Definition in psychology
Character (from the ancient Greek word χαρακτήρ - sign, omen, mark) is a combination of human personality traits. These qualities emerge and take shape over the course of life. The concept of “character” implies personal traits that influence the choice of a person’s method of self-expression and his actions. As a result, a specific strategy of behavior in different situations is formed, and a way of life is determined.
The study of human personal qualities is carried out within the framework of characterology and differential psychology. The formation of character is influenced by social conditions and other external and internal factors. It has been noted that people who grew up in the same conditions have similar characters. There are many classifications of character types using different criteria.
How to determine character by clothes
- Impeccably dressed people think through every detail. Always strive for the ideal. At the same time, these are responsible individuals, often arrogant.
- If a person does not change color or style , then this indicates that he prefers stability in areas of life. They plan everything many years in advance. They never get tired of monotony.
- If a person follows fashion , then his life often depends on other people's opinions. Their confidence depends on whether he is dressed fashionably. They are subject to outside influence.
- Creative individuals often change their clothing style. They do not like to push themselves into limits; they are always ready for change.
- Women who dress in sexy clothes have low self-esteem. This is how they establish themselves in society.
Finally: even a little knowledge of what types of character people have will help you get to know yourself and those around you better.
Leading groups
The list of character traits can be continued endlessly: mercy and cruelty, cowardice and courage, tactfulness and tactlessness, lack of initiative and determination, etc. All these qualities are divided into main groups according to a person’s attitude to different aspects of life:
- to yourself;
- to other people;
- to work (activity).
The main features are formed in relationships with other people, that is, during socialization. Also, a person’s character is assessed by the type of temperament, from a biological and personal position. Personal qualities often have a negative or positive connotation. Negative traits include those that interfere with the individual’s normal adaptation in society.
Attitude towards yourself
The most striking negative trait that expresses a person’s attitude towards himself is selfishness. An individual cares only about his own well-being, brings personal experiences to the forefront, without taking into account the feelings of other people. Another negative trait, along with selfishness, is egocentrism (thirst for attention). These qualities are often accompanied by increased self-esteem, resentment and vanity. The opposite negative qualities are shyness, tightness and lack of will.
If we talk about positive traits, then modesty will come first. But this quality must be combined with self-esteem, otherwise there is a risk of it turning into negative similar traits. Modesty is also accompanied by a tendency to self-criticism.
Attitude towards others
Collectivism is a more prominent trait in relation to other people. This is the desire to be part of a team, participation in the life of a particular community, and providing assistance to its members. The personal goals and aspirations of a collectivist are closely related to the team.
Another trait that determines relationships with others is sociability. It can spread widely and manifest itself superficially: a person makes many acquaintances and friends, but has few close friends. Another form of sociability is selective. In this case, the individual realizes his communicative potential with a limited circle of close friends. In contrast to sociability, secrecy, caution, and distrust are manifested. There are other character traits expressed in relation to people - caring, responsiveness, envy, etc.
Attitude to activity
In this category, the first thing to highlight is hard work. A person possessing this trait feels the need for work, regardless of the form of expression. This feeling is associated with responsibility and conscientiousness.
Such a person is disciplined, has high intellectual abilities, plans and thinks about his activities. In contrast to these traits, laziness, fear of difficulties, and negligence may appear.
READ Arrogance: how to recognize vanity and pride
Forming factors
Character is formed from the moment a person is born. At the age of 4-5 years, the basic structure of the personality is already visible. By the age of 10-12, the character is completely established. This process is influenced by factors of heredity, environment and other circumstances of internal and external nature. It happens that these circumstances include the death of a loved one, divorce of parents, family financial situation, etc.
At the initial stage of personality formation, parents play an important role. Their attitude is the basis with which the child will adapt to the outside world. If he was surrounded by attention, love and care, then he will share this with others. The principle also works in reverse.
Physiological
This group of factors includes genetic predisposition and characteristics of human physiology. Of course, many character traits are preserved and transmitted hereditarily. Studies on twins show that genetic information may contain information about certain behavioral traits that are also passed on from parents to children. In addition, behavior is influenced by hormonal changes characteristic of women and men at certain periods of life.
The message of human physiology is that people often have a lot in common in terms of behavior. Thus, most people are characterized by the same adaptation syndrome, which reflects the body’s reaction to an external stress factor.
Social
The next group of factors influencing the formation of human individuality is determined by the environment. Generally speaking, we can directly link the environment and the formation of personality. But the structure of this influence is more complex.
First of all, the individual character of a person is influenced by culture. Behavioral norms are established in the mind. Under the influence of works of art, a person acquires certain ideological attitudes, basic values and religious beliefs.
Character formation largely occurs under the influence of family. Here, specific stereotypes of behavior in various situations are transmitted to the child, life goals and attitudes towards the world around them are developed. Responsibility is fostered.
Some groups and organizations also greatly influence a person's personality. An individual begins to identify himself with a certain community, personify himself with a specific type of personality, try on stereotypes and ready-made patterns of behavior, reactions to external influences. Often such a model can turn out to be toxic, for example - sects, extremist organizations, etc.
In addition, individuality is determined by a person’s life experience and random events. This group of social factors can lead to significant personality changes.
Personal
Individuality also influences formation and helps to develop in the future. This is due to a person’s ability to self-develop. Human character is not only a product of genetics and the opinions of others.
It is worth analyzing someone else’s reaction, but there is no need to elevate a person or his ideas into a cult, since this creates a weak personality and incapable of solving problems.
Character by date of birth
Personality can be determined by date of birth.
Look at the example . Date of birth: 06/15/1986. Now add up all the numbers: 1+5=6, 0+6=6, 1+9+8+6=24. After that, add it this way: 6+6+24=36. Next, get a single-digit number: 3+6=9. Person code is 9.
Characteristics of numbers:
- a confident, bright, strong-willed person who achieves everything in life on his own.
- They are looking for peace in life, they do not strive to occupy leadership positions or start a family.
- people are creative, unpredictable, and can shock with their actions. Popular in bohemian circles.
- Fours are endowed with strong energy. They know how to defend their opinion, they are persistent people, they never give up, they go towards their goal. They know how to make decisions almost without thinking.
- Fives are cheerful optimists. Even if they have a dark streak in life, they do not lose heart and even perceive difficulties as a useful life lesson. They will cheer up any person and make them not give up.
- They take everything to heart and give a strong reaction to any changes in their lives. They are too impressionable, cannot stand loneliness, and often seek support from family or friends.
- Sevens are distinguished by a rich inner world, so they are often considered unusual people. They live in a fantasy world, oblivious to real life. Those who are very fixated on work or everyday hardships cannot be their friends. If they find similar people, then their friendship begins almost instantly.
- stubborn people are not ready to endure what they don’t like. They will only do what they find satisfaction in. They will not waste time on a person for whom they do not feel tender emotions. They are not afraid of change. If they are not satisfied with something in life, they can turn their life around 360 degrees and start all over again.
- Nine, these are real philosophers, can reflect on life for years, being alone, not wanting to solve routine problems. Creativity, science or dangerous, complex professions - this is their purpose.
Extroverts and introverts
The concepts of “extrovert” and “introvert” were introduced into English dictionary publications in 1755. Carl Jung officially introduced the terms “extroversion” and “introversion” into science at the beginning of the 20th century to describe two opposing personality types, distinguished by positive and negative attitudes to the object.
Jung emphasized that every personality has extrovert and introvert traits. The only difference is in the relationship between these qualities—for an extrovert, some are dominant, for an introvert, others are dominant. In other words, extroverts are focused on the world of external objects, and introverts are focused on their subjective inner world.
With this division of people, character traits from the social group are taken into account: sociability, ambition, activity, assertiveness and others.
Introverts are characterized by shy behavior and a search for solitude. They prefer reading books to traditional communication. Introverts behave with restraint and allow few people into their inner circle. At the same time, the person is very devoted in friendship. A representative of this type of personality establishes social contacts slowly, since it is difficult for him to enter into the emotional background of other people that is alien to him. Poorly mastering generally accepted norms of behavior from childhood, he may seem clumsy.
READ Ways to develop charisma in women and men
Another characteristic of introverts is their reluctance to deviate from their own beliefs. They usually have their own internal system of principles, which is of great importance to them. If one of these principles has to be compromised, the introvert becomes very upset and feels bad.
Aggression is unusual for this type of personality. These people are calm, slightly prone to pessimistic thinking, and often gifted in creativity. Strong vivid impressions are not for introverts; they prefer the peace and comfort of their inner world with clearly defined rules.
As for extroverts, they are open, optimistic and sociable people with a disarming straightforwardness. Representatives of this type communicate better verbally, are talkative, charming, persistent and proactive. These individuals prefer bright emotions, adventures (when the success of an action is determined by fractions of seconds) and change. Extroverts are not prone to long discussions and prefer action. They often show a tendency towards aggression and lack of restraint.
Extroverts are easily influenced and spend themselves on the outside world. They willingly do whatever the environment currently requires of them.
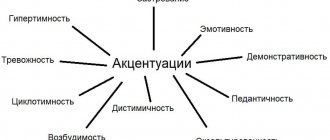
Classification of species with accentuation
If certain character traits are excessively strengthened, they speak of the presence of accentuation. From the standpoint of psychology, this is an extreme case of the norm, which has not yet passed into the pathological stage. But accentuations can be so pronounced that they disharmonize the personality. This leaves a mark on a person’s behavior and actions, as well as in all areas of relationships: to oneself, to the environment, to work.
The prevalence of accentuated behavior is observed in adolescents. With age, people gain the ability to smooth out rough edges and control their emotions. A. E. Lichko and K. Leongard studied accentuations. Each of them introduced their own typology. Below is a combined classification of these authors.
Hyperthymic
These people are active and talkative. At the same time, they prefer to avoid the topic of conversation. They are mobile and sociable, but non-verbal components predominate in communication. Hyperthyms bring anxiety into any environment where they appear and strive to take leadership positions.
Such people have a healthy appetite, sleep and a high level of vitality. They often have inflated self-esteem and do not take their responsibilities seriously enough. Conditions of strict discipline, loneliness and monotonous work activity are endured with great difficulty.
Disthymic
Representatives of this type are overly serious and often have a depressed mood. They act slowly, which is why their volitional efforts are reduced to zero. They are pessimistic about future prospects, have excessive self-criticism and low self-esteem.
They make contacts with difficulty and are silent in communication. Characteristic features of distims: often asthenic physique, lethargy, gloomy appearance, fixation on the dark aspects of life. At the same time, they conscientiously perform any work and have a sense of justice.
Cycloid
The cycloid type of accentuation in its development has 2 phases - hyperthymia (rise in morale) and subdepression (decline). These periods are expressed smoothly and do not last long - 1-2 weeks. This is followed by a long break, when the state of the cycloid is more or less balanced.
Subdepression or recession is accompanied by increased vulnerability and sensitivity to criticism. During this period, the cycloid resembles dysthyma with its pessimism and slowness. There is a tendency to procrastinate and fatigue increases. During the rise or hyperthymia, the cycloid, on the contrary, becomes cheerful, active and sociable.
Due to the existence of such “swings” in life, cycloids do not have constant hobbies and generally give the impression of superficial people.
Excitable
Increased impulsiveness and inability to control one’s urges and desires are characteristic features of the excitable type of accentuation. A person follows his immediate desires, becoming their slave.
READ What is envy, the reasons for its occurrence and ways to get rid of it
When emotionally aroused, it is very difficult to control. A representative of the excitable type easily enters this state and loses control over himself.
Pedantic
In people of this type, repression mechanisms are weakly expressed. They are slow to make a decision. They need to think everything over carefully, and this can take a long time. At this time, pedants analyze all possible ways to solve a specific problem to make sure that the proposed option will be the best.
The serious approach of pedants concerns both work and everyday issues. This is very annoying to others and is perceived as ordinary tediousness. Representatives of the pedantic type are very diligent and scrupulous, bringing every task to its logical conclusion. Prone to perfectionism.
Stuck
Another name for this type of accentuation is affective-stagnant. It is characterized by a long delay of affects (momentary experiences of great strength, often negative). People with this type seem to get stuck on specific thoughts and feelings.
This is especially true for feelings of pride and self-esteem. Typically, “getting stuck” occurs only in situations that directly concern a representative of the type. Injustice, social or in relation to others, is of little interest to them.
Anxious
Representatives of this type always doubt that they are doing or thinking correctly. On this basis, anxiety arises. It manifests itself in suspicious, worried behavior, fear of dangers lurking around the corner. Such people are characterized by timidity; they experience mistakes for a long time and painfully. The fear of repeating a mistake that has already happened once is the source of indecision.
Anxiety clearly manifests itself in childhood: fear of falling asleep in the dark, fear of animals, peers. Having matured, such a child will learn to hide external manifestations, but fear still remains.
Emotive
Deep, vivid feelings and emotions are characteristic of a representative of the emotive type of accentuation. He reacts with all severity to external stimuli - criticism and other triggers. At the same time, he does not express his feelings directly, but keeps them within himself.
Such people greatly experience life's troubles, successes and failures, often breaking into crying and other emotional reactions when it is no longer possible to keep what they have accumulated inside. These breakdowns are the reason why the type is also called “whiny.” At the same time, emotives are distinguished by their compassion and empathy.
Character traits
Stable properties of the psyche - “paths trodden by neurons” - these are character traits. They appear with enviable consistency and allow us to make predictions in human behavior. So, knowing the stinginess of an employee, it is not difficult to assume that he will not borrow money before payday. And the one who is now whispering another gossip in your ear will tomorrow say nasty things about you. However, not all shades of a person’s behavior are important or fateful for her.
Dominant traits
American psychologist Gordon Allport grouped character traits into three categories:
Dominant - determine the core of personality, are found in systemic relationships with the world: egoism - altruism
Ordinary - manifested in everyday life: honesty - duplicity
Secondary - manifested in various areas of activity: diligence, obedience, love of reading
Priority character traits are especially clearly manifested in critical situations, when there is no time to think, a person acts “automatically”. For example, in ordinary situations, all people prefer to put on a mask of modesty; some sincerely consider themselves to be so. But when they praise others, they suddenly lose their temper, begin to list their merits and achievements, and reveal deeply hidden vanity.
Mental sphere of character manifestation
The second way to classify characteristic personality traits is by the manifestation of stable mental properties.
Intellectual traits - curiosity, resourcefulness, frivolity, absent-mindedness Emotional traits - cheerfulness, sentimentality, gloominess, dispassion Volitional qualities - perseverance, courage, cowardice, humility Moral traits - justice, responsiveness, callousness, cruelty
Read also: How to develop a strong character
Positive qualities are formed only if a person is interested in acquiring them. It is impossible to impose intellectual properties by force. All character traits associated with a person’s mental properties are the result of his free choice in childhood and adolescence.
Systemic character traits
The core qualities of a person determine her relationship with the world and leave a mark on her behavior.
In relation to oneself, the dominant manifestations are pride on one pole and the opposite quality - humility. When characterizing connections with other people, one must pay attention to communication or isolation, altruism or selfishness. In relation to work - the main qualities are hard work or laziness. Connection with objects of the surrounding world is manifested in such traits as frugality and neatness or sloppiness and wastefulness
It is also difficult to create a clear portrait of a person in accordance with his character because the true motives of actions are not always clear. Fighters for justice, flaunting their integrity, may well turn out to be elementary envious people, indifferent to everything except their own benefit. And closed silent people will discover courage and resourcefulness in the moment of decisive action. The French writer V. Hugo said about this:
Every person has three characters: one attributed to him by his neighbors; the second - he attributes it to himself; and finally, the third, which actually exists
The relationship between character and temperament
The concepts are often confused, presenting character and temperament as synonyms. But in reality these terms are completely different. Nevertheless, they describe 4 active points of view, one of which still proclaims the equality of these concepts:
- The terms are equivalent.
- Temperament is the inner part of character, its core.
- The connection between temperament and character is of an antonymous nature.
- The natural basis of character is his temperament.
It is worth noting that temperament is a more physiological concept, related to the characteristics of the human nervous system directly or indirectly. Hippocrates spoke of temperament as a characteristic behavior that is determined by the predominance of one of the liquids called “vital juices.” So, if lymph predominates, then the person is phlegmatic (calm), yellow bile is choleric (explosive), blood is sanguine (joyful), black bile is melancholic (prone to sadness). After the introduction of this assumption, the concept of “temperament” (Latin “mixture”, “fusion”) was established.
At the same time, the formation of character is influenced by society and family upbringing. Character, including its accentuations, can be adjusted throughout life. Temperament is a property acquired from birth and unchanged throughout life. But their mutual dependence is not denied.
Character is a complex and multifaceted trait. It is like a boulder on the seashore, which is ground by the waves of the sea called Life. It can be changed, unlike temperament, but this will require intensive work on yourself. There are several classifications, a review of which allows us to obtain a more complete picture of information about this mysterious human trait.