From the outside, the person does not look quite ordinary, since he is detached from everything that is happening around him. Restrained behavior, phrases in fragments and conversations in which a person does not even look into the eyes of the interlocutor, but as if he is talking to someone else. Expansive schizoid accentuation is a kind of shell, a spacesuit that helps a person live in some kind of world of his own, detached from reality. Is this a pathology or just a manifestation of character?
Personality disorder or character?
The man behaves very reservedly. And the spoken speech seems to have been memorized in advance. An insensitive attitude towards anything and isolation, secrecy from everything that happens around.
This human behavior is called schizoid character accentuation. And this does not always mean a pathological condition. This is, in a way, a manifestation of extraordinary personality traits, which usually manifest themselves in certain, rather specific conditions and situations.
The very concept of accentuation among specialists is used to designate some special, pronounced personality traits that accompany a person throughout his entire life journey. And this kind of personality manifestation is within the clinical norm. There is just one serious nuance here. Under certain conditions, usually not favorable, these personality traits can go beyond this limit of norms and become a pathological condition.
The schizoid character type, like any other accentuation, is not a mental disorder, but a problem associated with certain difficulties in maintaining a normal lifestyle.
But this line between normality and pathology is quite thin, and it can break at any moment. Thus, if there are schizoid traits in a person’s personality, it is possible that a schizoid disorder will develop, which is already a mental illness.
So where is this fine line? The first thing that distinguishes an accentuated character from a real personality disorder is that with psychopathy a person begins to actively and very unconventionally express himself in any area of life, and not in any particular situation. Also, for a schizoid type of character, it is quite normal for a bright manifestation to occur at a certain period of life, for example, in adolescence, after which the sharp features of such a personal character gradually begin to smooth out.
If there is a mental disorder, then these traits will constantly manifest themselves, at any age, in any situation and under any conditions. Moreover, they can even intensify over the course of life. In this regard, people diagnosed with schizoid psychopathy are simply not able to adapt normally to society.
Description of the disorder
The clinical picture of schizoid disorder is varied and covers all mental spheres of the individual. The pathology is based on a tendency to social isolation and emotional callousness.
Socialization
Schizoids are solitary people. They prefer to spend time with themselves: reading books, walking in parks, enjoying nature, studying philosophy, writing fiction. They prefer a solitary way of working, where there is no need to contact people. It is rare to find schizoids among waiters, call center operators or baristas.
They find it difficult to communicate with people. Small talk is disgusting. They do not understand social norms and accepted rituals. The generally accepted path “school–university–family and work–old age in retirement” is not typical for them. They rarely start romantic relationships and avoid starting a family.
Schizoids often ignore social norms. Their behavior is determined by internal norms, not external ones. They don't wear fashionable clothes and sometimes dress strangely.
People with the disease have few friends. Over the course of their lives, they develop 3-4 close friendships. Superficial social contact is maintained with other people. However, some schizoids experience the symptom of “autism in reverse,” when they have many friends and acquaintances with whom they maintain light and shallow contact.
More often than not, the social life of these people is measured and quiet. They are not characterized by sudden trips to other countries, visiting nightclubs and wild parties with dozens of new acquaintances. People prefer to spend time alone.
High-functioning schizoids temporarily activate psychological forces and mimic a “normal” member of society: they communicate with new people, laugh at stupid jokes, talk about the weather. But this is temporary. This condition requires excessive effort from schizoids, after which they return home and exhale with ease. “Finally, this horror is over,” the schizoid thinks.
Often these people understand that they are different from the masses. They accept their individuality and try to use it for the benefit of themselves and society. Schizoids do not fit into socially accepted frameworks, and therefore often succumb to persecution from school. Their way of thinking and worldview is little understood by others. They are not accepted into groups and societies. Because of such non-acceptance, schizoids close themselves off even more.
Preferences
People with the disease have specific hobbies, often covering abstract areas: science, literature, research. Often people with the disease are not so much creators as historians and critics.
Inner world
Closed from others. The inner world is full of fantasies. The content of fantasies is predominantly those where the schizoid plays a decisive role: he saves the world, invents a cure, makes a brilliant film or writes books that change the consciousness of modern society. In fantasies, they compensate for their own shortcomings and punish offenders.
The inner world is rich and detailed. No other psychotype can boast of such a developed inner world. Schizoids invent dialogues that never happen; build situations that will never happen.
When a schizoid feels that someone is invading his personal space, for example, asking questions about feelings, experiences, interests, defense mechanisms are activated. He can leave the outside world for the inside - this is escapism. Or turn on aggression, which will scare the interlocutor away from asking questions on personal topics.
Emotions
Closed and unexpressive to others. Schizoids find it extremely difficult to share emotions and feelings with others. They try to avoid situations that are followed by violent emotions.
Outwardly, emotions are rarely displayed on the face of a schizoid. They are not expressed in intonation and gestures. However, at the same time, emotions overwhelm them. Inside, these people are extremely sensitive and easily vulnerable, but life has taught them to mask their emotions: any invasion of personal space causes emotional pain and discomfort.
Schizoids do not know how to feel other people. Their empathy is poorly developed. They cannot talk about their feelings.
Other people have a hard time with schizoids. They do not reflect emotions, poorly support a dialogue that is not interesting to them, often argue, resist, and rarely change their minds.
Behavior
Schizoids are eccentric. Often behavioral acts do not correspond to the situation and are not understood by the environment. People speak of schizoids as “strange”, “loners”, “eccentrics”, “abnormal”, “not of this world”, “he seems to be from another planet”. They easily ask unpleasant questions to their interlocutor, without seeing any awkwardness in it.
Main features of schizoid accentuation
The first and main sign that distinguishes such people from everyone else is the lack of desire and ability to communicate with people around them. Moreover, this happens not because a person with schizoid accentuation cannot do this, but because he simply does not want it. That is, the need for any communication is completely absent. Instead, they prefer to be alone with themselves, to withdraw into themselves, in search of some answers to inexplicable questions. And such a life suits them completely.
Appearance and behavior
Outwardly, a person with schizoid accentuation is also quite easy to identify. They usually have a cold attitude towards fashion. In terms of clothing style, they try to dress differently from everyone else, using very unusual combinations of clothing. Usually their appearance is absolutely not harmonious and paradoxical, and their facial expressions and body movements seem to be feigned and not real.
In terms of behavior, schizoids are very unnatural; visually they look sketchy, and they have no emotions at all. They are quite easy to spot among other people, since they seem to be aloof from everyone. They try to maintain a wall between the outside world and their own, inner world.
Schizoid accentuation in children
Unlike other accentuations, schizoid symptoms appear quite early, and from the very first years, a child can show them. For example, he may try to be alone in games; other children will not attract or interest him; instead of noisy games and companies, he will give preference to quiet and calm activities.
In this case, children usually try to avoid communicating with peers, and being in the company of the older generation will be more pleasant and interesting for them. Moreover, in such a society, schizoid children do not attract the attention of adults in any way; rather, on the contrary, they behave as calmly and quietly as possible, carefully listening to the conversations of adults, and thinking about these words as much as possible.
What is sex for: the physiological and psychological role of intimacy in a person’s lifeRead more
In childhood, schizoids may not show their emotions in any way; sometimes it seems that the child simply does not experience any feelings even for those whom he really loves (parents, for example). Instead of emotionality, schizoids exhibit a high level of intelligence. Such a child may not be at all interested in children's games and toys. But he will be interested in exact sciences, he will have many philosophical and abstract questions.
One of the reasons for the development of schizoid character traits in children is the lack of warmth and tenderness of the mother in the first months of the baby’s life. When a mother cannot accept him for who he is in the first months, feel and give him her love and attention, which, unfortunately, happens very often.
Another reason for schizoid accentuation since childhood is the presence of contradictions, when, for example, in a family there are double messages when communicating with loved ones. For example, “come here and stay here.” Or when words and actions do not coincide with each other.
Expansiveness Expansive
[Urmanov] was expansive, like a southerner. At meetings he flared up like
gunpowder, and quickly suggested the most extreme measures. And it cooled down just as easily.
Korolenko, On both sides
Expansiveness as a personality quality is a tendency to be unrestrained, impetuous, and ardent in the manifestation of feelings and expression of thoughts; make decisions and act in an excited, excited state; not being able to control oneself.
Once upon a time there lived a hot-tempered and expansive young man. And then one day his father gave him a bag of nails and punished him to drive one nail into the fence post every time he could not control his anger. On the first day there were several dozen nails in the pillar. The next week he learned to control his anger, and every day the number of nails hammered into the pillar began to decrease. The young man realized that it was easier to control his temperament than to drive nails. Finally the day came when he never lost his temper. He told his father about this and he said that this time every day, when his son manages to restrain himself, he can pull a nail out of the pillar. Time passed, and the day came when he could inform his father that there was not a single nail left in the pillar. Then the father took his son by the hand and led him to the fence: “You did a good job, but do you see how many holes there are in the post?” He will never be the same again. When you say something evil to a person, he is left with the same scar as these holes. And no matter how many times you apologize after this, the scar will remain.
Expansiveness is a tendency to violent outbursts of expression of feelings. Expansiveness is a passionate striptease of frankness. It's a parade of imbalance. An expansive person, due to his imbalance, is not able to have peace of mind and is inclined to react excessively strongly, inappropriately to the current situation, to the circumstances of life. He perceives every word or action of an imaginary rival as unreasonable, offensive, and mocking. Therefore, he immediately takes an attacking position. He does not want to listen to or accept other opinions and points of view, because he considers his position to be the absolute truth. The slightest objections from the opponent are taken as a challenge, as a manifestation of hostility. Hence the short temper, irritability and lack of restraint. Psychologist Ershov writes: “The expansive person adheres to extremes: at the slightest provocation, he is ready to count his partner both among his closest friends and among his worst enemies; in the balance of forces, he is inclined to consider himself either a complete insignificance, or the owner of undeniable power. This attraction to extremes also affects the exchange of information. An expansive person, in contrast to a balanced person, is either extremely stingy or extremely wasteful.”
According to Pushkin scholars, the clash with Dantes was at least the twenty-first challenge to a duel in the poet’s biography. He was the initiator of fifteen duels, of which four took place, the rest did not take place due to the reconciliation of the parties, mainly through the efforts of Pushkin’s friends; in six cases the challenge to a duel came not from Pushkin, but from his opponents. Pushkin's first duel took place at the Lyceum.
The expansive Pushkin was very fond of his lyceum friend Kuchelbecker, but often played pranks on him. Kuchelbecker often visited the poet Zhukovsky, pestering him with his poems. Once Zhukovsky was invited to some kind of friendly dinner and did not come. Then they asked him why he was not there, the poet replied: “I had upset my stomach the day before, and besides, Kuchelbecker came, and I stayed at home...” Pushkin, having heard this, wrote an epigram:
I overate at dinner
Yes, Yakov locked the door by mistake
- So it was for me, my friends,
Both Kuchelbecker and sickening...
Kuchelbecker was furious and demanded a duel! The duel took place. Both fired. But the pistols were loaded... with cranberries, and, of course, the fight ended peacefully.
An expansive person is hot, that is, he is inclined to perceive life situations vividly and keenly, and to react with ardor to opponents - irritants..
There is such an interesting fact from the life of Pushkin. Several young people wanted to make fun of him, to make him laugh, and then, when the last one entered the hall where the jokers were already present, one of them shouted loudly so that everyone could hear: “I give the poet a donkey’s head.” - And you yourself will stay with which one? - Pushkin immediately retorted. “And I’ll stay with mine...” the joker said in confusion. “So you gave it now,” the poet concluded.
An expansive person is quick-tempered, that is, prone to inadequate, excessive reactions - emotional incontinence, explosive irritability to ordinary stimuli, predisposed to anger.
Pushkin was not an evil person by nature, but very expansive. He suddenly, for no apparent reason, began to show absurd, annoying bullying. He often behaved defiantly. The former police had special lists that included people who were not entirely convenient for public peace. The name of Alexander Pushkin was on these lists. And he was by no means accused of freethinking and other high matters here - he was in one of the honorable places on these lists as a card punter and duelist.
Psychologist Ruslan Narushevich believes that at some point an expansive person may focus too much on his point of view, on his decisions, desires, considering them the only correct and acceptable for others, which, of course, will not always be the correct perception of the situation and from -for this, a person can show an excessive, expansive nature. That is, a person can impose his desires, his assessments on others in a rather assertive, aggressive form, completely disregarding their opinions.
Expansiveness is a pure child, vigorously expressing its feelings. In a very cramped orchestra pit, an overly expansive conductor risks piercing the eye of the first violin. F.M. Dostoevsky wrote about one of his heroes: “He was, indeed, a child of forty years old, expansive to the highest degree, always cheerful, who considered all people to be angels.”
An expansive person is characterized by intemperance, that is, a tendency to not properly control his thoughts, words, emotions and actions. He has great problems with self-control, because he is unable to maintain inner calm and act rationally and carefully in difficult life situations. An expansive personality is characterized by impulsiveness (the tendency to act spontaneously, on the first impulse under the influence of external circumstances or emotions) and ardor (the ability to quickly get carried away, be imbued with passion, be ignited by the fire of love, suffer, experience something with heat, fervor).
Petr Kovalev 2020 Other articles by the author: https://www.podskazki.info/karta-statej/
Schizoid character traits in adolescents
Schizoid accentuation manifests itself at its worst during puberty, and it is during adolescence that it brings many problems. At this age, the child’s communication with other peers and teenagers is very important. And it is quite difficult for schizoids to find that same contact with society and the world around them in general.
The main value of such teenagers lies in their own uniqueness, and their biggest fear is the possibility of losing themselves in such a big world. In their hearts, such children want to be in society and want to be accepted by them, but despite this desire, schizoids do not leave their protective shell so as not to stumble again.
As a result, such a lifestyle without any communication begins to become a habit that burdens the teenager. This leads to the fact that the child simply chooses between communication and a possible mistake, non-acceptance of society, his unique individuality.
Schizoids are never distinguished by a large number of friends, and those friends whom he managed to find must respect the personal space of the schizoid. Otherwise, he leaves his social circle. Difficulties also develop when communicating with members of the opposite sex.
Interesting fact:
Schizoids often avoid physical contact, especially with the opposite sex, and may not tolerate loud and harsh sounds and smells.
Therefore, when communicating with a schizoid teenager, it is important to take into account his individuality, trying to understand this approach, principles and aspirations. It is important to support the desire to develop in a creative direction and respect the personal space of such a teenager.
Features of schizoid character in adolescence
Schizoid accentuation causes a person the greatest number of problems during adolescence. During this period, the need to belong to a group and communicate with other teenagers is of great importance, and the most difficult thing for a schizoid child to achieve is contact with the outside world. The main value for him is his own uniqueness, his greatest fear is to get lost in the outside world. In his heart, such a teenager really wants to be accepted by society and at the same time is most afraid of breaking out of his shell. The loneliness he is so familiar and still so beloved begins to weigh on him, the established picture of the world is collapsing. It is difficult for him to give up his uniqueness, to begin to imitate others in order to be accepted by the environment. A schizoid teenager never has many friends, and he is only friends with those who are able to respect his personal space. Difficulties also arise when contacting the opposite sex, since the schizoid tries to avoid physical contact; he also does not tolerate sharp sounds and smells. In relationships with such a teenager, it is important to take into account his uniqueness, try to understand his aspirations and motives, support his desire for creativity, respect his individuality and right to personal space.
Schizoid personality disorder
However, everything has its own limits, including in the case of schizoid accentuation, which can manifest itself both within the norms and can reach a severe form of a pathology such as schizophrenia.
What can lead to the development of schizoid personality disorder:
- psychological trauma, especially in childhood;
- crisis periods in life;
- absence or lack of emotional contact and warmth from the mother at an early age;
- prolonged and frequent stressful situations;
- hereditary predisposition;
- violation of compensatory processes of schizoid character accentuation.
In cases where schizoid disorders are severe, a person is practically unable to accept the world as it is, he cannot love himself, and then there is no point in talking about the people around him.
Causes
The causes of this personality disorder are biological and social:
- Biological. There is an assumption that parents with mental disorders, in particular schizophrenia, increase the risk of having a child who will develop schizoid personality disorder. The likelihood also increases if the parents themselves were schizoid. Some psychologists argue that the fact that a child is unwanted provokes schizoid personality disorder. Biological factors include: features of intrauterine brain formation, bad habits of the mother, the influence of the environmental environment on the health of the fetus. The characteristics of infancy testify in favor of the biological theory. From an early age, schizoids grow up to be extremely sensitive: they are disturbed by loud sounds and bright lights, and close contacts with their mother. They cry when they are picked up; they don’t like to be “squeezed” and cherished.
- Socio-psychological. The likelihood of developing pathology increases if the mother raised the child in an overprotective manner. The mother invades personal space, which is why the child closes down, tries to isolate himself from the outside world and withdraw into himself. Presumably, the disorder also develops due to a lack of parental care. From infancy, children feel that they are neglected, that they are not wanted, that their parents are not interested in them. They realize early that they are alone and no one needs them in this world. “So,” the schizoid thinks, “I don’t need anyone either.”
When a small child realizes that he is ballast for his parents, he is overwhelmed by many emotions. At 2-3 years old, these emotions are not understandable to a child. These are unbearable feelings associated with rejection from parents. The child cannot tolerate them - he blocks emotions. In the future, intellectualization develops - a mechanism of psychological defense. That is, instead of feeling an emotion, a person mentally explains his feelings to himself.
Blocking emotions subsequently gives rise to the clinical picture of schizoid personality disorder.
Diagnostics
Schizoid accentuation of an obvious degree is a rather rare phenomenon, but the presence of certain schizoid traits that are simply observed along with another personality type is a more real and frequently encountered picture.
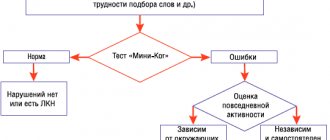
According to statistics, men with schizoid accentuation are much more common than representatives of the fairer sex. To identify this type of personality, you need to be diagnosed by a psychotherapist. To detect schizoid accentuation, specialists use the Lichko questionnaire and the following diagnostic criteria:
- lack of trust in people;
- disregard for established social norms;
- desire to be alone in any kind of activity;
- lack of interest or minimal interest in members of the opposite sex;
- lack of reaction or reduced reaction to praise or, conversely, criticism;
- lack of emotionality and vivid feelings, even in emotional situations (wedding, funeral, etc.);
- coldness and emotional detachment;
- lack or decrease in the ability to enjoy something.
If three or more of the signs listed above are present, along with other symptoms of a personality disorder, a diagnosis of schizoid psychopathy is usually made.
How to distinguish a schizoid externally?
First of all, take a closer look at the person’s manners, movements, behavior and appearance. Typically, people with mental disabilities do not follow fashion, and they have no sense of style at all. Therefore, he may be dressed awkwardly, while the elements of his wardrobe will absolutely not be combined with each other. Clothes can be quite strange, untidy, and inharmonious.
In addition to the wardrobe, schizoids are also identified by their movements, which are usually quite unnatural, illogical, and may be completely incomprehensible to a normal person. The facial expressions and actions of such a person are not endowed with emotions, so one gets the impression that there is some kind of invisible barrier between the person and society.
People with schizoid accentuation are quite educated and intelligent, and most of them are very talented and very creative individuals. Schizoids are very often found among scientists, programmers, philosophers; they can withdraw into themselves while reading a book or some article. At the same time, reading will be in first place for them, and communication will be somewhere in the very last place.
Difficulties that await schizoids in reality
In the first place for people with schizoid accentuation is their own independence and independence. They prefer activities in which they can be alone with themselves. This could be reading, studying something, some kind of individual sport, programming, and so on. And they keep their preferences and interests for themselves, without disclosing them even to close people.
As a result of this behavior, schizoids usually have virtually no relatives, friends, and often have problems creating a family and with the opposite sex. Due to high self-esteem and self-love, a person simply cannot realistically and correctly assess the situation.
Schizoids are afraid that someone can destroy their inner world, so they are always on the alert. Suspicion, aggression, anxiety and irritability are the main signs that distinguish a schizoid. Such behavior creates an even greater barrier between the world and society.
But even if a schizoid truly wants to be closer to someone, wants to make a family and friends, he cannot do this on a subconscious level, since he avoids such a life for fear of being rejected by society. People with schizoid accentuation live not by emotions and feelings, but by fantasies, and the best defense for them is the absence of any emotions. Therefore, the main problem, which in this case is not so easy to solve, is loneliness.
What difficulties do schizoid people face in life?
People with schizoid accentuation of character greatly value their independence and independence, prefer hobbies that involve solitude, for example, collecting, reading, studying narrow areas of knowledge, individual sports. Among other things, they are not inclined to share their interests and preferences with other people. This leads to the fact that it is difficult for such a person to make friends and close relationships with the opposite sex. Inflated self-esteem and belief in one’s own exclusivity leads to a misunderstanding of the situation when others do not recognize the special talents and uniqueness of a schizoid. Since people with this type of accentuation are most afraid of intrusion into their inner world, they become suspicious, aggressive, show anxiety and irritability, which further interferes with establishing relationships with people. Desiring intimacy with all his soul, the schizoid avoids it, is afraid of attachments, because he fears being rejected. Such people live not by feelings, but by fantasies. Avoiding emotions is their natural defense mechanism. The main problem of such people can be called loneliness.
Treatment of schizoid psychopathy
Another serious problem of schizoid psychopathy is the lack of ability to somehow cure this pathology. It just so happens that personality and character traits haunt a person throughout his life. Therefore, the main therapy is usually aimed at improving the process of social adaptation. Psychologists and psychiatrists must help a person with schizoid psychopathy understand what emotions are, and must help them learn to cope with these emotions and not be afraid of them.
Treatment with drugs will not give any result, so the main emphasis should be on various methods of psychotherapy. Thus, cognitive therapy techniques will help in understanding one’s own emotions and will help a person learn to enjoy different events or what a person is doing.
To improve the social skills of a schizoid, it is better to refer him to group treatment, since it is in society that more gentle stimulation for communication occurs, while maintaining safe conditions that will not cause other psychological trauma.
In childhood and adolescence, it is important to provide support so that the child can adapt more easily and painlessly to the team; sometimes help is needed in finding a profession.
If schizoid psychopathy is of a moderate degree, and parents and specialists have provided comfortable conditions for the development and growth of the child and helped to choose the right type of activity, then there will be a favorable prognosis in the future. Such patients adapt more easily to society, work calmly surrounded by other people, and have close people and friends, albeit in small numbers.
Treatment methods
To treat borderline conditions, antidepressants and antipsychotics are used, as well as drugs with nootropic effects and vitamin complexes. The doctor selects the type of drugs, dosage, and duration of therapy. Non-drug treatments include:
- Diet food.
- Sleep deprivation (limitation of duration).
- Water procedures (contrast shower, water hardening).
- Lateral therapy (zonal-lateral electrical stimulation - directed change, modulation of interaction between the hemispheres of the brain).
- Physiotherapy.
- Physiotherapy, reflexology.
- Psychotherapy.
Treatment is indicated if people of the schizoid type experience difficulties in social adaptation that interfere with professional activities and personal life. In most cases, no correction is required. In order to communicate meaningfully and live comfortably next to such people, you need to be able to find an approach to them.