins or towels, which are necessary to remove the gel after the procedure. Therefore, it is preferable to take them with you. You may need to buy shoe covers or slippers.
Why do you need a psychotherapist?
The participation of psychotherapists in most cases is necessary to solve problems with VSD.
For example, patients may complain of chest symptoms, but testing does not indicate a heart problem, and the person experiences panic attacks several times.
The neurologist considers this situation as typical for VSD and conducts therapy according to a standard regimen, focusing on treating the nervous system. However, the condition worsens after treatment.
It is typical for such an example that the specialist misses the mental disorder, since this is not his professional area. Further, the specialist is unable to identify any mental disorders on his own initiative. This is not indicative of the ethics and overall workings of the medical industry.
Reorientation to psychotherapy immediately gives a positive result, the patient managed to restore his health, and nervous disorders stopped making themselves felt.
Here is a list of common medications:
- Antidepressants.
- Tranquilizers.
- Neuroleptics.
- Nootropic drugs.
Gastroenterologists
As a result of nervous shocks and overstrain, people experience digestive problems. You should contact a gastroenterologist in the following situations:
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Colic in the intestines.
- Flatulence.
- Stomach ache.
Digestive system disorders with VSD are a separate situation. To identify vegetative-vascular dystonia, a gastroenterologist will have to conduct the following examinations:
- Laboratory.
- MRI.
- Ultrasound.
- Additional procedures.
When determining the disorder, the diet is determined, physical activity on the body is reduced, etc.
Neuropathologist
In most examples, it is the neurologist who is involved in the treatment of VSD. Nervous system disorders are considered the main cause of autonomic dysfunction.
Let's figure out in what situations they turn to this specialist:
- Intense sweating.
- The eye twitches.
- Aggression, increased irritability.
- Sleep problems.
- Unstable psychological state.
Cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by signs of neurological asthenosyndromes, pinched nerve tissue, intercostal neuralgia and other factors. To determine the causes of this condition, a specialist prescribes an MRI, X-ray, and other types of procedures, and a visual examination is performed. Panic and neuroses appear in stressful situations, the blood is poorly supplied with oxygen.
Recommendations from experts
In order for the treatment result to be positive, you need to follow these recommendations:
- Perform psychotraining exercises.
- Use natural energy as medicine.
- Direct impulses to improve the digestive system.
- Relax the circulatory system under a contrast shower.
- Smile at strangers on the street, feed a hungry animal.
- Try to please someone close to you.
By thanking people for such actions, you can get more positive results than going to the doctor. This is everyday psychotherapy that allows you to improve your well-being.
Source: https://nevrology.net/sindromy-i-zabolevaniya/vegetativnoj-nervnoj-sistemy/vegetososudistaya-distoniya-vsd/kakoj-vrach-lechit-3.html
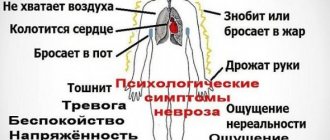
Symptomatic picture
The manifestation of neurosis in VSD is divided into two types - somatic and mental. Somatic symptoms are a deterioration in a person’s physical condition due to the effects of a disease:
- headache;
- frequent visits to the toilet;
- tightness in the chest;
- continuous feeling of fatigue;
- drowsiness;
- sweating;
- pressure surges.
Psychological symptoms:
- constant anxiety;
- oppression;
- irritability and aggression;
- obsessive thoughts;
- panic attacks;
- sudden change of mood.
During attacks, a person develops a fear of a stroke. Often the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia resemble a stroke, so every time the patient is afraid of death or disability. The patient is able to cause these kinds of symptoms himself by focusing on negative emotions or memories from the past.
Signs can intensify either in a person with low self-esteem, or when character traits such as categoricalness and restraint are present.
Cardiologist
Since patients quite often experience heart problems (rapid heartbeat, tingling), consultation with a cardiologist is necessary. The following studies are usually prescribed:
- monitoring heart function throughout the day using Holter;
- echocardiogram;
- electrocardiogram;
- X-ray;
- MRI or CT;
- tonometry.
You should contact a cardiologist if you have the following complaints or symptoms:
- Feeling of heaviness, discomfort in the chest area.
- Changes in blood pressure.
- Pain localized on the left.
- Breathing problems.
- Heart pain of varying intensity.
- Rhythm disturbances.
If at least one of the signs is present, it is necessary to conduct a study, since it is possible to identify pathologies of the circulatory system, disorders of the heart, which can be controlled with early diagnosis. The following treatments are used: diet, vasodilators, as well as medications that reduce heart rate, strengthen myocardial endurance and improve metabolism and blood circulation.
Treatment methods
VSD neurosis should be treated by a qualified specialist. He prescribes a full diagnosis of the body, including:
- detailed blood and urine analysis;
- cardiogram;
- encephalogram, which determines brain performance and predisposition to epilepsy;
- determination of pressure.
After diagnosis, the doctor may refer you for consultation to a more specialized specialist: a cardiologist, neurologist or psychologist. Medical rehabilitation for VSD neurosis consists of complex treatment, consisting of psychological and drug therapy. Psychological is the main element in the treatment of neuroses.
Therapy includes lifestyle adjustments:
- sleep at least 8 hours a night;
- correct diet;
- eliminating caffeine-containing products;
- rejection of bad habits;
- exclusion of stressful situations.
Medicines
Treatment of neurosis and VSD is carried out with the help of medications that serve as auxiliary therapy. Medicines suppress or increase excitation in the brain center, depending on the symptoms and progression of the disease.
They use 4 categories of medications with different effects. The most severe cases of neurosis with vegetative-vascular dystonia, accompanied by panic attacks, obsessive states, numbness of the limbs, are treated with tranquilizers or antidepressants, which are dispensed strictly according to a doctor’s prescription.
Due to the fact that when taking antidepressants, dependence on the drug may occur, you should strictly follow the instructions. The category of strong drugs includes: Afobazol, Phenazepam, Zolpidem.
Lighter medications that have a sedative effect are also used. The recipe in this category contains herbal mixture. A sedative will help relieve tension and irritability, improve sleep: “Valerian”, “Barboval”, peony tincture.
In order to properly restore the body during intense mental activity or overstrain at work, you should use a nootropic category of drugs that will help restore the neurotransmitter connection and improve blood flow to the brain. Use: “Glycine”, “Phenibut”.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic treatment method includes a number of procedures aimed at normalizing blood circulation and general muscle relaxation. Several directions are used simultaneously or separately after a doctor’s prescription:
- massage with aromatic oils;
- acupuncture;
- swimming;
- breathing exercises;
- yoga.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise will have a beneficial effect on the general condition of the body and neutralize muscle spasms that prevent you from relaxing. Light physical activity will strengthen the immune system and speed up metabolism.
For VSD neurosis, the following will help:
- walking in the fresh air;
- aerobics;
- morning jogging;
- light exercises.
To bring the cardiovascular system back to normal, overexertion should be avoided, so it is recommended to perform a set of light exercises, consisting of a warm-up for all muscle groups.
Symptoms
Medicine includes many diseases that have specific mental symptoms. There is no clinical manifestation.
Neurotic disorders can manifest themselves:
- Hysterical. A patient with this type of neurotic disorder is often nervous and irritable, behaves inappropriately and unpredictably. Hysteria is determined by autonomic and motor disorders, hypotension (the patient has had low blood pressure for a long time) and obsessive movements.
- An obsessive state. The patient becomes afraid of getting very sick or getting into hopeless situations. Such people constantly examine their body, study medical literature, but at the same time they are haunted by the thought that they are very sick.
- Neurasthenia. At the beginning, you may notice that the patient is very irritable, but there is no mental impairment. Then he loses his ability to work, which greatly depresses him. And in the end the patient becomes weak, lethargic and apathetic. As a result, asthenic syndrome occurs.
Symptoms of VSD and neurotic disorders often manifest themselves in the same way:
- the patient experiences unpleasant discomfort and pain in the cardiac region, there is no angina pectoris;
- breathing becomes difficult and shortness of breath appears;
- the patient is unreasonably afraid of dying, he takes one position and can remain in it for a long time without moving;
- anxiety;
- blood pressure rises or falls sharply;
- pain syndrome on the left side of the sternum;
- heart rhythm is disturbed;
- headache with increased sweating;
- spasmodic sensations in the esophageal system;
- decreased appetite, subsequently decreases body weight;
- gag reflexes accompanied by heartburn;
- in female representatives, hormonal levels are disrupted;
- the skin dries out;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- there is a lack of potassium in the blood;
- body temperature is below normal;
- the mucous membrane in the oral cavity dries out;
- general weakness of the body.
If you do not consult a psychotherapist, the condition may worsen. The patient, thinking that he is seriously ill, begins to take pills that can harm the body.
If the patient gets carried away with something, he forgets about the problems for a while, then the symptoms subside, but not for long.
Symptoms of neurotic disorders during vegetative-vascular dystonia:
- Cardiac disorders. Discomfort and pain appear in the area of the heart and chest. Heart rate increases and blood pressure fluctuates.
- Nervous system disorders. Acute headache and dizziness. Trembling throughout the body, gradually developing into a convulsive state. Sleep is disturbed, the patient suffers from insomnia, and coordination of movements worsens. The tips of the fingers become numb and their sensitivity is lost.
- Respiratory system disorders. The patient cannot breathe fully, a lump appears in the throat, and shortness of breath may appear after minor physical exertion.
- Gastrointestinal tract disorders. The patient begins to have problems with bowel movements and becomes constipated. Nausea causing vomiting. Increased gas formation and loss of appetite.
- Problems with the urinary system. Patients often go to the toilet in small amounts. Sexual desire fades.
- Thermoregulation is impaired.
Autonomic neurosis is characterized by non-constant regulation of the nervous system; its nature is functional. The patient must be under the supervision of specialists. There are cases that this pathology can cause a heart attack, a tumor of the temporal lobe, which have symptoms of a disease of the cardiovascular system.