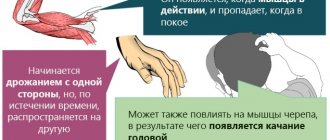
Types of locus of control:
A person’s tendency to believe that his life, actions and decisions are primarily influenced by external factors, which are also the reasons for the results achieved (success or failure) - this is an external locus of control
or
externality
.
The ability to evaluate the causes of the consequences of decisions made and the current life situation based on internal factors (efforts, knowledge, skills and experience, one’s own qualities and characteristics, and so on) is the internal locus of control.
or
internality
.
Emotional eating behavior
The most important and interesting type. It occurs very often.
If the number is much higher, then this indicates that it is difficult for us to control our appetite and there is a desire to eat delicious food when we are in the rage of our passions.
- Work with emotions . It’s simple to say, just 2 words “Work with emotions”, but in practice it’s extremely difficult to do. There are nations that express their feelings very violently, Italians for example. And we Russians are not the most emotionally open people. But when we don’t understand what we feel, then we don’t know how to safely get out of this state. The easiest way is to stupidly “eat!” We are not used to working with our feelings; we were not taught this since childhood. We often have this condition in our tongue: “You give me a headache. I'm already sick of you. Or, I’m just sick of this situation.” It turns out that we get worked up and relieve stress by overeating.
- Create rewards for yourself . For example: going to the Spa, reading an interesting book, meeting loved ones, going on a trip for 1 day. What are our traditions? We did something, so let’s go and celebrate? How do we celebrate, should we go to the pool with our girlfriends or something?
- Avoid unhealthy, high-calorie foods . We still want something tasty, right? Eat more fruits!
- Pay attention to sleep and relaxation . Without proper attention to the cycles: tense-relaxed, you will not be able to be in psychological balance. When we are just going uphill, going uphill all the time is chronic stress, which exhausts us incredibly. If we don’t relax in time and don’t know how to get out of this state correctly, there’s nothing left but to eat.
- Play sports . It helps cope well with stress and improves the sensitivity of our cells to the necessary hormones.
External and internal personality types:
As a rule, externalities
– these are people prone to an external locus of control; they are more aggressive, anxious, lack confidence in their abilities and are afraid to take responsibility, trying to postpone completing tasks. Their constant companion is the idea that absolutely nothing depends on them and they obediently go with the flow.
Internals
– individuals with an internal locus of control are characterized by balance, a tendency to introspection, knowledge of their positive and negative traits, and a persistent desire to achieve their goals. They believe that they are able to influence the situation and change it in their interests.
Let's simulate the situation: Business negotiations were unsuccessful, the deal was not concluded.
- The external personality type is not able to admit the presence of his guilt and will try to explain the failure by the influence of external factors:
. ”
- The internal type of personality will not look for excuses and will turn to searching for internal reasons: “I didn’t have enough strength of character to insist on my own, I wasn’t convincing enough, I couldn’t properly prepare for the meeting
.
Internals or externalities in their pure form practically do not exist; any person combines a share of self-confidence and his talents, and a share of psychological dependence on external factors, their ratio is approximately 50/50.
Restrictive eating behavior
It shows how we control the amount of food we eat. Constantly thinking about how not to eat too much or not what we need, we drive ourselves down. Because it is very difficult to stay in such a tough regime for a long time. Is it true? And there is always one way out: breakdown, overeating, weight gain.
If, on the contrary, the number is extremely low, this indicates that we have poor control over ourselves.
We want to see something pleasant on the scales tomorrow, right? Here it is important not to rush, to calculate the time until victory. Determine how much excess weight there is, make a plan for several months, what number we are going to in 1, 3, 6, 12 months. So that there is adequate expectation.
Practical benefits:
Knowing your locus of control can give you a very effective tool for improvement, self-analysis, understanding your strengths and weaknesses, changing your attitude towards what is happening to you - a powerful impetus for personal growth and development.
Sometimes a superficial analysis is enough; probably, while you were reading this article, you were able to notice similarities with one of the personality types.
The predominance of external traits indicates the need to learn to take responsibility for what is happening, to be more proactive, and to see one’s contribution in addition to external influences.
People inclined to internality should strive to understand that it is impossible to keep absolutely everything under control, especially since not everyone needs this control, no one is able to know and be able to do everything.
Achieving a balance of these traits is the key to harmonious personal development.
Communication and social cognition
10.1. Concept of communication
It is known that the most difficult concepts to define are those that are widely used. This is exactly what happens with the concept of “communication”.
There is still debate on the definition of this concept in the pages of Russian psychological literature. If we talk about the problem of communication in general, then we should, first of all, emphasize its specificity in domestic social psychology. This term “communication” does not have an exact analogue in traditional (Western) social psychology and, as G.M. notes. Andreeva, “its content can only be considered in the conceptual dictionary of a special psychological theory, namely the theory of activity” (Andreeva, 1976, p. 76).
Therefore, in the domestic literature there are such terminological expressions as “communication activity” or “communicative activity”. However, controversy is possible here too, since sometimes communication is defined not only as an activity, but as a condition of activity or an aspect of it.
Communication is a necessary condition for any joint activity and is the process of establishing and developing contact between people, the exchange of information, the participants’ perception of each other and their interaction. A similar approach to understanding communication and its structure was first formulated by B.D. Parygin in the early 1970s. He identified “several basic parameters” of the communication process: a) mental contact that arises between individuals and is realized in the process of their mutual perception of each other; b) exchange of information through verbal or non-verbal communication; c) interaction and mutual influence on each other (Parygin, 1971, p. 221).
In accordance with this approach, it has become generally accepted in Russian social psychology to distinguish three sides in the structure of communication: communicative, perceptual and interactive. True, today, Parygin notes, this approach “needs to be supplemented with new components when characterizing the structure of communication” (Parygin, 1999, p. 342).
Communication research has a long tradition in Russian psychology. I.M. spoke about the importance of this issue for the study of moral feelings. Sechenov. V.M. was the first to conduct experiments to study some aspects of communication. Bekhterev. Contributed to the development of communication problems A.F. Lazursky, L.S. Vygotsky, V.N. Myasishchev. Considering the question of the psychological structure of a person as a subject of activity (i.e., producing material and spiritual values), B.G. Ananyev emphasized the role of communication. He noted that communication is the most important activity that arose on the basis of labor and in the process of socio-historical development became an independent type of activity.
Currently, communication problems are the focus of attention of many domestic psychologists. Communication in ontogenesis is considered as one of the factors in the mental development of the individual, the connection between the need for communication and other human needs, the importance of communication for the regulation of individual behavior, the relationship between communication and the emotional sphere of the individual, features of mental processes in conditions of communication, etc.
Since the subject of communication is a person, it is very important to determine his functions in the communication process.
V.N. Panferov, who is engaged in the development of this issue both at the theoretical and empirical level, identifies the following six functions of a person as a subject of communication (Panferov, 1987):
- Communication functions. In the process of communication, through these functions, the interaction of people is carried out at the levels of individual, group and social interaction. This relationship is achieved through speech and other natural expressive means of man (facial expressions, pantomime, gestures, voice, objective human actions), as well as technical means (writing, printing, telegraph, radio, television, etc.). Communication functions also serve the purposes of social integration of people into various forms of communities.
- Information functions. In the process of communication, the content of people's practical experience accumulates and information is transferred from one person to another. The information function here is carried out in unity with the communicative one. According to the purpose of the message, information can be divided in the most general form into informational, regulatory and emotional. If only information about an object is transmitted, then the information has an informational purpose. If a message is designed to encourage a person to take a specific action, then this information acquires a regulatory burden. If the information is aimed at awakening any feelings, then it acquires an emotional character.
- Cognitive functions. In the process of communication, perceived meanings are comprehended through representation, imagination and thinking. Cognitive functions are manifested in the processes of human cognition by a person. These functions are realized more fully with mutual understanding between the participants in communication. In general, the relationships that arise between them depend on the content of people’s mutual interpretation. This is how the cognitive functions of communication are connected with the emotional ones.
- Emotive functions. They manifest themselves in a person’s experience of his relationships with other people. These experiences find secondary expression in various types of relationships (sympathy - antipathy, love - hate, friendship - enmity, etc.). Emotionally rich relationships determine the psychological background of interaction, bring joy or sorrow, and are for many the highest value, purpose and meaning of life.
- Conative functions. They provide a controlling influence on the individual in all life processes, are associated with a person’s desire for certain values, express his motivational forces, regulating the behavior of partners in joint activities through the process of communication. Through the exchange of thoughts and feelings, the interaction of communication partners is coordinated.
- Creative features. Aimed at transforming people in communication processes, changing and educating personality. This is achieved through special mechanisms of mental activity that promote mutual influence between partners. These include: imitation, emotional contagion, suggestion, persuasion. Thanks to these mechanisms, changes occur in attitudes, behavior and personality traits.
Proposed by V.N. Panferov’s classification of human functions as a subject of communication allows for a generalization of various phenomena of the human psyche, based on the logic of their functioning in the process of communication.
External type of behavior
Quite a common type.
We are more inclined to overeat when we are not alone, when there is a lot of delicious food, the table is beautifully set, there is a smell of fresh baked goods, everyone is in high spirits and eats appetizingly. How to prepare here?
- Find out these situations for yourself in order to understand where is my weak point? “When I am invited to a party where there will be a feast, then I will not be hungry, I will have a hearty breakfast. If guests come to me, I set the table so that it has everything necessary, healthy and tasty: a lot of fresh salad, fruit, if there is meat or fish, then without frying. From alcohol, I will supply not only strong drinks, but also dry wines.”
- Not only sit at the table, but also spend active time. Dance, play games, have fun, tell the latest news interestingly.