Gestalt therapy helps you live here and now, understand and accept your body, deal with childhood grievances, unfinished relationships and loneliness. But most importantly, it is necessary not only for people with depression or anxiety disorders. This is a normal practice in order to improve mental health. And confusion arises due to a lack of understanding of the principles of the psychotherapeutic approach.
In the article we talk about ways to distinguish a competent Gestalt therapist from an amateur, the specifics of the work and the problems being worked on. We reveal the pros and cons of therapy. We give examples of exercises for each of the four stages of interrupted contact.
General information
Gestalt, translated from German, literally means form, but in its meaning the word means integrity, composure, structure.
Gestalt appeared as a term at the end of the 19th century, but its active development occurred at the beginning of the 20th century, when scientists, using the example of works of art, formed the idea of gestalt: when a person looks at a picture, he perceives it as an integral object, irreducible to the properties of its individual elements, then there is a person perceives a work of art as a combination of factors.
Later, the term began to be used in psychology, and after some time it became an integral part of psychotherapy thanks to the research of Edgar Rubin. The scientist argued that human reality is a kind of background, and its individual elements, on which the individual’s attention is focused, are a figure.
Thus, when needs arise, a person is able to remove figures from the background, and upon completion of the interaction, allow them to dissolve into it again. This process can be compared to the need for food, when a hungry person focuses on the desire, and having satisfied it, forgets about eating for some time.
Along with the creation of Gestalt therapy, any process of life activity began to be associated with the figure - hobbies, relationships, business started.
The main feature of Gestalt therapy is tension, which allows a healthy person not to forget about his needs. It is completely normal to pick out certain processes and feel anxious until they are completed.
But often tension arises in the human psyche due to the many unfinished gestalts in the past, which for a long time force people to “replay” unfinished scenarios over and over again, without ever bringing them to their logical conclusion.
We can conclude that Gestalt therapy is aimed at getting rid of unfinished Gestalts , which do not allow patients to build healthy relationships with people and live in the present day without a constant feeling of anxiety.
When does Gestalt occur?
A morning cup of coffee, a conversation with a random travel companion, relationships with parents, falling in love, a quarrel in a store, weeding zucchini - all these are gestalts. Our whole life consists of them, big and small.
A gestalt is formed when a person has a need that at the moment most strongly requires satisfaction, and contact occurs with the outside world.
Gestalt has a beginning and an end: it arises against our will at the moment a need or desire appears and ends when satisfaction is achieved. Alas, needs are limitless, and resources are limited, and not all desires are fulfilled.
Ideally, the gestalt cycle looks like this:
- The emergence of a need (want to drink).
- Searching for an opportunity to satisfy it, assessing the feasibility of this opportunity (we are looking for water).
- Satisfaction (drinking).
- Exiting contact (thirst quenched - put an empty glass on the table).
As a result of such a cycle, the gestalt is completed (destroyed). The process of the emergence and completion of a gestalt can take a second, a minute, hours, years or a lifetime. But external or internal events can interfere with this process. The cycle will stop at some phase, the contact boundary will break and an unfinished situation will arise.
The completed gestalt is sent for disposal, storage or a shelf of consciousness, and the unfinished one remains with us. As long as there is no satisfaction or internal acceptance of the impossibility of getting what you want, the gestalt, together with many of its own kind, puts pressure on the consciousness, parasitizing on other events.
An unfinished gestalt can become a multi-ton Sisyphean stone of guilt in front of a deceased relative or a cardboard folder of unfulfilled promises. The essence remains the same - the past prevents the present from being realized.
Our fears, addictions, conflicts, crises and stress can be represented as a box filled with unfinished gestalts. If the box is not filled to the top with something heavy, then it is easy to move with it. But the heavier the load, the more necessary the help of a psychologist is.
The fact is that incomplete gestalts can cause malfunctions in the mechanisms that protect our psyche from overload.
What can break?
- Projection is the tendency to shift responsibility to the environment for something that originates in a person. They resort to it when faced with rejection of a number of their needs and feelings, which are easier to attribute to the outside world. Normal projection helps to establish contacts and understand other people; pathological projection constantly appears out of place and in some cases replaces reality.
- Retroflection is the desire to do for oneself what one would like to receive from others or do with others. With pathological manifestations of retroflexion, psychosomatic illnesses arise, the desire to hurt oneself, the highest form of retroflexion is suicide.
- Introjection is the inclusion of other people’s assessments, motives and attitudes into a person’s inner world without a critical attitude towards them. For a child, introjection is the most important tool for identifying oneself as a member of society and further understanding the world. Pathological introjection occurs when ideas, habits or principles are perceived as a whole, without checking for incompatibility with existing experience.
- Confluence (fusion) is a state of absence of contact boundaries, when a person loses awareness of himself. Normally, temporary fusion exists in mother and baby, in lovers. A healthy psyche, after a while, returns to normal and self-identifies. With pathological confluence, normal contacts with other people are impossible, since there is a constant desire to control their behavior beyond necessity.
Where is Gestalt therapy used?
Gestalt therapy is a set of techniques and methods of working with the psyche that helps the patient cure neuroses, get rid of internal fears, overcome panic attacks and gain confidence in their abilities.
This approach to psychotherapy can be applied in different social spheres:
- working with family problems;
- pedagogical activity;
- clinical psychotherapy;
- professional trainings;
- consulting organizations;
- trainings to improve public relations and personal growth.
Goals and objectives of Gestalt therapy
The fundamental goal of Gestalt therapy is the creation and strengthening of a holistic image of the client’s personality, as well as ridding him of neurosis, which includes symptoms such as self-doubt, impaired communication skills, problems in his personal life, inability to determine goals and life priorities.
To help get rid of a neurotic state, a specialist needs to find sources of unfinished gestalts and only then begin gestalt therapy.
The objectives of this activity include:
- Working with feelings and emotions . Group therapy is best suited for this type of work, where a person can open up to other people, work on their feelings and the ability to express them.
- Analysis of your condition . Self-analysis is necessary in order to know the source of your own feelings and emotions. Understanding the root of the problem is already a big step towards solving it.
- Attention to your body . Gestalt therapy involves a conscious attitude towards the body, movements, and understanding of physical sensations that were previously ignored by the patient. All this, together with psychoanalysis, helps to establish a physical and spiritual connection and achieve self-awareness.
- Distinguishing past and present . Therapy talks about the ability to distinguish the past from the present, not to hide your experiences and live “here and now.”
What is Gestalt and why does it haunt us?
The word itself comes from the German (who would doubt it, based on its sound) Gestalt . Literally translated, it means figure, image, form or structure (you can look it up in Google Translator yourself). In other words, it is a holistic image that is more than the sum of its parts.
A German philosopher introduced it into use more than a century ago, and gave a more accurate, but less understandable explanation (it is given in the video below).
Would you like an example of such an image (gestalt)? Well, take the tune. After all, it is much more than the individual sounds of its components. The same can be said about the painting. This property of the psyche is to look for the whole in the scattered.
We can mentally collect some separate things into a single image. This is how our psyche works and it has helped us survive for centuries (for example, recognizing the figure of a predator hiding in the bushes).
The most important property of Gestalt is the desire for completion . Surely you have a better memory of a movie that you didn’t manage to finish watching. Search your head. And how many times have you seen when an injured athlete still strives to at least hobble to the finish line. The desire for completion is something we all have.
All this happens at the subconscious level and an ordinary person (who does not know how to professionally delve into his head) simply does not realize all this. However, some unfinished gestalts “sit in the head” very deeply and haunt us (sometimes throughout our lives), leaving their mark on behavior. People who are susceptible to melancholy, that is, with a temperament type close to melancholic, are most prone to this.
A person repeatedly pulls out of his memory some problematic, still unresolved situation, and it torments him. This can last for years, often going back to childhood. The whole problem is that we are simply not aware , which prevents us from getting out of it.
It's like a splinter from which we feel discomfort, but we cannot understand the root cause. Gestalt psychology is precisely recognized to point a person to this thorn and help him get rid of it. No, not even that. Not to point out, but to teach how to find this relationship yourself and get rid of such mental splinters in the future on your own.
Such therapy is designed to teach a person to independently get rid of destructive gestalts , so that he can go through life without limping on both legs, but calmly and constructively building his future (without unnecessary unfinished psychological problems behind him).
The root cause of all problems in Gestalt psychology is recognized that this particular person cannot live in the present and drags with him from the past all open gestalts. He constantly retrieves them from his memory, scrolls through them and suffers because he did something wrong then. To close all these problems and teach a person to live in the present - this is the task of a therapist practicing this technique.
Advantages and disadvantages of Gestalt therapy
| Advantages of Gestalt Therapy | Disadvantages of Gestalt Therapy |
| A fairly in-depth analysis that can reveal hidden motives, traumas, causes of neurosis and anxiety of the client | Therapy involves independence. The doctor does not give advice; the patient is responsible for his choice |
| Ability to work with different levels of complexity of psychological problems | Provides for fairly long work (from 3 sessions) |
| Therapy approach is person-centred, methodology is of secondary importance | Requires a fair level of intelligence, not suitable for children |
| Therapy is process-oriented; the patient comes to the result independently | It is necessary to use feelings, emotions and experiences, as they play an important role in therapy |
Who is Gestalt therapy suitable for?
Gestalt therapy is a direction of psychotherapeutic activity that is focused on the patient’s feelings, emotions and experiences. Therefore, this technique is not suitable for all people.
Generally, Gestalt therapy is popular among women due to their greater openness about their feelings.
But this does not mean that men cannot benefit from undergoing Gestalt therapy; the results of the sessions depend solely on the client’s openness and his lack of embarrassment of his feelings and emotions.
How to close a gestalt
An open gestalt is not a situation in which time heals. Rather, time here only aggravates, strengthens this very wound, and sometimes it covers it so much with sand that it is possible to get to the bottom of it only through long-term therapy.
An open gestalt is not a situation in which time heals.
How can you help here? Close that notorious gestalt. In the vast majority of cases, working with a psychologist will be effective. Some will be able to cope with their situation in one session, while others will need much more time, because it is not immediately possible to identify what actually caused the discomfort.
Basic concepts of Gestalt therapy
List of concepts:
- Figure and background . These concepts are taken from Gestalt psychology and mean the patient’s attitude to reality and focusing on its individual elements. The relationship between figure and ground is very dynamic, since a person’s emphasis and needs often change. Any receipt of information consists of a changing background and a change of figures, so the entire life experience of the patient consists of such changes. Some processes or changes may remain unfinished when a person finds a new subject of interest, and then they are postponed, forming some of the person’s views and beliefs. A healthy figure-ground relationship includes interest, caring, and enthusiasm. In a person with mental disorders, the formation of the background and figure is difficult and occurs with a feeling of apathy, indifference, boredom, and anxiety. Also, in a healthy person, during the course of life, there is a frequent change of figures and background, and these processes are characterized by completeness and satisfaction. A sick psyche is distinguished by a fixation of a figure or an inability to form it and complete the gestalt.
- Gestalt clarity . A healthy perception of reality allows a person to calmly identify and complete gestalts that are understandable to perception. Painful and incomplete gestalts are formed as a result of unfinished experiences or traumatic situations, the scenario of which is often repeated and cannot be released.
- Awareness . Awareness is one of the main concepts in Gestalt therapy, meaning adequate consciousness, understanding of one’s internal processes. F. Perls, the founder of Gestalt therapy, says that a violation of consciousness is the cause of neurosis, which prevents one from completing gestalts, realizing one’s experience and adequately perceiving oneself and the world around us.
- Completion. The concept of completion plays a key role in Gestalt therapy and means the logical conclusion of an experience. Problems with closure cause a person to dwell on unfinished experiences, relive them, and hold back emotions.
- Integrity and Personality . These concepts are closely related to each other, since personality in Gestalt therapy is a holistic structure, which internally consists of interactions of internal understanding, relationships, beliefs, connections with the outside world. A healthy personality, according to Gestalt psychology, consists of dynamic connections of internal interactions.
Features of Gestalt therapy as a new direction in psychiatry
Gestalt therapy was developed and put into practice in the middle of the last century by the German psychoanalyst Fritz Perls (1893-1970). This is an independent direction of psychotherapy, including elements of bioenergetics, psychoanalysis and psychodrama, valuable for its humanistic, existential approach to the patient’s personality.
Its essence can be briefly described by the “Gestalt prayer” of the founder of a new method in the treatment of mental disorders:
“I do my thing and you do your thing. I am not in this world to meet your expectations, And you are not in this world to meet mine. You are you, and I am me, And if we happen to find each other, that’s wonderful.”
That is, I can help you, but you yourself must want it and believe in yourself. And then the meeting between the patient and the Gestalt therapist will be useful.
It should be distinguished from Gestalt psychology, the latter as a scientific direction operates with such a concept as Gestalt (German - representation, image). This first part of the name is perhaps the only thing they have in common, although some ideas are still borrowed.
It is believed that Gestalt therapy is based on the feminine principle in psychotherapy, when one should not fight problems that have arisen in a purely masculine way - by willpower, but accept them, realize them and gradually change one’s attitude towards them, based on the conviction: “I am small, but the world is big." All emotions cannot be considered bad; they must be treated with respect, the cause of their occurrence must be understood and gradually, without excessive effort, extinguished.
Gestalt therapy is based on the concept of authenticity - the authenticity of feelings and experiences that allow you to live in harmony with your inner world. “Harmony of feelings” should prevail over “harmony of mind”, in other words, trust your feelings more than your consciousness. Rely on your internal “barometer” of behavior, but do not ignore the realities that stand in your way.
It’s worth listening to them so as not to come into conflict with the outside world, which will inevitably affect your mental health. Authenticity is manifested in congruence; this is when words do not diverge from deeds, a person lives in complete harmony with his personal values.
Principles
The principles of Gestalt therapy differ from the principles of other methods of psychoanalysis in that in the therapy under consideration there are no clear and rigid instructions that must be followed.
The system of principles of Gestalt therapy is quite flexible and sets the direction for the development of work with the patient:
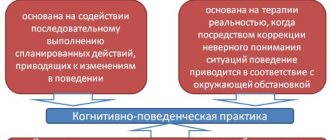
- The principle of “here and now” is one of the main ones in Gestalt therapy. He talks about concentration on the current moment of his life, attention to feelings in relation to the environment, events occurring at the moment. The principle helps the patient to distance himself from frequent immersion in the past or dreams of the future and feel his life in the present.
- The “me and you” principle plays an important role, as it speaks of a person’s open contact with others. Most often, the patient has difficulty communicating with people, so during therapy the doctor pays attention to his relationships with other group members by performing verbal and nonverbal exercises.
- The principle of subjectivization is important in therapy, as it allows you to establish a person’s awareness and develop his understanding of his own problems and failures. The principle is to formulate one’s condition, for example, a psychotherapist may ask the patient to express his thoughts in the form of “I can’t do this” rather than “this bothers me.”
- The principle of continuity of awareness . Awareness, as one of the basic concepts of therapeutic activity, largely influences the progress of work with the patient, as it helps to track the flow of experiences and feelings, navigate one’s own state, and identify cause-and-effect relationships of thought processes. Awareness focuses on the “what” and “how” rather than the “why” and “why.”
What is the role of a Gestalt therapist?
Gestalt therapy is a type of work with a patient where the therapist plays a vital role in the session:
- the therapist conducts experiments and observes the phenomena identified in his process, that is, asks the person to talk about a life situation or problem, and then observes his reaction, feelings and emotions, analyzes behavior and plans further steps in the work;
- the doctor can intervene in the experiment, direct it in the right direction, push the patient to self-awareness, and focus his attention on key elements;
- After the session, the Gestalt therapist discusses the identified phenomena, asks the client about his expectations and needs and correlates the answers received with the results of the phenomena identified during the session;
- in accordance with the humanistic approach to therapy, the doctor analyzes the experiment together with the patient, avoiding the position of a mentor and teacher. The therapist discusses the identified phenomena with the client on an equal basis, reveals himself as a person and shares his experience.
Thus, the personal qualities of the doctor play an important role in the effectiveness of therapy. One of the main concepts of this area of work with a patient is dialogue, therefore, without the proper qualities of a therapist, building the most comfortable communication with a client is impossible.
How does an open gestalt arise?
There are many social phenomena that lead to the emergence of incomplete gestalts. Most of them are associated with outdated traditions, norms and religious dogmas.
An example of how parental influence can lead to serious problems in a person’s adult life has already been described above. But this is only one of the common situations in which an unclosed gestalt arises.
In general, the mechanism of disturbance in the perception of the world is as follows. A person learns some information that he is afraid to challenge or considers to be the only true one. For example, those around him tell him that talking to strangers is impolite and even dangerous. This information remains in his subconscious, preventing him from building social connections. Over the years, the problem worsens, making a person’s life more and more difficult.
In order for incorrect information leading to a violation of the objective perception of the world to be refuted in a timely manner, you need to analyze your actions and the reasons for your behavior. But it’s not always possible to do this on your own. In this case, you need to contact a Gestalt therapist.
Kinds
Types of Gestalt therapy are divided into “projective” and “dialogue”. The “projective” type of therapy is based on an analysis of the patient’s feelings and emotions and involves working with dreams, images, imaginary dialogues and internal characters, and projections. The second technique represents direct contact between the therapist and the client, their relationship, and dialogue.
The patient’s trust factor and, in general, the role of each participant in Gestalt therapy are very important here. It is necessary that during the session the doctor and the patient feel like equal partners. The patient is responsible for making decisions independently, which is an important component of the work process.
It is worth noting that both techniques are rarely used separately; for the most complete analysis of the patient’s condition, it is necessary to first work with his feelings, emotions and dreams, and then discuss with him the important factors identified during the “projective” technique in the already “dialogue” type of therapy .
Conducting Gestalt therapy
Gestalt therapy in its form can be carried out in the form of group and individual work with clients. Group therapy aims to bring the patient into contact with other participants. Here the client analyzes the behavior of other people, projects his feelings and emotions onto them and thereby becomes closer to self-awareness.
Gestalt therapy can be either individual or collective.
Working in a group helps you feel like you are in a small society, where the patient is part of it, who can implement roles, show flexibility and variability in behavior, open up from different sides and find a source of resources. Individual work involves a personal approach based on identifying the healthy and neurotic in the client.
Here the therapist plays the role of an interlocutor and partner who helps to understand the patient’s internal processes, feelings, emotions and the source of anxiety.
The main feature of Gestalt therapy is building a unique relationship with each patient, awakening their awareness of their own relationships with the environment, understanding their emotions and feelings.
Also, a distinctive feature of the sessions is the client’s attentiveness to his own feelings, his ability to separate his feelings from reactions to them, that is, the independence of each participant in therapy plays an important role, regardless of whether the session is group or individual.
In any case, patients learn to independently monitor their condition, take responsibility for it, distinguish the past and future from the present, and be able to focus on the very process of experiencing the problem, rather than searching for its cause.
Pros and cons of Gestalt therapy
Like any other method of qualified and scientifically based psychological assistance, Gestalt therapy has its advantages and disadvantages. Main advantages:
- Group or individual work is equally effective;
- Correction of disorders is as painless as possible for the patient;
- Based on the Gestalt method, you can develop interesting exercises and techniques for correcting psychological problems;
- While working with a specialist, the patient learns to “live for today” without focusing on the past and future.
Art therapy - what is it, definition
Among the disadvantages, it should be noted that only a highly qualified psychologist can conduct gestalt sessions, so correction of disorders, as a rule, has a high cost. Also, if there are serious problems, correctional work can take quite a long time. However, despite this, in Russia this method of psychological assistance has many devoted fans - the creators of private psychological clinics.
Interesting. Unlike numerous new directions, Gestalt technique is reliable and time-tested. You can work with this method with people of any gender and age. Only severe disorders that require additional consultation with a psychiatrist cannot be corrected.
Basic techniques and techniques of Gestalt therapy
Gestalt therapy is a type of work with a patient that does not require strict adherence to special techniques and techniques. During the session, the main role is played by the contact between the doctor and the client, therefore there are special recommendations aimed at building the most productive and competent dialogue with the patient to effectively solve his problem.
They are as follows:
- Focusing . The therapist’s focus during the session is on the client’s direct experience of the situation, concentration on feelings and sensations. The patient's story about a past event must be described in the present tense in order to achieve the most complete experience and disclosure of emotions. The therapist, in turn, must note non-verbal signs of the client’s behavior and compare them with verbal manifestations of emotions in order to arrive at the patient’s current problem and needs using a comprehensive analysis.
- Reflection . The reflection technique involves returning the client’s words in order to get closer to him and understand his feelings and experiences. Often, the patient, discussing his problem, speaks without awareness of his own speech, which in turn is often compulsive in nature. The therapist's constant questions in response to such client behavior can contribute to care in projection, that is, distraction from the patient's actual needs. Sometimes the speaker needs confirmation that he is being heard and understood, so the technique of reflection can have a positive impact on the further development of therapy.
- Mirroring. This technique differs from the previous one in its nonverbal component. The therapist needs to repeat certain nonverbal manifestations after the client so that in his subconscious the patient feels trust and a desire to open up to the doctor. Mirroring helps you feel heard and understood, which is very important for a comfortable session.
- Returning the trajectory of a figure . Otherwise, this feature of the work process can be called “shuttle running”. During therapy, the doctor may forget about the patient’s key request, follow it into projections and the content of situations without a productive search for the actual and main problem. To avoid such situations, the therapist needs to periodically return to the client's original request, not lose focus and summarize the storylines, comparing them with the key problem.
These techniques are aimed at establishing a trusting relationship between the doctor and the client and are distinguished by their dialogical and generally humanistic orientation.
Exercises
Gestalt therapy is characterized by special exercises aimed at focusing attention on feelings, self-awareness, and releasing pent-up emotions. Therapy exercises are divided into several groups depending on their focus and method of implementation.
Awareness of your own feelings
List:
- Exercise 1 . The patient needs to focus on external factors (what is within sight, audibility), and then concentrate on his internal sensations (images, thoughts, emotions, muscle tension). Gradually, it is necessary to focus on each internal process, try to penetrate to its origins and track the emotions, desires and actions that arise.
- Exercise 2 . The client needs to focus on bodily sensations, pronounce to what extent and clarity he sees his body. The patient should note pains and tensions that he had not previously paid attention to, and feel them. It is also important to ask the client whether he feels his body as a whole, whether he sees connections between body parts, feelings and physical sensations.
Integration of Polarities
List:
- Exercise 1. In group therapy, this exercise looks like patients playing roles in the presence of other therapy participants. For example, an overly shy person is asked to play the role of a person with the same character traits, but exaggerate them a little. Or, if the client is aware of his communication problems, he is asked to portray a personality with completely opposite character traits. After a five-minute role-play process, therapy participants are invited to discuss their impressions.
- Exercise 2 . This exercise is suitable for those patients who feel their internal conflicts and cannot resolve them. The client is asked to imagine two chairs on which his conflicting parties are sitting. Next, the person is asked to imagine a dispute between these parties, talk through their dialogue, and try to find a compromise for them with the help of a therapist.
Working with dreams
List:
- Exercise 1 . The client needs to tell his dream in the first person in the present tense, select its most emotional moments and reproduce them. Next, you need to try to speak a dialogue between the characters or elements of the dream, and compare the identified experiences with your own life problems.
- Exercise 2 . This exercise is suitable for group therapy. One group member tells the dream, and the other patients choose one object and sketch it. Next, the chosen roles are played between the therapy participants, as a result of which it is necessary to note one’s own feelings that are reflected in this dream.
Overcoming Resistance
List:
- Exercise 1 . The patient needs to note his habits. If they seem ineffective or interfere with his life, he is asked to imagine changing his usual actions to something new. It is important to tell the client how he will feel when changing habits, whether he will enjoy doing something different, whether he will feel strong resistance and how he can overcome it.
- Exercise 2 . The client is asked to think each morning about feeling and acting differently for the coming day. The person is not required to make binding decisions. The patient needs to visualize their day with small changes in simple things that are easy to change.
Incomplete gestalt - what is the essence of the problem
Gestalt is integrity, completeness. Refers not only to classic relationships between parents, friends, couples. In general, to satisfy desires, achieve goals, etc.
When someone is in a quarrel with a loved one or cannot find a job for a long time, it is very depressing, you must admit. Let's look at a couple of common life situations to understand what's what.
Examples
Imagine the situation. The man really wanted to become an artist, tried to draw, but then abandoned it. Time passes, everything goes as usual, but when he reaches into the closet for some things, he accidentally stumbles upon his work.
What's happening? He is upset because he remembers his desire, which he did not achieve . Then he walks around the apartment sad for a whole week.
Let's consider an unfinished gestalt using the example of a separation between a man and a woman. Let's say one of them decides to separate. As a rule, such news will come out of the blue in the middle of summer. The person will be discouraged and upset.
Perhaps he will fall into a state of hopelessness, deepen into a depressive state. He will be tormented by thoughts that it is impossible to return everything as before, to fix something.
This situation will remain unresolved if it is not worked out correctly in your head on your own or with the help of a psychotherapist.
Duration of the Gestalt therapy course
Gestalt therapy is a direction of psychotherapeutic activity in which the duration of therapy depends on many factors depending on the patient’s request and his personal characteristics.
For example, a client’s problems can be divided into situational and existential, that is, related to certain life situations or global personal problems that have been troubling a person for a long time.
Gestalt therapy can be built in a consultative and in-depth mode.
The first way of working involves several meetings with a therapist, as a result of which the assigned tasks are solved. The second type of therapy differs in depth and duration from one to several years. In any case, Gestalt therapy is focused on the patient’s needs, so the duration of the work depends solely on his individual characteristics.
Reviews
Quite a lot of patients, speaking about Gestalt therapy, note that the session process is a huge independent work. Therapy does not provide answers to questions; it forces you to find a way out of the situation yourself and take responsibility for your decisions.
Almost all clients note that before undergoing Gestalt therapy they were constrained in their emotional manifestations, embarrassed by their feelings, limited by public opinion, stereotypes and imposed standards.
Working with a therapist helped these people gain inner freedom, begin to defend personal boundaries, stop devoting all their time to fantasies, dreams, past mistakes and begin to enjoy life “here and now.”
Such a humanistic direction as Gestalt therapy, which seeks to help a person not by ignoring problems and artificially cultivated optimism, but with the help of the ability to notice different aspects of life, experience feelings in all their diversity, be “here and now” and independently deal with internal restrictions.
Author of the article: Anna Fleyman
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Basic methods and techniques
Art therapy for preschool children - what is it?
The Gestalt approach involves the use of a wide range of different methods and techniques of psychological influence on the client. Basic methods and techniques of work:
- Expansion of human consciousness;
- Resolution of personal contradictions (this method is based on the fact that each personality is contradictory by nature and combines incompatible qualities);
- Increased intensity of feelings and sensations;
- Correction of the patient's fantasies and desires.
The specialist also tries to instill in the patient the idea that only he himself is responsible for his actions and the problems caused by them. Increasing the sense of responsibility helps to successfully correct many neurotic disorders.
The purpose of the basic methods and techniques is to help the client look at himself with new eyes