In addition to pharmacological and psychotherapeutic treatment of depression, other methods have been proposed for its treatment.
Such methods of treating depression, often effectively combined with pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy, include: intravenous laser irradiation of blood, magnetic stimulation (transcranial low-frequency alternating magnetic field therapy, right-sided pair-polarization therapy), extracorporeal detoxification (plasmapheresis), periodic normobaric hypoxia, craniocerebral hypothermia, light treatment, sleep deprivation, dietary therapy (including its fasting options), balneotherapy (warm baths have been used for a long time to alleviate the condition of a person who is depressed), massage and physical therapy (breathing exercises and physical activity helps to alleviate the symptoms of depression).
Among biological methods of treating depression, electroconvulsive therapy occupies a special place.
| Find out more: Inpatient treatment for depression |
Intravenous laser irradiation of blood
According to the recommendations of domestic scientists, intravenous laser irradiation of blood should be carried out using a low-intensity helium-neon device (FALM-1). The wavelength of laser irradiation is 0.63 microns. The radiation power at the output of the light guide is 8 mW. Session duration is 15 minutes, course of therapy is 8-12 sessions. It was noted that after laser therapy while taking psychopharmacological drugs, the severity of depressive symptoms in 60% of people suffering from depression is almost halved. Patients with manifestations of apathy and melancholy are especially sensitive to laser therapy; a less clear effect is observed in complex depressive syndromes, including symptoms of depersonalization, obsessive states and hypochondria. Laser therapy is ineffective for anxiety and depression. It should be borne in mind that the effect of laser therapy as a non-drug treatment method, as well as of treatment with antidepressants, may be delayed and appear some time after completion of the course of treatment. Currently, there are various modernizations of laser therapy. An example is a differentiated method of low-intensity magnetic laser therapy. This method of treatment includes an individual stage program of a course of combined laser exposure, which consists of venous irradiation of the tissue with continuous red light (0.63 μm) and transcutaneous irradiation with pulsed infrared light (0.89 μm) of projections of a number of biologically active zones and organs using standard magnetic attachments. Laser irradiation usually does not cause side effects or complications.
Reviews
Reviews about antidepressants are different. On the positive side, mild antidepressants and anxiolytics generally do not cause any side effects, are good for calming, elevating mood, and increasing performance. But only if the depression is shallow. In severe forms with the addition of other mental disorders, more effective drugs are used. And they have many side effects. Withdrawal syndrome is often observed, this indicates that the body is becoming accustomed to the drug. In any case, antidepressants should be prescribed and discontinued only by the attending physician. It is not recommended to do this yourself.
Electroconvulsive therapy
Currently, one of the most effective non-drug methods of treating depression is electroconvulsive therapy, which is used both as an independent method of treatment and in combination with other methods of therapy (Nelson A.I., 2002).
Electroshock therapy methods have been used since ancient Greece. In the temples of Asclepius, depression was treated with electric snakes. In the Middle Ages, it was believed that a strong shock to a patient could bring him out of a state of depression.
Treatment of depression with electric shock was recommended by Hill in 1814 (commotions electriques) (Kempinski A., 2002). Particular interest in this method of treating depression was noted in the early forties of the twentieth century. Electroconvulsive therapy is now generally recognized to be highly effective in treating depression.
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of electroconvulsive therapy for those patients for whom pharmacological treatment is contraindicated (pregnancy, certain somatic diseases, etc.), as well as if it is necessary to overcome depression resistant to other types of therapy.
Typically, to obtain a therapeutic effect from electroconvulsive therapy, about 8-10 shock discharges are required at a frequency of 3 sessions per week.
Subject to monitoring the condition of patients, it is possible that they can be treated with ECT on an outpatient basis or as a day treatment for depression in a hospital.
In general, the combination of ECT with antidepressants is not recommended; the use of small doses of tranquilizers is possible.
Complications of electroconvulsive therapy include spinal injury and circulatory disorders, states of confusion after convulsive attacks, as well as periods of anterograde and retrograde memory impairment have been reported. The latter can persist for a month after the end of ECT. ECT causes a temporary rise in blood pressure (often to quite high levels) and increases the heart rate.
Relative contraindications to ECT include coronary heart disease and arrhythmias, as well as some location of the brain tumor.
Most patients are afraid of this method of therapy, so the importance of professional psychotherapeutic work with the patient, as well as its subsequent support during the ECT therapy itself, should be emphasized.
Indications for use
Antidepressants are recommended and widely used in the treatment of:
- neuroses;
- phobias (fears);
- increased anxiety;
- chronic depression;
- prolonged stress;
- panic states;
- anerexia or bulimia;
- sexual dysfunctions;
- affective disorders;
- giving up drugs, alcohol, nicotine.
Patient reviews of taking antidepressants are varied. Sometimes, when they are discontinued, symptoms of depression or anxiety reappear in patients; also, some drugs are not used in women using a diet to lose weight, as they can contribute to excess weight gain.
Therefore, it is very important to choose the right drug and carefully study its side effects. Only after weighing all the pros and cons at an appointment with a doctor (neurologist, psychotherapist, psychiatrist) can you go to the pharmacy to purchase an antidepressant.
Why are pills needed?
A great many people suffer from depression around the world. In our age, when the world is constantly developing, moving forward, and any information is available for study, most of the world's population lives with an incorrect understanding of what depression is.
People are put off by the idea that depression is a disease and requires treatment. They do not turn to specialists for help, but try to eliminate it themselves, mistaking it simply for a bad mood, temporary difficulties, or “well, this is such a stage in life.” Meanwhile, the condition continues to progress.
By the way, depressive disorder, as scientists say, causes stroke. WHO noted that by 2030, depression will take 2nd place, after AIDS, in the list of world problems.
It’s worth thinking about whether this disorder is as safe as most people believe. Learn to differentiate your condition. And if you can't handle it, don't hesitate to ask for help. You just can’t imagine how many people live with the same problem!
Drug therapy for depression will be needed in the following cases:
- when a person refuses to perform ordinary, daily manipulations - get out of bed, get dressed, brush his teeth;
- if the cause of the disorder is a disease of the internal organs;
- lack of effect from psychotherapy;
- re-development of depression;
- when the disease affects health, it causes decreased appetite, poor sleep, and painful sensations in the body.
Magnetic stimulation
Repeated transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) was proposed for the non-drug treatment of depression in 1985 (Barcer A., et al., 1985). This method of treating depression, as well as vagal nerve stimulation, currently represent new methods of treating depressive spectrum disorders.
Low-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation has been proposed as an alternative treatment for depression to electroconvulsive therapy where stimuli do not reach the seizure threshold.
Compared to electroconvulsive therapy, this treatment method has an important advantage: a more precise effect on those brain structures that are involved in the pathogenesis of depression (hippocampal region). In addition, with TMS there are no cognitive impairments that occur after ECT. However, if the effect of TMS and ECT treatment is approximately equal in the treatment of mild or moderate depression, then in the case of severe depression ECT may become a more preferable method (Grunhaus L., et al. 1998).
Studies have shown that TMS induces changes in beta-adrenergic receptors similar to those that occur after ECT and has a positive effect on astroglial tissue in the brain.
TMS has proven effective not only in the treatment of depression, but also in the treatment of schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (George M., et al., 1999). However, it was noted that the positive effect of TMS in the treatment of depression is observed only in 50% of cases. In addition, most patients experienced frequent relapses of depression after several months of remission following TMS. The combination of high-frequency and low-frequency magnetic stimulation appears to be more preferable for the quality of remission and its duration.
From the point of view of the pathogenesis of depression, the method of cyclic transcranial magnetic stimulation seems promising, since weak magnetic fields can reduce circadian rhythms (Mosolov S.N., 2002). Currently, this method of therapy is used to overcome treatment-resistant depression.
The first TMS studies proved the superiority of fast stimulation over slow stimulation, however, the number of such studies was quite limited and the area of influence was not precisely localized. Recent studies show a higher effectiveness of low-frequency magnetic stimulation compared to high-frequency (Klein E., et al., 1999).
Typically, magnetic stimulation is carried out using a unilateral technique: on the projection of the left dorsolateral prefrontal region (high frequency or fast stimulation - < 10 Hz), less often stimulation of the right prefrontal region is performed. Low-frequency magnetic stimulation affects a selective area of the anterolateral prefrontal cortex of the left hemisphere.
A course of low-frequency magnetic stimulation for non-drug treatment of depression is 10 sessions, with an average duration of 30 minutes. Sessions are held every other day; stimulation parameters - 1.6 T/1 Hz. The therapeutic effect is noticeable after the first therapy session and most often manifests itself as calming, reducing the severity of anxiety, and restoring sleep. This method is of interest due to the rapid development of effect and the absence of complications. As noted above, unlike ECT, TMS does not require the use of anesthesia.
Types of drugs
All stress and nerve medications are a huge group of medications that affect the function of the nervous system.
According to their pharmacological effects, they are divided into:
- Neuroleptics are a class of drugs that are prescribed for neuroses, as they provoke inhibition of the central nervous system. They have a sedative, soporific effect and relax muscles. Admission is associated with side effects.
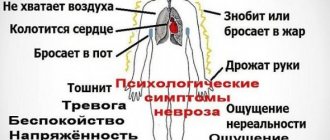
- Antidepressants are drugs that fight depression. Signs of depression include lack of mood, suicidal thoughts, and disordered thought processes. Antidepressants help cope with these symptoms, but also have a number of negative effects.
- Tranquilizers are substances that should only be taken under the supervision of a physician. By pacifying a person’s emotions, pills help relieve anxiety, fear, and free oneself from phobias, although they can be addictive.
- Nootropics are drugs that improve blood circulation in the brain and restore nerve fibers. Medicines improve mood and prevent depression. You can drink it to normalize brain function.
- Sedatives are sedatives made from natural ingredients. The composition contains mint, valerian, motherwort. They relieve nervous tension, have a relaxing effect, and do not cause drowsiness.
Vagal stimulation
Vagal stimulation for the non-drug treatment of depression was proposed in 1994 (Harden C., et al., 1994). When conducting vagal stimulation, areas of the lateral and orbital regions of the anterior parts of the brain, as well as the parabrachial nuclei of the nerve and the locus ceruleus region are affected. The impact on the last part of the brain ensures that this method influences the functional activity of the thalamus and hypothalamus.
After the use of vagal stimulation, an increase in the content of biogenic amines in the limbic region of the brain was noted (Ben-Menachem E., et al., 1995)
Sleep deprivation
A relatively gentle non-drug treatment for depression is sleep deprivation, which was actively developed in the early 70s of the twentieth century. Three types of sleep deprivation were used: total, partial and selective. Total sleep deprivation involves being awake for 36-40 hours, partial sleep deprivation means sleeping from 5 pm to 1 am, then staying awake until the next evening or sleeping from 9 pm to 1 hour 30 minutes then staying awake until the next evening - sleep duration 4, 5 hours and selective sleep deprivation, focused on selective deprivation of only REM sleep. For the treatment of depression with symptoms of melancholy, the combination of total sleep deprivation with light therapy at night turned out to be most effective. It should be noted that with complete sleep deprivation, lethargy and drowsiness are more often observed. In most cases, sleep deprivation is carried out two days later on the third; the therapeutic course includes an average of 5 sessions.
Sleep deprivation, both partial and complete, changes the structure of sleep, lengthens the latency period and reduces the duration of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. As a rule, an improvement in mood in patients is observed after just one sleepless night, however, this effect is usually short-lived and lasts about three days. Improvement in mood occurs gradually, expressed in the form of a feeling of general relief, a decrease in the feeling of lethargy, apathy, and the disappearance of experiences of mental pain and bitterness.
In prognostic terms, the relationship between the change in the mood of a depressed patient after the first and second sleepless night is important.
The mechanism of the therapeutic effect of sleep deprivation is difficult to reduce only to the simple elimination of one of the phases of sleep or the resynchronization of a time-shifted circadian rhythm. Probably one of the mechanisms for improving the condition of a depressed patient after sleep deprivation is the activation of adrenergic structures.
Light treatment
Non-drug treatment of depression has been tried for more than twenty years using light, hoping to normalize human biological rhythms altered by the disease. Natural ways to treat depression include taking a temporary vacation in the winter to places where there is more daylight and longer hours. In addition, prolonged exposure to the street on sunny days helps overcome depression. Light therapy or phototherapy is most indicated for seasonal mood disorder, especially if episodes of worsening depression occur in the winter or spring seasons. According to some authors, with a course of light therapy from three to fourteen days, the effectiveness of this method reaches 60-70%.
It has been experimentally proven that changes in biological rhythms occur when the patient is illuminated with a light source of increased intensity. Attempts have been made to prevent seasonal exacerbation of affective psychosis by “lengthening the daytime period” using artificial lighting and sleep deprivation.
It is assumed that bright and intense light has a multifaceted effect on the centers of circadian rhythms: suppression of the secretion of the pineal gland hormone melatonin, changes in the concentration of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, increased synthesis of catecholamines, normalization of the function of the autonomic system. Most experts associate the positive effect of light therapy with an increase in the regulatory function of the cerebral cortex, as well as with the normalization of the activity of the autonomic system.
During light treatment, the patient stays daily, preferably in the morning, for several hours (less than half an hour) in a brightly lit room or next to an intense light source specially designed for this purpose.
It was previously believed that to obtain a therapeutic effect, a room illumination of at least 2600 and no more than 8000 lux was required. Such illumination was achieved by using incandescent lamps located on the ceiling of the chamber at a height of about 2.5 meters. Typically about 30 200 W incandescent lamps were used. It was noted that the effectiveness of light treatment increases when the therapeutic room is painted white or green, as well as when the patient’s body is exposed to the maximum (more than 25%).
Before starting light therapy, the patient is carefully examined, usually paying attention to the state of the autonomic system and indicators of the cardiovascular system.
Long therapy sessions were recommended - from 1.5 to 3 hours, with a total number of sessions - 15, however, it was emphasized that these numbers, as well as the time of the therapy session, should be determined based on the characteristics of the clinical picture of depression. Currently, 30 minute phototherapy sessions are recommended.
Some researchers recommend light treatment at any time of the day, both daily and with two- to three-day breaks. Phototherapy sessions are especially effective in the morning, immediately after waking up.
During the therapy session, patients, who are asked only to keep their eyes closed, are free to move around the room. To avoid getting used to the light, once every 3 minutes. should be looked at periodically for 1 second. on the lamps.
After a therapeutic session, there may be an increase in blood pressure, less often a decrease, probably due to the thermal effect, the body temperature usually increases. Quite often, patients report slight drowsiness. Changes in the RR interval on the ECG can be a reliable predictor of the effectiveness of light therapy. In some cases, the therapeutic effect is possible both during the session and 2-3 days after its completion.
The most common complications of phototherapy are: insomnia, increased fatigue, irritability, headaches. These complications usually occur in people who try to work hard during light therapy.
It is interesting to note the sensitivity to light therapy in patients with symptoms of anxiety. Patients with symptoms of melancholy and apathy respond to this type of therapy to a lesser extent. Speaking about the mechanism of the therapeutic effect of this therapy, we should emphasize the thermal effect of light. General contraindications to light treatment are cancer and eye pathology.
Currently, special table-top and stationary devices have been developed for non-drug treatment of depression using light. Full spectrum lamps are more effective because they produce light that is close to natural light. To ensure that the patient does not suffer from light treatment, special filters are used that block ultraviolet rays and thereby protect the patient’s retina from intense radiation (prevention of cataracts).
Recent studies have shown that the effectiveness of light exposure is determined by three characteristics: intensity, spectrum and exposure time. In connection with the above, phototherapy techniques are being developed to enrich the light flux with long-wave ultraviolet radiation, which has a biologically active effect. This technique involves using a full-spectrum light source, since it is as close to natural light as possible.
Modern achievements of phototherapy include “artificial dawn” (a special electric lamp at the patient’s bedside that intensifies its illumination before dawn).
Biofeedback
Non-drug treatment methods include biofeedback, which by and large refers to psychotherapeutic methods of treating depression. To carry out this method of treatment, special psychophysiological equipment is used, which implies the possibility of printing various psychophysiological indicators: bioelectric activity of the brain, muscles, heart, galvanic skin response, etc. 20-25 sessions of therapy are carried out, based on the use of biofeedback and aimed at increasing power of alpha waves in the left occipital region. Most patients experienced a 50% reduction in the severity of depressive symptoms.
Anxiolytics
For manic and depressive states, medications against anxiety and fear are used, they are called anxiolytics, or sedatives (sedatives).
As the instructions for use indicate for the product “Phenotropil”, it is part of the group of nootropics, improves blood supply to the brain and cognitive functions. It has a psychostimulating effect, improves endurance in case of tension, increased stress, mood swings and other similar conditions. Prescribed for cerebrovascular insufficiency, neuroses, asthenia, depression, apathy in schizophrenia, abstinence after drinking alcohol or drugs. This is confirmed by the instructions for use for the drug "Phenotropil".
In addition, in cases of nervous disorders, doctors prescribe Tenoten or Afobazol. These drugs help with excessive suspiciousness, stress, and anxiety.
"Afobazole" belongs to the group of axiolytics. It has a double effect - it reduces nervous tension and slightly stimulates. The mental and physical condition of a person improves with this effect.
It is difficult to say which is better - Afobazol or Tenoten. Reviews confirm that Tenoten is a homeopathic medicine that contains special antibodies to the S-100 protein. Available in tablets. Normalizes the number and ratio of nerve mediators in the brain.
The result is the restoration of plasticity processes in the nerve endings. Calm occurs, anxiety disappears, and mood improves.
Levomepromazine tablets are a phenothiazine derivative. Blocks the action of dopamine receptors in various structures of the brain, thereby providing an antipsychotic effect. This increases the secretion of prolactin by the pituitary gland. Levomepromazine reduces the productive symptoms (such as hallucinations, delusions, psychomotor agitation) of psychosis. It is taken orally, intravenously. Gradually switch to taking 50-100 mg per day (maximum - up to 400 mg).
Therapeutic massage and breathing exercises
Auxiliary methods for treating depression include breathing exercises, therapeutic massage (especially if the onset of depression is triggered by mental trauma) and meditation.
Such breathing on the seashore, in a pine forest, is useful, since such breathing increases the amount of oxygen. The massage is usually performed for 30 minutes and its therapeutic effect is associated with a decrease in stress hormones in the blood. In addition, massage relieves internal tension and normalizes sleep.
Diet food
The effectiveness of dietary nutrition as a non-drug treatment for depression has also not been confirmed by scientific research.
However, it is generally accepted that the diet of a patient with depression must necessarily include complex carbohydrates, which naturally contribute to an increase in the production of serotonin by brain neurons, the deficiency of which during depression (especially with symptoms of anxiety) is well known. Complex carbohydrates are found in legumes and whole grains. An increase in the production of norepinephrine and dopamine - neurotransmitters, the concentration of which is reduced in depression with symptoms of apathy, is promoted by a diet high in protein (beef, poultry, fish, nuts, eggs). At the same time, there is an opposite point of view about the inadmissibility of a high protein content in food that should be consumed when suffering from depression. It is recommended to exclude sugar, alcohol, caffeine, convenience foods and canned food. Foods high in saturated fatty acids are undesirable. Return to Contents
What is depression afraid of?
Willpower is what can help you overcome a disorder and never return to it again.
It should be immediately noted that this quality does not appear suddenly, out of nowhere. It needs to be developed and cultivated step by step. Of course, it is more convenient and comfortable for our psyche to lie in bed, laze around, looking at the ceiling. But you must understand that laziness, negativism, powerlessness are excellent fertile soil for cultivating depressive ideas. And even antidepressants, without your efforts, will turn out to be the remedy that can only lift you out of despondency for a short period of time: after you stop taking them, everything comes back again.
Know: depression does not like efficient, positive, active individuals. Learn to counteract your fears, laziness, and despondency. If you want to lie down and mope, get up and start doing something: anything, even just wash the dishes. If you want to complain about a difficult fate, instead, say something positive or interesting, give a compliment to your interlocutor.
Work on yourself, even if it is difficult at first. And get results!