Frequent feelings of anxiety and excessive agitation are the first signs of agitation
page » Hysteria » Frequent feelings of anxiety and excessive excitement are the first signs of agitation
Danger and anxiety overcome every person from time to time. This could be fear for your family, for your health, for your future, or for the stability of your usual lifestyle.
However, if fear and anxiety groundlessly penetrate a person’s life, this is already a serious cause for concern.
Experts call this human condition agitation and classify it as a mental disorder.
Causes
The causes of agitation, like any mental illness, are very vague. It is difficult to say with certainty what became the basis of this disorder. Usually it is influenced by a complex of reasons, ranging from a predisposition to such diseases and ending with overwork or stress.
At the moment, researchers put forward a number of reasons that may trigger agitation:
- Severe stress associated with sudden fear.
- A job that involves constant risk, exposure to something dangerous, and constant change and change.
- The result of drug intoxication, or “delirium tremens.”
- Pathological effects of certain medications.
- Disorders of the endocrine system (for example, a disease such as hyperthyroidism).
The risk group includes older people - usually due to serious traumatic events, they can be susceptible to this disorder. It can also manifest itself against the background of age-related mental disorders (dementia, Alzheimer’s, etc.).
Complications and consequences
If depression is left untreated for a long time, it gradually worsens , negatively affects the patient’s personality, and increases the likelihood of other mental illnesses, such as obsessive-compulsive, anxiety, and panic disorders.
Also, advanced depression, like any other somatic or mental illness, is much more difficult to cure.
As the disease progresses, the symptoms will worsen : for example, melancholic raptus, which initially manifested itself moderately, may become more pronounced and will pose a serious threat to life and health.
Depression affects not only a person’s mental health, but also his physical health. Its influence is especially strong on people over 40-50 years old.
It aggravates the course of chronic diseases, becomes one of the causes of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular, endocrine, and nervous systems, and increases the likelihood of Alzheimer's disease, dementia, stroke, and heart attack.
Who is susceptible to agitation?
People with infectious or mental illnesses are also susceptible to agitation. This condition is characterized as prepathological within the psychological norm.
For example, police officers, firefighters, military personnel, stuntmen, pilots, submariners. An attack can be triggered by physical and mental overload that a person has been experiencing for a long time. Severe fatigue also provokes this condition.
It may be one of the symptoms of a number of diseases:
- neurosis
- depression (involutional, agitated)
- catatonic schizophrenia
- Alzheimer's
- senile decline
- endocrine disorders
- avitaminosis
- alcohol addiction
- drug addiction
- dementia
- withdrawal syndrome
The manifestation of agitation affects the human psyche and the autonomic system. In this state, the patient ceases to control himself and there is a danger of causing physical harm to himself and those around him.
Causes of agitation
Sometimes the emotional state of human subjects can be considered as a symptomatic manifestation of individual pathological processes. With such symptoms, it is necessary to carry out corrective drug and non-drug therapy. The conditions under consideration also include agitation, which is qualified by doctors as intense emotional arousal, giving rise to a number of unpleasant manifestations. Sometimes the state of agitation is absolutely natural, but in other circumstances it can act as a “bell” signaling the presence of quite dangerous pathologies.
It should be understood that the described disorder does not develop in a vacuum. It is provoked by external factors and internal reasons.
So what is agitation in medicine? This term refers to the excited state of an individual, accompanied by motor restlessness, fear and anxiety. Speech anxiety may also occur. In principle, agitation is considered a natural response of the body of human subjects to tension caused by severe stress. In other words, the described condition is detected under the influence of stressors or psychological trauma. In some individuals, the phenomenon in question appears as a result of severe fright or sudden changes in the environment surrounding the person. In addition, this condition is sometimes inherent in people whose work activity is dangerous to the individual’s life.
Among the external factors that provoke agitation, in addition to the effects of stressors, one can highlight increased physical stress, accumulated fatigue, and excessive mental stress that persists for a long period. Attacks of the affective state in question are often caused by pharmacopoeial drugs, consumption of high doses of alcohol-containing drinks, caffeine, and dependence on psychotropic substances.
Since the state of agitation can be a manifestation of an illness, a number of ailments can be identified that are internal factors that give rise to emotional overexcitation:
- infectious diseases;
- intoxication;
- endogenous depressive moods;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- anxiety neurosis;
- worsening senile changes that occur in the individual’s psyche, for example, with dementia;
- catatonic schizophrenia;
- senile decline;
- bipolar disorder.
In addition to the above, the described condition can also be provoked by endocrine ailments, advanced vitamin deficiency, and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In psychiatric science, agitation is considered a serious problem that occurs in extreme circumstances. An individual, being in a similar state, is at risk of displaying aggressive behavior towards the environment and himself.
With a pronounced anxious depressive state, an individual often causes damage to other people's property. In addition, this disorder in patients is often the main cause of injury to medical staff.
Mental disorders are considered a rather big scourge of modern society, since every year more and more human subjects are exposed to these disorders.
In psychology, agitation is considered a disorder generated by a strong surge of emotions, which is accompanied by strong fear and anxiety, manifested in unconscious speech and motor excitation.
Main features
It is necessary to pay attention to how agitated activity will manifest itself, since it will be somewhat different from other disorders. We should also not forget that the patient himself may not notice these signs; it is important for relatives or close people to pay attention to this in order to seek help as early as possible.
The main signs of agitation:
- Agitation begins to unfold with the manifestation of fussiness and restlessness in movements.
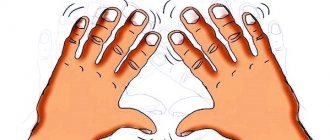
- Trembling appears in the hands, the skin turns pale, sweating increases, breathing and heart rate increase.
- Thinking becomes confused, speech becomes confused. It is difficult for a person to complete a sentence; he seems to rush from one thought to another or repeats the same words.
- The more serious the disease, the more pronounced the symptoms will appear - moreover, during attacks the patient can cause harm to both himself and others. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the signs of the disorder as early as possible.
- If agitation acts as a symptom of other diseases, then it can be accompanied by visual or auditory illusions, sometimes by attacks of spontaneous shouting of curses, as well as motor tics.
Agitation
Agitation is an intense emotional impulse, which is accompanied by an anxious feeling and fear, turning into motor restlessness and the need to move. An individual who is in such a mood becomes quite fussy.
It is capable of performing only simple automated motor operations. He has a feeling of lack of thoughts, the ability to reason and identify complex cause-and-effect relationships between phenomena is disrupted.
Thus, the meaning of the word agitation implies a clinical disorder expressed in motor restlessness and the need to move.
The condition in question occurs under severe stress and certain mental illnesses, such as catatonic schizophrenia, depressive states, Alzheimer's disease, and anxiety neurosis. Also, the described phenomenon can be provoked by drug exposure or alcoholic libations.
Symptoms of agitation
The emergence of agitation marks a number of different manifestations, but often the individual himself does not notice their presence.
The literal translation of the word agitation is excitement. Therefore, a characteristic manifestation of the pathological condition in question is the occurrence of motor disinhibition or speech anxiety.
In addition, the individual may experience trembling of the limbs, excessive sweating, and increased heart rate. The listed manifestations are often accompanied by rapid breathing.
In a state of agitation, the dermis becomes pale in color.
In psychology, agitation is a behavioral defect consisting in the uncontrolled transition of affective tension into motor restlessness. It is a concomitant symptom of various mental illnesses, for example, anxiety neurosis, involutional depression, catatonia.
When the state in question occurs, the individual “meets” a feeling of absolute absence of thoughts, his head seems empty. The patient becomes unable to reason sensibly or identify complex causal relationships.
Agitation is accompanied by a feeling of fear and anxiety, turning into speech disinhibition or motor restlessness. An individual in such a state is forced to perform unconscious motor acts of the same type. In addition, he is characterized by fussiness. The patient can only perform simple automated operations.
Agitation is determined by the presence of the following signs. The individual's behavior changes when the violation in question occurs, but he himself is not aware of it. Speech disinhibition, fussiness in motor acts, hand tremors, pallor of the dermis of the face appear, sweating increases, and the heart rate increases. In this case, the individual is in a hyperexcited state.
Particular attention is paid to the emergence of a state of agitation against the background of Alzheimer's disease, since depressive moods, hallucinations are added, behavioral disorders intensify, and a person is drawn to wandering.
If the disorder in question is a symptom of other ailments, then it is often accompanied by attacks of spontaneous shouting of swear words and motor tics.
Signs of agitation in depressive states are somewhat different from those given above. This illness manifests itself as a combination of various symptoms characteristic of ordinary depression (apathy, dream disorder, depressed mood) and those inherent in agitation. First of all, people suffering from agitated depression develop causeless anxiety.
They begin to worry about loved ones and their health. Patients have a premonition of something bad. The speech of such patients changes; they reproduce the same phrases that convey their excitement. Often this comes to the point of endless repetition of just a few words. Behavioral changes are also noted. It is difficult for an individual to sit in one place.
He has to constantly move.
Treatment of agitation
Therapeutic intervention, first of all, must begin with diagnostic measures, including, first of all, observation of the individual.
After all, what is agitation in medicine? This term is a state of extreme excitement, which is accompanied by anxiety of inexplicable etiology and fear. Therefore, agitation will be accompanied by vegetative symptoms, namely: pallor, rapid breathing, increased heart rate, sweating, and tremor.
While in the described state, an individual may involuntarily injure himself or cause harm to those around him.
If agitation has developed against the background of a mental illness, then therapeutic correction is carried out with the help of psychotherapy and the prescription of pharmacopoeial drugs.
It is psychotherapy that is rich in simple behavioral techniques aimed at helping the patient eliminate the symptoms of agitation. In addition, psychotherapeutic techniques will also increase the patient’s resistance to stress.
Although agitation is assessed as a condition that is within the psychological norm, that is, prepathological, the prescription of pharmacopoeial drugs is still practiced:
– antipsychotic drugs – drugs prescribed to relieve manifestations of paranoia and treat states of clouding of consciousness; they have a number of side effects: drowsiness, unusual motor operations, rigidity;
– antidepressants, which are psychotropic drugs and are used for depressive conditions, they are also characterized by some negative effects: drowsiness, constipation, dry mouth;
– anxiolytic drugs used to suppress anxiety, feelings of emotional tension, anxiety, and fear.
In order to prevent relapses of manifestations of agitation, it is recommended to take psychotherapeutic courses that increase stress resistance. If the disorder in question is provoked by the presence of mental pathology, then it is necessary to act on the underlying illness.
Psychoneurologist Hartman N.N.
Doctor of Medical and Psychological
The information presented in this article is intended for informational purposes only and cannot replace professional advice and qualified medical care. If you have the slightest suspicion of agitation, be sure to consult your doctor!
We are on Telegram! Subscribe and be the first to know about new publications!
Source: https://psihomed.com/azhitatsiya/
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease should be carried out carefully and comprehensively. Agitation is a condition similar in symptoms to the disorder akathisia, which occurs from taking antipsychotics. If the diagnosis is incorrect and an increase in the dose of antipsychotic is prescribed, this only aggravates the patient’s condition.
At the beginning of the diagnosis, doctors conduct long-term observation of the external manifestations of the patient’s behavior. Then various studies are prescribed:
- Analysis of urine
- blood analysis
- thyroid examination
- MRI or CT scan of the brain
- screening of medications used by patients
- heart rate measurement
- blood pressure determination
- somatic and infectious diseases
This integrated approach allows us to obtain objective reasons for the occurrence of agitation. Based on the results obtained, the patient is prescribed appropriate treatment. Late diagnosis of the disease can lead to the patient needing urgent care and large doses of medications.
- Constant anxiety. The initial stage of the disease in all patients proceeds the same way, manifesting itself in the form of anxiety and worries about loved ones. A person with agitated depression begins to feel (for no reason) that something terrible will happen to his loved ones or to himself - an accident, unexpected death, murder, etc.
- Anxious verbigeration. In a conversation with a patient, you may notice that he begins to pronounce and often repeat the same phrase or words. The phrases themselves are often short and monotonous.
- Motor agitation. This symptom is expressed in a behavioral disorder of the patient - he can jump up in the middle of a conversation or in a calm environment, wave his arms, walk somewhere, constantly change his position.
- Melancholy raptus. At an early stage of the disease, a person begins to wring his fingers; in more severe cases, he may begin to harm himself, even causing serious injury.
- Delusional ideas, thoughts (Cotard's delirium, for example).
Anxiety, loneliness, depression, fear, hatred and self-rejection are what a person with agitated depression experiences. If you do not provide the patient with qualified assistance in time, everything may end in his suicide.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of agitated depression may hide serious somatic pathologies , such as hyperthyroidism, benign and malignant neoplasms in the brain, and vascular dementia.
Therefore, a person with symptoms of depression should undergo testing to ensure that their physical health is not affecting their mental health.
After this, it is important for him to talk with a psychotherapist or psychiatrist and take tests that may be offered by them. Among them:
- Beck scale and Zung scale, which allow assessing the level and characteristics of depression;
- Spielberger Anxiety Scale;
- Luscher color test, which reflects the patient’s psycho-emotional state;
- Sheehan and Zung Anxiety Scale.
Tests may also be done to show how cognitive abilities are functioning. After this, a diagnosis is made and treatment methods are determined.
Help and treatment
So, it is important to know that agitation as an independent disease is currently completely curable. But if it is a sign of another disease, certain difficulties may arise.
First, it is important to establish the cause of the disease. After the specialist determines the factors that led to the development of the disease, treatment is prescribed.
1. Often such patients are offered to undergo a course of individual psychotherapy. Once the patient becomes calmer, he may be referred to a psychotherapy group, where he can practice skills for interacting with other people.
2. It is also important that the psychotherapist be visited by the patient’s relatives, since the need to create a certain atmosphere at home falls on their shoulders.
We recommend: What to do if you have bad dreams?
3. Most often, the treatment of agitation is medicinal, since psychotherapy alone is not capable of returning a person to normal life. Medicines are prescribed depending on the characteristics of the disease; these can be both antidepressants and antipsychotics.
Diagnostics and therapy
To diagnose agitation, a specialist needs to observe the patient’s behavior and correctly differentiate this condition from akatasia, which has similar symptoms. This aspect is very important, since some medications used for agitation are absolutely contraindicated for akatasia.
In addition to an external examination, as prescribed by a doctor, diagnostic tests such as a clinical analysis of urine and blood, analysis of thyroid hormones, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, screening of medications used by patients, measurement of blood pressure and pulse can be used.
Treatment of agitation, as a rule, turns out to be quite effective, since many causes of the pathology are easily correctable. If agitation is not caused by an infectious or mental illness, its treatment is usually carried out using a complex method, in particular, with the help of drugs from the following groups:
- Sedative antidepressants. Such medications can be used as a sedative, taking into account possible side effects such as drowsiness, dry mouth, stool disorders, etc. They are prescribed in cases where agitation is combined with a depressive disorder;
- Antipsychotics. Drugs in this group can be prescribed if the patient exhibits clouding of consciousness and paranoia;
- Antianxiolytic medications. These medications should also be taken with caution and strictly as prescribed by your doctor. Daytime drowsiness is possible as a side effect.
Agitation in some cases involves treatment using common psychotherapeutic techniques. As a rule, patients are offered fairly simple behavioral techniques that will help them learn to control their own emotions and promptly switch from a stressful situation. Regular psychotherapy helps to increase stress resistance and emotional stability in general.
Treatment
In order for psychotherapeutic treatment to be successful and a person to quickly feel better, medications that block the symptoms of depression. Among them:
- antidepressants (Prozac, Clomipramine);
- sedatives (leonwort tincture, Novo-Passit);
- neuroleptics (Haloperidol, Droperidol), but only in the presence of severe delusional states;
- benzodiazepines (Diazepam, Clonazepam).
But without psychotherapeutic help, drug therapy will only have a temporary effect.
In the treatment of agitated depression, the following psychotherapeutic directions :
- cognitive behavioral therapy;
- art therapy;
- hypnotherapy;
- Gestalt therapy;
- psychodynamic therapy;
- existential therapy.
The psychotherapist helps the patient rethink the current situation, look at it from different angles and find a way out. He also teaches him to cope with the symptoms of depression and find strength for activity.
Middle-aged and elderly people may be skeptical about psychotherapy, and it is important to try to convey to them the idea that these are the same doctors as, for example, a therapist, cardiologist, traumatologist, they simply work in an area related to the psyche and personality of a person.
- Give examples from your life : tell us about people you know who, after undergoing treatment, felt much better.
- Offer to take tests on the Internet , for example the Zung or Beck scale. If a person sees that, according to the test results, he should visit a specialist, this may change his mind.
- Find a qualified psychotherapist and show their website to a loved one so they can read the information.
- Show articles about psychotherapy, depression and anxiety so that a person better understands what exactly is happening to him and how psychotherapists work.
- Explain that no one forcibly locks people in a mental hospital with depression. This practice has long disappeared.
Physiotherapeutic procedures (light therapy, therapeutic sleep, hydrotherapy), massage, and physical therapy have a positive effect.
Practical recommendations for people who have agitated depression:
- Play sports . If you don't like classical physical exercises, you can do yoga or race walking. Physical activity has a beneficial effect on physical and mental well-being, triggers the production of pleasure hormones, and improves immunity.
- Adjust your daily routine. It is necessary to get up and go to bed at a certain time, and it is important to sleep, especially in old age, at least 7-8 hours a day.
- Take a walk in the fresh air more often: a walk will have a beneficial effect on your well-being and provide additional physical activity.
- Change your diet so that it contains enough nutrients. For example, a lack of vitamin B12 provokes depressive symptoms, especially in older people.
- Communicate regularly with loved ones who treat you kindly and warmly.
- Do things that bring you joy or have brought you joy in the past.
Symptoms
The symptoms of agitation are quite pronounced, but for the patient himself, changes in behavior will not be too noticeable.
We are talking about the following signs:
- blood pressure surges;
- increased sweating;
- increased heart rate, pulse and breathing;
- pale skin and trembling hands;
- problems in establishing cause-and-effect relationships and controlling one’s own thinking;
- emptiness in the head and inability to think rationally.
In the presence of mental illness as a provoking factor, other psychological signs are observed:
- manic and depressive disorders;
- hallucinations;
- involuntary movements and obscene swearing.
It often comes to the point that a person can be dangerous to others and to himself.
In addition to the usual general signs of depression (depression, impaired need for food, insomnia, indifference to everything, etc.), agitated depression has periodically recurring symptoms that are unique to it:
- Increased anxiety, feeling of imminent disaster. It seems to the patient (without apparent reason) that something terrible will happen to him or to people significant to him - a fatal illness, a car accident, an accident, and so on.
- Then comes the syndrome of anxious verbigeration. The patient often, monotonously, continuously, anxiously repeats a short phrase or phrase. All topics of conversation come down to his experiences related to the past or fears about the future.
- The syndrome of excessive motor restlessness is well expressed. The patient is physically agitated, cannot stay in one place, and rushes about.
- In severe forms, an acute attack of the desire to commit violent acts against oneself appears - the so-called melancholic raptus. The patient is capable of inflicting physical injuries of varying severity on himself. Suicidal attempts are possible, which is especially dangerous.
- In advanced stages of agitated depression, hallucinations and delusions (for example, hypochondriacal delusions) may occur.
Symptoms of agitated depression
A lot depends on the understanding of the situation by those close to the sick person. It can be very difficult to differentiate his gradually changing behavior from the precursors of the disease. You need to understand that the patient cannot get out of this state without qualified help. The situation will worsen significantly if he is faced with misunderstanding or irritability of relatives.
Causes of agitated depression
For a long time it was believed that the development of agitated depressive disorder is associated with age-related changes in mental processes, such as rigidity and inability to adapt to changing conditions. This statement is due to the fact that middle-aged and older people are most susceptible to developing a mental disorder, but currently there is a tendency to reduce the age of patients with this diagnosis.
Modern researchers associate the development of agitated disorder with psychological problems and personal characteristics of patients. People with accentuated character traits often turn to specialists for this type of mental disorder:
Pedantic individuals are distinguished by discipline, hard work, and perfectionism.
For such people, it is important not only to draw up a detailed action plan and carry it out efficiently, but also to take part in the implementation of the tasks of others. The development of a mental disorder occurs due to overstrain of the nervous system. Pedantic people are also thrown out of their state of psychological balance by new situational demands that they cannot meet, which becomes a traumatic event.
Another fear of pedantic people is related to the possibility of repeating similar mistakes when performing any duties. Such people expect troubles that will cause a decline in their performance. To prevent such situations, they regularly organize self-tests that increase anxiety. Anxious people question their thoughts, actions, and decisions.
Excessive anxiety of such individuals is complemented by impressionability, suspicion and suspiciousness. This combination leads to depletion of the protective mechanisms of the nervous system. Anxious people tend to underestimate their abilities and feel insecure in new situations.
- Shy and timid people have difficulty establishing various contacts. Failures in the professional and personal spheres are endured by such people with great difficulty; they can act as a psychologically traumatic factor.
- Emotive individuals are characterized by excessive sensitivity and mercy. People of this type tend to sacrifice their interests for the well-being of others. They are always ready to help loved ones, as they fear breaking off relations with them. This condition is based on the fear of loneliness, which intensifies with age.
Agitated depressive disorder develops gradually; the patient’s psycho-emotional state can be aggravated by the following factors:
- rethinking life values;
- lack of life guidelines and prospects;
- difficulties of self-realization;
- problems in interpersonal relationships;
- financial instability;
- dissatisfaction and criticism from colleagues and close people.
Signs of agitated depression can be found in mentally healthy people. However, experts have established a relationship between the disease and a hereditary component.
Prevention
For people of any age, it is easier to prevent the onset of depression if:
- alternate mental activity with physical activity;
- get enough rest on time;
- increase resistance to inevitable stress with a healthy lifestyle;
- promptly resolve your intrapersonal conflicts with the help of a psychologist;
- get carried away by your favorite activity or find something interesting for yourself.
Prevention of agitated depression in people of the older age group, who are most susceptible to this mental disorder, consists of sensitive and attentive attitude towards them from relatives and friends, in confirming the significance of their social role.