Postpartum depression is a mood disorder in women associated with the birth of a child. It manifests itself in the period from 1 month to 1 year after childbirth. Symptoms may include deep sadness, lack of vitality, irritability, and sleep or eating disorders. According to statistics, the pathological condition affects every 7 women giving birth annually and can negatively affect the newborn baby.
Postpartum depression (PPD) is also called postnatal depression.
Psychological state of the mother and ways out
Postpartum depression in our society is a relatively new phenomenon, although the problem as such has existed for a long time. In the era of industrialization, when people flocked to big cities, and each family began to live separately from the older generation, it turned out that, on the one hand, here it is - a little happiness - separate housing. On the other hand, in such a situation, a woman with a child in her arms finds herself completely alone within four walls, and there is not always someone nearby who is ready to lend a helping hand to the young mother and be constantly nearby.
After a happy event in the life of a young family and returning from the maternity hospital, the mother, in fact, lives in increased activity mode all 24 hours a day - wash, feed, put to bed, clean up the house, and if there are other children, then the task becomes more complicated. factor of. It’s good if the child’s father takes an active part in caring for the baby, giving the mother at least a little rest. But if there is no such opportunity, the woman finds herself “on the brink.”
Postpartum depression is a depressed and depressed mental state that occurs in approximately 20% of women. This is a signal that a woman has exceeded the body’s mental, physical and emotional capabilities of adapting to new conditions, and she requires immediate help. And the advice of “well-wishers” - to pull yourself together, not to let yourself go - further aggravates the already difficult condition of the young mother.
Complications
Unpleasant consequences include the following:
- Prolonged depression (more than one year).
- Suicide attempts.
In addition to medical complications, quite severe social consequences are possible. First of all, this is the breakdown of the family. Indeed, constant changes in a woman’s mood, dissatisfaction with her own life, increased irritability - all these factors often push both spouses to divorce. In addition, some women, in a fit of despair, decide to abandon the child. As a rule, this kind of situation is common among single mothers.
How is this condition expressed?
In depressed women, all emotions and desires are suppressed. She doesn't feel like eating, she takes food nominally, without pleasure. She doesn’t want to work around the house or communicate with people, she avoids contacts.
Postpartum depression manifests itself in different ways, it can appear immediately after childbirth, or a month, or 3-4 months after childbirth. Postpartum euphoria has already ended, but the baby has not yet responded to maternal care and affection.
Depression usually lasts from several days to several months. The cause of postpartum depression is to a certain extent related to the hormonal changes that occur in a woman’s body after pregnancy and after childbirth.
© Vostock Photo
However, there are other factors that increase the likelihood of depression : - if a woman has experienced depression in other periods of her life; — there are problems or difficulties in the relationship with your husband/partner; - the child was born premature, is sick or has developmental disorders; - if a woman has lost a loved one in the recent past (for example, her parents or someone else very close died).
There is an opinion that depression occurs more often in women with high social status and level of education. However, this is not always the case. The risk of depression is much higher for women who live in difficult conditions, do not receive support from loved ones, have problems with finances, work, or are exposed to violence. Famous and educated women are in plain sight. They simply can afford to talk openly about their feelings and seek help.
Another cause of depression may be the difficult childhood of the mother herself. It is more difficult for a woman who grew up without maternal care and affection, in an orphanage or in a family where there were often scandals, to care for a child. The earliest memories are not erased from memory; they continue to influence a person. Relatives do not understand the woman’s condition, because the birth of a child should be a happy event! If depression does strike, don’t be afraid. However, it is worth remembering that depression is not “the blues” and “a whim,” as some people believe. Depression is a disease, and it should be treated by seeking help from specialists.
The first step in getting out of depression is awareness of your condition. This is a normal stage in the life of every woman. And it doesn’t matter what kind of child was born.
This condition is temporary and will not last long. And most importantly, each person has his own internal resources to overcome this condition. And communication with the child, joyful moments from touching him will help, first of all, to cope with the internal state.
Often a depressive state is associated with a feeling of guilt . The mother thinks that she is doing something wrong or is not paying enough attention to the child, especially if the baby was born prematurely or with health problems.
In this case, it is advisable to establish good contact with the pediatrician and ask questions to the doctor. You have every right to information about the state of your child’s health and the prognosis for his further development.
The more information a woman has about the state of her child’s health, the easier it will be for her to establish a daily routine, organize care for him, and then she can learn to recognize “alarming” symptoms!
Treatment methods
How to cope with postpartum depression on your own? It is impossible to answer this question, since the treatment of PDD syndrome requires complex measures carried out by the joint efforts of specialists from the field of psychiatry and neurology. To determine a treatment strategy, it is very important to undergo a brain function test. Organic lesions of this organ can significantly complicate treatment. In order to find a solution to the problem, you should first visit a qualified psychologist.
In order to overcome this disease, most women need several consultations with a specialist. However, in more complex situations, the use of medications is required to normalize brain function. In this case, women in labor are prescribed a course of antidepressants, which help get rid of the feeling of depression.
It is necessary to combat depression with the help of professionals, namely psychologists and psychotherapists.
The influence of hormones on stress after childbirth
Immediately after childbirth, a woman's hormonal background changes. The amount of female hormones - estrogen and progesterone, which were produced by the ovaries in large quantities during pregnancy, begins to decrease after the baby is born, returning to pre-pregnancy levels. Changes in hormonal levels have a strong impact on the nervous system, well-being and emotional state of a woman. This condition stabilizes by the end of the first month after birth. Breastfeeding women are less likely to experience postpartum depression than non-breastfeeding women. It's all about prolactin, a hormone that stimulates lactation and protects against depression.
Prevention
How to avoid postpartum depression? The exact causes of this condition still remain unexplored. That is why experts cannot offer effective measures to prevent it.
However, psychologists name a number of activities that, to one degree or another, help reduce the likelihood of depression:
- Pregnancy planning.
- Preliminary preparation for future motherhood (reading specialized literature, a course at the maternity hospital, conversations with a psychologist).
- Identification and timely treatment of the so-called postpartum blues (this condition, characterized by emotional instability and tearfulness, develops after the birth of a child).
- Psychological support of pregnancy.
Internal conflict
The birth of a child imposes on a woman a number of responsibilities that did not exist before. Constant physical and emotional “attachment” to the child makes the mother realize that she will have to give up her usual way of life and freedom of behavior. Now you need to give all your strength to the baby, all this becomes problematic. A conflict arises between the new social role and previous demands and habits - this can give rise to a feeling of dissatisfaction with life and depression.
© Vostock Photo
Relatives
A young mother, especially in the first months after the birth of a child, lives at the limit of her mental, physical and emotional capabilities. But it is important to understand: she gave life to the child and has the right to the attention of others! It makes sense to turn to close people for help: husband, mother, mother-in-law, friends, and if possible, then inviting a nanny or au pair - this will be a great solution. It’s better to do this in advance, and not at the moment when your nerves are already at their limit. You can arrange a “mom’s day off” once a week. Plan your exit in advance; a change of scenery is beneficial. It is important for a woman to learn to talk about what is happening inside, about her internal state, her fears, anxiety, since no one can guess about it if she does not know how to clearly articulate it to others.
Consequences
It is worth mentioning the dangers of postpartum depression. As already mentioned, it leads to suicide. Or worse, the woman gets rid of the newborn. But there are complications for the baby too. Mom stops breastfeeding him, the emotional connection is lost. The child is stressed. As a result, growth and development are delayed, sleep disturbances, and problems with the child’s activity occur. The baby develops a defense mechanism against the mother. He doesn't want to see her. All this results in big problems in adulthood.
What to do if a woman or those around her suspect postpartum depression?
A woman can first turn to a prenatal or clinical psychologist or psychiatrist who will help distinguish a bad mood from clinical depression. Drug treatment is prescribed only by a psychiatrist. There are special techniques and tests that will help identify this. Every woman has a bad mood, but it is temporary and passes quickly. Depression is protracted, with a feeling of guilt and inner emptiness, which a woman cannot cope with on her own for a long period.
The impact of postpartum depression on child development
Numerous studies show that mothers with postpartum depression find it more difficult to establish a connection and attachment relationship with their child and give him a sense of security and self-confidence. Mom is often self-absorbed, feels unhappy and tired, and finds it really difficult to enjoy what she does with her child. Some mothers cannot cope with emotions and break down. This makes some people angry or desperate; others simply ignore the child.
In such cases, it is more difficult for babies to feel safe. After all, a mother is the whole world for a child, and her reactions help the baby form his or her idea of the world.
As a result, children develop two opposing behavioral strategies:
"Restless" . Such babies cry a lot and often, and are capricious. They are difficult to deal with and seem perpetually unhappy. Babies are tense and ready to cry at any moment. They often have difficulty feeding and sleeping. It is very difficult for a mother to be away from her baby even for a minute; she is constantly haunted by the child's cry. Such babies are sensitive and often get sick.
"Quiet" . These kids even look too calm. They are practically inaudible. They make few sounds (humming and babbling) and show little interest in their surroundings. Often their gaze is directed into space. These children are not demanding; they are content with what they have. They appear less curious than their peers and smile and laugh less. In the future, children with either behavior strategy may have great difficulty adjusting to kindergarten (they cry a lot or behave badly). They are more demanding and capricious. They may have difficulty establishing contacts with peers, numerous fears, as well as other behavioral problems. Research shows that children often continue to have difficulties even at school age if the family and child have not received professional help.
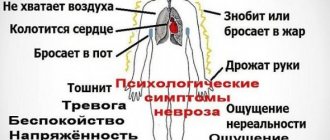
Symptoms
Let's consider the characteristic features of the mental state of a young mother, how postpartum depression manifests itself. The first sign of pathology is a depressed state that the young mother is unable to cope with. It especially manifests itself in the evening or morning.
Internal manifestations of depression
- Lack of meaning in life;
- feeling of guilt towards the newborn if he was born with pathological abnormalities;
- insomnia, lack of proper rest;
- despondency, lack of joy in life, inability to have fun;
- hypochondria, that is, looking for threatening symptoms of dangerous diseases;
- dizziness and headaches;
- sudden lack of appetite, which leads to physical exhaustion.
Depression may cause skin itching, rapid heartbeat, digestive system upset, frigidity, suicidal thoughts and a desire to harm yourself or your baby.
External manifestations of depression
- Increasing aggression and irritability towards family members, mental breakdowns;
- scattered attention, lack of concentration;
- frequent changes in emotional state;
- tearfulness and painful sensitivity to any external stimulus;
- loss of strength, emotional exhaustion;
- excessive concern for the condition of the baby, his health;
- coldness and indifference to the newborn, lack of maternal instinct;
- the feeling that the baby was replaced in the maternity hospital;
- memory losses;
- excessive talkativeness;
- acceleration of gait and body movements;
- slowness of body movements, slow and sluggish gait.
Other
A woman can cry for no reason at any time of the day. The reason for frustration can be a minor detail that the woman did not pay attention to before. Also, a young mother can find a reason for frustration in excessive worry about the fate of the baby: what if some kind of misfortune happens to him?
Some people panic and put their ear to the baby's chest to check the baby's heartbeat and breathing. The responsibility for raising a baby turns into a phobia: what if I can’t?
Frustration can occur at the thought that no one needs a young mother, and her baby will certainly fall ill with an unknown disease. A thousand negative thoughts and fears fill the head and can lead to a mental breakdown if the woman is not stopped and reassured in time. A dangerous condition for the psyche is sleep disturbance: due to obsessive thoughts, it can be very difficult for a young mother to fall asleep. Chronic lack of sleep deprives you of both physical and mental strength.
Coldness towards your husband is another problem that postnatal depression provokes. A woman doesn’t care about her man, because now she only loves the baby. However, indifference to your husband is not the worst thing: hatred of the male sex may appear.
Based on the listed signs, you can determine the condition of a young mother and provide timely assistance. Untreated postnatal depression can lead to psychosis, which cannot be treated at home. A woman in a state of psychosis must be hospitalized in a hospital in order to be brought out of the crisis. In a state of psychosis, a young mother can harm the baby or herself, which often ends in death.
Why is postpartum depression so rarely diagnosed?
The explanation for this is the reluctance of mothers to seek help due to negative stereotypes that have developed in society about visiting a psychologist in such a situation. Reluctance to seek help is most often due to fear of being misunderstood or feelings of guilt; fear of any change is one of the typical symptoms of depression.
Talking about difficulties with strangers is not easy, admitting that you do not feel happy after the birth of your baby is even more difficult. Therefore, women suffer alone, thereby increasing their difficulties. Sometimes depression is confused with another condition - postpartum psychosis. This is a mental disorder of the postpartum period.
Some mothers believe that the only way to get rid of depression is medication, but since they are breastfeeding, they cannot even think about antidepressants. And women often don’t believe in psychological help. In case of psychosis and severe depression, a woman should seek help from a specialist in order to start treatment earlier, rather than suffer and suffer from her inferiority. Treatment can be done at home with antidepressants. And only in severe cases is hospitalization in a specialized clinic suggested.
Treatment lasts individually, depending on the severity of the condition. After treatment, the woman gradually returns to a normal lifestyle, this does not mean that she will no longer be able to be the same or “normal”; no one recognizes a woman as insane in such a situation. This does not mean that she will be prone to relapse after treatment. This will be her personal experience and, perhaps, the woman will learn to help herself not to become exhausted and to accept the help and care of loved ones. And this experience will help those close to you to be more sensitive to the woman’s condition after childbirth. Fathers may also need help in this situation.
© Vostock Photo
How to fight?
Postpartum depression, its symptoms and signs - what to do? Accept! The same principle underlies the complaints against the husband, that he does not help. If there is a stereotype inside a woman that a good housewife should do everything herself, then she, with a baby under her arm, viciously scrubs, smoothes and cooks until she drops. And then she nags her husband, reproaching him for not wanting to help. So he won't help. Because he is not allowed to do this by the “I must do everything myself” program in a woman. The program will fall off, self-love and permission to be less than ideal will come, and the husband will take the initiative. It's simple.
With jealousy towards your husband in the postpartum period - the same song. And with resentment for the lack of tenderness and love on his part, too. This woman fears that she is not good enough and that someone is better. It’s she who doesn’t value herself, who doesn’t consider herself beautiful, who doesn’t love herself, who doesn’t care about herself. An empty woman with zero resources. But the emptiness weighs heavily and requires filling.
Postpartum depression hit me, all its symptoms and signs. However, instead of starting to “feed” herself on her own, the wife begins to gnaw at her husband. Although if she had paid attention to herself, it would have changed the situation in the family exactly the opposite. It would lead to the restoration of lost harmony. After all, like attracts like. Internal approval is external approval. Care and sensitivity to oneself - care and attention from loved ones, and so on.