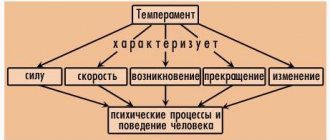
Deviation is any behavioral deviation from an established sociocultural norm. The concept of deviation denotes the behavioral response of individuals that does not correspond to sociocultural norms. Various crimes, abuse of narcotic or psychotropic drugs, alcoholism are all the clearest examples of deviation. However, petty hooliganism, actions of a revolutionary nature, and the absence of a greeting at a meeting are also considered deviations, since all human actions and deeds are included in a system of relationships and social interactions that has general normative regulation. An example of this is family relationships, teamwork, contacts with the street environment, etc. As a result, behavior that disrupts the stability of interaction processes with society is considered deviant.
Causes of deviation
Deviation in society is determined by the adequacy and inconsistency of actions with the expectations of society. One person is characterized by deviations in behavioral response, another by defects in the structure of his own psyche, and a third by simultaneous pathology in behavior and mental functioning.
In addition, disorganization of a personal nature (that is, individual deviation) and group deviations can be observed in the behavior of individuals. Personal disorganization arises when an individual subject denies the norms of the subculture in which he grows up.
Examples of individual-oriented deviation: an individual grew up in a prosperous family, but in adolescence he rejected accepted norms and became a criminal. Behavioral responses that deviate from the norm can be negative or positive.
Positive deviation can act as an individual’s aspiration for superiority, self-affirmation in a new way in socially useful activities (for example, heroism, self-sacrifice, altruism, the highest devotion, etc.).
Group deviations are considered as the collective behavior of group members characterized by deviant behavior. For example, teenagers from unfavorable families lead an abnormal lifestyle, condemned by the normative prevailing morality of society. They have their own rules and cultural norms.
Sociologists tirelessly strive to explain the nature and causes of behavioral deviation. Some believe that individuals, due to their biological nature, are initially predisposed to certain behavioral styles, and the “criminal type” is the result of hostility and degradation. Others associate deviant behavior with the specific structure of the human body, the pathology of sex chromosomes. The third group of deviation researchers substantiates the occurrence of deviant behavior with dementia, degenerative processes, psychopathy, in other words, mental defects. In addition, there are explanations of deviation from a cultural point of view, which is based on the recognition of a “clash between sociocultural norms”, a manifestation of “labeling”.
The most substantiated explanation of the causes of deviant behavior is considered to be a theory based on disruption of the course of personal socialization. When a child is raised in a “normal” family, he develops social interest, develops self-confidence, and develops a perception of surrounding sociocultural norms as the only true and fair ones. When a child is surrounded by unfair treatment, misunderstanding, constant confrontations between parents, he develops a negative attitude towards the surrounding society, lacks orientation towards the future, develops anxiety and anxiety, and the result is deviant behavior.
However, deviation and deviation in behavior can be observed in adolescent children brought up in quite prosperous families, since the family is not the only source of socialization of an individual in a complex, dual, constantly changing society. Many norms in different subcultures often contradict each other. The family upbringing of an individual comes into confrontation with the beliefs of social groups and the ideology of institutions. As a result, parents are faced with excessive ideologization of their children, the influence of commercial sentiments of street groups, etc. The result of this is the emergence of contradictions between the values instilled by parents and the norms established by social groups or subculture. Children think that what their parents tell them is wrong, as a result of which the conflict between them intensifies and a confrontation between fathers and children arises.
Teenage deviance is often expressed in graffiti and vandalism. Scientists have not identified a relationship between the desire for vandalism and adolescents’ belonging to a particular social stratum. In addition, the peculiarities of adolescent deviation lie in the discrepancy between children's deviant behavior and the patterns of adult behavior deviating from norms.
Real life is saturated with a large number of norms that confront each other and is filled with uncertainty of social control, which creates difficulties in choosing a strategy for individual behavior. This leads to a phenomenon called “anomie of society,” that is, to a state of lack of foundations in which the subject is not confident in choosing a strategy of normative behavior. According to the teachings of E. Fromm, a subject in such circumstances loses a sense of belonging and devotion to society, identity with the team and himself, loses the need to establish contacts, feels a feeling of loneliness, detachment and alienation, isolation from political foundations and moral norms.
E. Merton believes that anomie is the result of the inability of a group of individuals to follow the rules that they wholeheartedly accept, and not of freedom of choice. He sees the main reason for the difficulties in the discrepancy between cultural foundations and instrumental legal means by which such goals are realized.
The inequality that exists in society is the factor that forces an individual to look for illegal ways to achieve goals, in other words, to deviate from accepted sociocultural norms and moral values. If a subject is unable to achieve his own goals with the help of talent and abilities, then he may use illegal means that are not approved by society (for example, deception or theft).
Thus, three variations of the theory of deviation in behavior can be distinguished:
— the concept of physical types, which consists in the predetermination of various deviations from sociocultural foundations by existing physical features;
- psychoanalytic teaching sees the cause of deviation of children and adults in the conflict arising in the human consciousness;
— sociological theory takes as its basis changes in the intrapersonal structure that occurred as a result of unsuccessful socialization in a group.
Clinical observations and experiments of recent decades have made it possible to discover a certain relationship between personal and situational reactions and the main types of deviations, on the one hand, and character accentuations, on the other.
Problems of education
This category includes:
- Age-related crises, which are accompanied by accelerated and uneven development of the body during puberty, underdevelopment of certain organ systems, which significantly affects the child’s well-being, both physical and mental. Hormones and disruption of the endocrine system, which is fraught with emotional instability.
- Conflicts with the older generation, misunderstanding between elders and younger ones.
- Critical attitude towards the actions of adults (teachers and parents).
- The need for self-affirmation, which leads to conflicts with peers in their negative manifestation and to deviations in social behavior.
But despite the psychological and biological factors, shortcomings in upbringing are of paramount importance. These include:
- Social deviations are omissions and mistakes of the family in raising a child.
- The constant exclusion of children from life's troubles, from work and any active activity, which gives rise to infantilism, lack of a sense of compassion, inability to make an important decision in a critical situation, and so on.
- Disadvantages in training and education in kindergartens and schools.
- Negative environment in the process of upbringing, dysfunctional family, negative influence of the company and comrades, and so on.
- Lack of interaction in matters of education between family and school.
- Problems with the child’s self-esteem, deviations in personal aspirations, complete indifference to values and reluctance to improve themselves, and so on.
We must never forget that all problems come from the family and only decent upbringing and work on mistakes can protect an individual from the development of deviant behavior. From an early age, a child absorbs everything that surrounds him like a sponge. The behavior of parents, their friends, society - all this has a strong influence on the development of the child as an individual.
Theories of deviation
Deviation in society is a process determined by social factors. There are a number of theories aimed at explaining deviant behavior. The first attempts to explain deviant behavior were predominantly biological in nature. Followers of the concept of physical types explained the reason for the tendency to deviate actions by the innate properties of the human individual. In other words, the basic premise of all concepts of physical types is the dependence of deviations on certain innate physical personality traits.
The theory, created by criminologist and psychiatrist from Italy C. Lombroso in the seventies of the 19th century, interpreted the causes of deviation by certain anatomical features. Lombroso, having studied the external characteristics and physical data of criminals, hypothesized that individuals of the criminal type are characterized by a protruding lower jaw and a low pain threshold, which are considered signs of regression, a return to earlier evolutionary stages of human development. At the same time, he recognized that the formation of criminal behavior can be influenced by social conditions. However, he believed that most offenders are mentally retarded. Because individuals have not fully developed as human beings, their actions usually do not conform to the norms of human society. The described concept was further developed in the forties of the last century in the theory of psychologist W. Sheldon.
He considered the problem of deviation from the perspective of the dependence of deviant behavior on the constitution of the human body. His theory states that subjects with a certain body constitution are inclined to commit actions that are inconsistent with the sociocultural norm and are condemned by society. He identified three core physical types: endomorphic, mesomorphic and ectomorphic.
The endomorphic type is manifested in roundness and excess weight, mesomorphic – in muscularity and athletic build, ectomorphic – in thinness and thinness. Sheldon Bull is sure that mesomorphs, that is, individuals with physical strength, hyperactivity and reduced sensitivity, are most predisposed to deviant behavior.
The described theories are far from the truth, since history knows many cases when the most severe crimes were committed by people with the appearance of cherubs, and individuals with so-called “criminal” facial features turned out to be good-natured people who could not offend even a fly.
Psychological theories of explanation for the essence of deviation, like biological concepts, believe that the reason for the deviation of a behavioral response lies in the individual himself, and not in society. Conflicts occurring within personal consciousness are the main psychological theories that reveal the essence of deviation. Freud argued that under the layer of active consciousness in each person there is a sphere of the unconscious - psychic energy that unites everything natural, primordial, knowing no limits and pity. The unconscious sphere is the biological essence of an individual who has not experienced the influence of culture. A person is able to protect himself from his “lawless” state through the development of his own “I” and “Super-Ego,” which constantly inhibit the forces existing in the unconscious sphere and limit base passions and human instincts. A state when the internal confrontation between the “I” and the unconscious area, the confrontation between the “Super-Ego” and the unconscious destroys the defense, and the internal content, which does not know culture, bursts out. This is how deviation is formed - the deviation of behavioral norms from cultural foundations formed by the social environment of the individual.
There is a grain of truth in the described point of view, but identifying and diagnosing possible deviations in the structure of the subject’s “I” and possible social anomalies is extremely difficult due to the secrecy of the object of study. In addition, although every individual has an internal confrontation between the needs and limitations of culture, not every person will become a deviant.
Some followers of this concept have suggested that a small number of human individuals develop a psychopathic or immoral personality type. Individuals with this type of personality are characterized by isolation and emotional coldness. They often act impulsively, and they rarely feel guilty for their actions. It is impossible to talk about the consistency or inconsistency of this point of view, since all studies of individuals with similar traits were conducted exclusively among prisoners in prison. Restriction of freedom and detention do not have the best effect on the personal traits of individuals.
It follows that the analysis of a specific psychological characteristic and conflict is not able to explain the concept of deviation and its essence. Thus, we can conclude that deviation is the result of the joint interaction of several factors (psychological and sociocultural).
The starting point of sociological theories that explain the causes of the origin and characteristics of deviation can be considered the works of E. Durkheim, who formulated the concept of anomie, that is, a mass departure from the foundations existing in society as the core cause of deviation.
Merton later refined the concept of anomie, classifying it as a tension that appears in human behavior when he finds himself in conditions of confrontation between sociocultural norms and reality. Merton believed that anomie arises not due to freedom of choice, but due to the inability of many subjects to adhere to norms that they fully accept. He saw the main reason for the difficulties in the imbalance between sociocultural goals and legal means of achieving such goals.
However, the lack of legal means and the desire for welfare do not always lead to the emergence of deviation. Only when society proclaims universal symbols of success for the entire people, while limiting the access of many individuals to recognized methods and legal means of achieving established symbols, are the conditions for antisocial behavior formed. As a result, Merton identified five responses to the task of choosing a goal and a means, four of them are abnormal adaptation mechanisms to the conditions of anomie.
Conformity is the first possible reaction. It represents a passive adaptation to the existing order of things. It appears when members of a social group accept the achievement of material well-being as cultural goals, and also use socially approved means to achieve their goals.
Innovative behavior is observed when subjects fully adhere to sociocultural goals, but at the same time reject the ways of achieving them established by society. People who use this type of response can sell drugs, cheat, steal, engage in prostitution, and blackmail.
Ritualism occurs when members of a social group either completely reject sociocultural goals or belittle their importance, but mechanically use the means established by society to achieve them.
Retreatism is the rejection of cultural goals and socially approved means of achievement. Followers of retreatism reject everything, offering nothing in return. Such individuals include alcoholics and tramps.
Rebellion involves the rejection of sociocultural goals and means of achievement and their replacement with new attitudes and norms. Such goal setting is characteristic of some youth subcultures and revolutionary movements, and it can also be embodied in crimes with a political background.
Critics of this theory point out that Merton overlooked the social interaction through which individuals form their own worldviews and plan their actions. Merton considers violators of social norms to be individualists, mostly self-sufficient people who develop ways out of stress for themselves, without taking into account the actions of others. In addition, psychological deviations cannot always be explained by the confrontation of goals and means. Among other concepts that explain psychological deviations and their origins, the following theories can be distinguished: imitation, differential association and stigma.
The French sociologist G. Tarda is considered the founder of the theory of imitation. It is based on the fact that subjects turn into criminals because of the criminal environment in which they grew up. That is, the environment for such children is a reference group. E. Sutherland, developing Tarde's concept, proposed his own theory of differential association, in which he emphasized that much of the deviant behavior of subjects depends on their surrounding social environment, in other words, on who teaches them what exactly.
The deviation of adolescents is directly proportional to the length of their stay in a criminal environment. The longer a teenager stays in criminal conditions, the greater the likelihood that he will become a criminal in the future. Sociologists G. Becker and E. Lemert developed the theory of stigmatization.
The problem of deviation, according to the teachings of these sociologists, is caused not so much by a behavioral response or the content of certain actions, but by group assessment, labeling an individual as a delinquent and applying sanctions to him.
Signs of deviant behavior
Psychologists determine an individual’s propensity for deviant behavior based on a number of characteristic features. Sometimes such personality traits are symptoms of mental illness. Signs of deviation indicate that an individual, due to his status, health, character, is prone to antisocial behavior, involvement in crime or destructive addiction.
Signs of deviant behavior:
- Aggression.
Aggressiveness indicates the constant internal tension of the individual. An aggressive person does not take into account the needs of other people. Goes ahead towards his dream. Does not pay attention to criticism of other members of society about his actions. On the contrary, he considers aggression a way to achieve certain goals.
- Uncontrollability.
The individual behaves the way he wants. He is not interested in other people's opinions. It is impossible to understand what actions such a person will take in the next minute. The violent temper of an uncontrollable individual cannot be curbed by anything.
- Sudden change in mood.
The deviant's mood constantly changes without any apparent reason. He can be cheerful, and then scream and cry a few seconds later. This change in behavior occurs from internal tension and nervous exhaustion.
- The desire to be invisible.
The reluctance to share your thoughts and feelings with others always has reasons. A person withdraws into himself because of psychological trauma or when he wants to be alone so that no one interferes with living as he wants. You cannot live separately from the society of people. This behavior often leads to degradation.
Negative signs of deviant behavior are a social pathology. They cause damage to society and the individual himself. The basis of such behavior is always the individual’s desire to act contrary to the norms and rules accepted in society.
Types of deviation
Today there are many classifications of deviant behavior. According to Clayburgh's systematization of deviations, three groups of deviant behavior are distinguished: - socially neutral (begging), positive (self-sacrifice) and negative deviation (drug addiction).
Positive deviation is a form of deviant behavior and is perceived by most as non-standard, strange behavior, but at the same time it does not cause disapproval or censure in society.
Negative deviation definitely causes rejection and condemnation among most people.
E. Zmanovskaya generalized various typologies of behavioral deviations, as a result of which she identified the type of norm violated and the negative consequences of deviation as the main criteria for classification. She identified three groups of antisocial behavior:
- antisocial behavior, that is, actions that do not comply with legal norms and threaten the well-being of citizens and social order;
- antisocial behavior, which consists in evading moral and ethical standards and ethical principles, which threatens the well-being of interpersonal relationships;
- self-destructive behavior, manifested in suicidal attempts, fanatical, autistic, victimized, risky actions. This type also includes various dependencies.
Nadezhda Maysak has developed a matrix of social deviations that differentiates many forms of deviations within two dimensions that intersect with each other. Deviant behavior can be divided according to the nature of its manifestation and direction, as well as the degree of social approval.
According to the nature of manifestation and direction of deviation of children and adults, there are:
— constructive – various types of creative self-expression;
— autodestructive, which in turn are addictive (various dependencies) and suicidal;
- externally destructive, which can also be illegal and communicative.
According to the degree of social approval, deviations are:
- socially approved and prosocial (that is, adapted to the principles of a certain group of people);
- socially neutral (that is, the actions of individuals do not pose a danger to society or they cannot be assessed, since the criteria are ambiguous);
- socially disapproved, namely asocial actions, that is, actions that deviate from moral principles and moral standards, antisocial behavior, that is, actions that deviate from the norms of the law.
Pros and cons of doors with deviators
The main advantage of doors with a multi-channel “crab” system is providing maximum protection of the interior from unwanted penetration.
There are some disadvantages. An additional locking mechanism makes the door structure heavier, and in places where there are channels for mounting rods, there is no insulation.
Otherwise, metal doors with a deviator perfectly perform their main function and can last a long time, providing complete safety for the house and residents.
Metal doors with a “crab” system are slightly more expensive than standard models equipped with a conventional locking lock. But when it comes to safety and property protection, is it worth saving the budget?
Forms of deviation
In the context of the functioning of modern society, the main forms of deviation include: alcoholism, drug addiction, crime, suicidal behavior, prostitution.
According to most sociologists, negative and positive deviation are inevitable in modern society. It is impossible to completely eradicate deviant behavior. As long as there are norms established by someone, there will be deviations from them. Researchers of this problem note that the emergence of deviations is natural in societies that are undergoing transformation, where, in conditions of increasing crisis, dissatisfaction with their own position begins to grow among human subjects, which leads to the emergence of a feeling of dissatisfaction and alienation from society. The progressive growth of deviant behavior and their inevitability require coordinated actions and targeted measures from society.
Prevention of deviations should include the search for methods of influence and technologies for working with maladjusted individuals, rehabilitation of adolescents, prevention of the occurrence of deviant behavior, that is, the elimination of conditions that have a negative impact on the actions of minors.
Prevention of deviations is a complex of government actions, organizational, educational, socio-medical measures focused on prevention, elimination or aimed at neutralizing the key causes and eliminating the conditions that provoke various types of deviations and social behavioral deviations.
The fight against deviations, first of all, should occur by influencing the relevant social groups and subcultures, that is, the negative social environment, and certain of their carriers; conditions and causes producing such phenomena as drug addiction, crime, etc.; connection of such phenomena with crime.
Consequences of social deviations
Determining the consequences of such behavior is difficult, since this issue is very controversial. For example, there is a theory that those rules that regulate victimless crimes should be removed from criminal law. This could be, for example, prostitution, recreational drug use, and so on. And every society is always divided into two camps - opponents of these phenomena and those who advocate legalization.
Replacing the shower/spout switch mechanism
Ball switches are the most reliable, but, unfortunately, they cannot be repaired, so if you have a mixer with just such a switching mechanism, and it breaks, then you will have to buy a new one.
For cartridge, axle box and eccentric switches, the repair work will be as follows:
1. Remove the decorative plug on the shift knob. In some faucets, you need to use a wallpaper knife to remove the plug and use a screwdriver to unscrew the fixing screw that covered it. In our case, it itself is such a screw. We turn it away.
2. Remove the handle.
3. Under the handle there is either axle box mechanism or a nut securing the mechanism (cartridge or eccentric). Turn it away.
4. Take out the mechanism. The axle box or cartridge is removed entirely. With eccentric ones, only one part will be removed - the eccentric itself.
5. To completely dismantle the eccentric switch, it is necessary to remove its internal part. To do this, unscrew the spout nut by hand.
6. Remove the spout downwards.
7. Under the nut you will find a removable part of the housing. It will have to be turned away. This is very difficult to do. Wrap this part with a cloth so as not to damage the chrome plating during dismantling, and use a gas (not adjustable) wrench to unscrew this part using the body itself.
8. If you manage to do this, the inner part of the mechanism can be easily removed from the case. Overall it will look something like this:
On the right is the eccentric part, which turns away first, on the left is the inner part. If you cannot remove the inner part, you will have to change the mixer.
9. After dismantling, using the samples received, we buy the necessary spare parts in the store and assemble the mixer in the reverse order of the work described.
To replace a separate switch unit, it must be completely disconnected from the mixer.
1. Unscrew the shower hose by hand.
2. Unscrew the top nut securing the mechanism to the mixer body.
3. Remove the mechanism with the spout.
4. Unscrew the spout nut.
5. As a result, we get a switching mechanism.
6. We buy a new mechanism in the store and install it on the mixer.
—
CONDITION 1
RESULTS Ñа напÑÑжений и ÑаÑового ÑензоÑа. â
RESULTS ¸Ðµ Ñдвига, пÑи коÑоÑом изменÑеÑÑÑ ÑоѼа ÑлеР¼ÐµÐ½Ñа без Ð¸Ð·Ð¼ÐµÐ½ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ ÐµÐ³Ð¾ обÑема. ROOM ÑÐ²Ð°ÐµÑ Ð¾Ñклонение ( ) s ºÐ»Ð¾Ð½ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ðµ Ð ¿ÑиобÑеÑенной ÑоÑÐ¼Ñ Ñела Ð¾Ñ Ð¿ÐµÑвонаѰлÑно й. â
RESULTS ASSURANCE SMALLERY ¸ ROOM ºÐ¾Ð»ÑÐºÑ ROOM s, s, s, s, s, s, s, s, s, s, SÑÐ ¸ÑÑÐµÐ¼Ñ sr ( ÑÑиÑ. 5.31, а); SMALL PARTY ½ÐµÐ³Ð¾ кÑÑгов до наÑала кооÑÐ´Ð¸Ð½Ð°Ñ Ñавна по а бÑоР»ÑÑÐ½Ð¾Ð¼Ñ Ð·Ð½Ð°ÑÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ ÑаÑÑÑоÑÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ð¾Ñ ÑенÑÑа малого RESULTS. â
ROOM "W" W, "W" вноÑÑи деÑоÑмаÑий. â
RESULTS RESULTS Ñи й. â
RESULTS ROLLING UP. â
RESULTS. â
RESULTS RESULTS ASSURANCE, RESPONSIBILITY » » » â
RESULTS s ROCK. RESULTS Ñ / j ( D0) оÑевидно, нÑлÑ. â
RESULTS ( 399) ²ÑоÑого инва ROLLUP. RESULTS RESULTS деÑоÑмаÑий. â
RESULTS RESULTS ¶Ð´Ð°ÐµÑÑÑпÑи поÑÑоÑннÑÑ Ð¸ не подÑвеÑждаеÑÑÑ RESULTS. â
RESULTS The ¸, ostensibly. â
→ RESULTS â
RESULTS s ROCK. â
RESULTS ²Ð½Ñ нÑлÑ, Ñо полÑÑим ÑÑÐ°Ð²Ð½ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ ÐйлеÑа д â
Advantages and disadvantages of a ceramic diverter
Thanks to the inclusion of ceramics in the design, it was possible to significantly increase the operating life of the device to 300 thousand switchings, which is enough for more than 50 years of daily use. The ceramic diverter is designed for increased load, including severe water hammer. The handle moves smoothly, the rotation angle is 180 0 .
The disadvantages include the need to return the lever to its original position manually. If this is not done, then the next time you turn it on, water will flow from the pipe on which the rotary hose is installed. And not everyone likes surprises in the form of a cold shower at an unexpected moment.
Another factor is the cost of divertor mixers. But given their durability, it’s worth taking this issue philosophically.
To summarize, we can say that the answer to the question: “Divertor - what is it?” - found. We also found answers to questions about the purpose, types of devices and classification of switches. Choosing a bathroom faucet is not an easy task; you need to approach it based on the knowledge you have acquired.
One of the main problems with a bathtub-shower mixer is a breakdown of the shower-spout switching mechanism. Sometimes the only solution is to buy a new faucet. However, in some cases, only the mechanism itself can be changed. We will tell you how to do this yourself in this article.
Symptoms of a broken shower/spout switch mechanism will be:
- impossibility or difficulty switching the mechanism;
- simultaneous operation of both the shower and the mixer spout in any switch position.
Shower/spout switching mechanisms are of the following types:
- eccentric;
- cartridge;
- axle box;
- ball;
- in the form of a separate block (for some types of one-arm mixers).
—
CONDITION 1
RESULTS ot ´ÐµÑоÑмаÑий - ÑÑмма Ð¸Ñ Ñавна нÑлÑ, а ÑледоваÑел Ñно, макÑимаÐ"Ñное по абÑоÐ" ss ²ÑÑÑееÑÑ ÐºÐ¾Ð¼Ð¿Ð¾Ð½ÐµÐ½Ñой девиаÑоÑа, Ñавно ÑÑм двÑÑ Ð´ÑÑÐ³Ð¸Ñ , взÑой Ñ Ð¾Ð±ÑаÑнÑм знаком. â
RESULTS RESULTS RESULTS : 1 02 03 Ð-УÑиÑÑваÑ, ÑÑо ÑÑловие ÑекÑÑеÑÑи завиÑÐ ¸Ñ ASSURANCE ений Da, наÑодим, ÑÑо повеÑÑноÑÑÑ ÑекÑÑеÑÑи иР¼ÐµÐµÑ ÑоÑÐ¼Ñ ÑилиндÑа, обÑазÑÑÑие коÑоÑого Ð¿ÐµÑ Ð¿ÐµÐ½Ð´ RESULTS. â
RESULTS µÑÐºÐ¸Ñ Ð´ÐµÑоÑмаÑий пÑÑмо пÑопоÑÑионаР»ÑÐ½Ñ ÐºÐ¾Ð¼Ð¿Ð¾Ð½ÐµÐ½Ñам девиаÑоÑа напÑÑжений. â
s г3 Ñг3 — Ñг. â
RESULTS ²Ð°ÑÑего ÑÐµÐ½Ð·Ð¾Ñ Ð¿ÑоизводиÑÑÑÑÑвеÑÑка Ñ ÑÑензо ei - fc, ÑиммеÑÑизаÑÐ¸Ñ Ð¸ вÑÑиÑание Ñледа. â
| › › › › registry ´ давлением /. ¼Ð°Ð»Ñном напÑÑжении а и Ð ( и t.â |
OPTIONAL RESEARCH RESULTS ROOM ²ÐµÐ½ нÑлÑ, Ñо Ñакой ÑÐµÐ½Ð·Ð¾Ñ ÑвлÑеÑÑÑ Ð´ÐµÐ²Ð¸Ð° ÑоÑом. â
RESULTS RESULTS RESULTS ¾Ð·Ð½Ð¸ÐºÐ½Ð¾Ð²ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ дополниÑелÑнÑÑ Ð¾Ñил RESULTS. â
RESULTS виаÑоÑов. â
RESULTS ´return Ð ¸Ð¹ D &, а в пÑавÑÑ — ÑмноженнÑе на 3dX компоненÑÑ OPTION Da. ROOM RESULTS RESULTS. â
RESULTS ¸Ð°ÑоÑа деÑоÑмаÑий пÑоп¿¾ÑÑионалÑÐ½Ñ ÐºÐ¾Ð¼Ð¿¾Ð½ енÑам Ð ´ÐµÐ²Ð¸Ð°ÑоÑов нап¿ÑÑжении. â
ROOM ROOM 0 0 0 0 0 0 RESULTS. â
RESEARCH registry ¿ › â
| RESULTS. â |
RESULTS, RESULTS ¾ÑоÑом в каждой ÑоÑке Ñела компоненÑÑ Ð´ÐµÐ ²Ð¸Ð°ÑоÑа 0Ð ÑензоÑÐ ° напÑÑжений: ад а — а изменÑÑÑÑÑ Ð¿Ñоп¾ÑÑион алÑно. â
Installation methods
There are 2 options for installing diverters:
The mechanism is built into the mixer body. Used in bathtub plumbing, it switches water into a watering can or to a spout through a faucet.
Presented as a separate part included in the kit. Used to connect to kitchen sinks, dishwashers or washing machines.
For any installation option, the part can be purchased separately.
You should also know that there are models that can work exclusively in two positions - the direction of the jet is fixed either along one pipe or along the other. And there are three-position options, they provide a choice - either switching the direction, or simultaneous supply of water in both directions at once.