Greetings, friends!
Most often, the phrase “deviant behavior” is used in relation to teenagers to emphasize their rebellion, tendency to break rules and other features of a “difficult age”. In addition, this concept is almost always given a negative meaning in order to emphasize that this is an undesirable and even dangerous deviation from the norm.
But from a psychological point of view, deviant behavior is not always a negative phenomenon, especially considering that generally accepted social norms can be illogical, meaningless and even destructive. Today we will analyze in detail what deviant behavior is, why it occurs, what it is like, how to recognize it and how to avoid negative consequences.
Definition of the concept
Deviation from generally accepted social norms is defined as deviant behavior. There are quite numerous examples of this phenomenon. At the same time, specialists from various fields define deviant behavior in their own way:
- From a sociological point of view, we can say that this is a phenomenon that poses a real threat to human survival in society. In this case, we are talking about both the deviant himself and his environment. In addition, there is a disruption in the processes of assimilation of information, reproduction of generally accepted values, as well as self-development and self-realization.
- From a medical point of view, disruption of interpersonal interactions and behavioral deviations are caused by the presence of neuropsychic pathologies of varying severity.
- From a psychological point of view, deviant behavior is an antisocial way of resolving conflict situations. At the same time, there is a desire to harm one’s own and public well-being.
Signs
The characteristics of deviant behavior are formed by psychologists using several signs. A person's condition can be diagnosed through simple observation. Signs of behavioral deviations are:
- Aggression. Assertiveness, aggressiveness, and intransigence allow a person to defend a position without taking into account the opinions of others. Other people avoid interaction with the deviant, which allows them to go undetected for a long period.
- Uncontrollability. A person is prone to total control, but due to continuous tension he is not able to reason logically and make decisions. The deviant may be confused in his reasoning, which leads to self-doubt.
- Change of mood. A deviant personality is characterized by impetuous jumps in the emotional background caused by overstrain of the nervous system and depletion of the body’s resources.
- Stealth. To achieve a goal, an individual needs to remain unnoticed by others for as long as possible. Secretiveness gives rise to suspicion and reluctance to communicate, which leads to emotional vacuum and exhaustion.
Main reasons
Unfortunately, psychologists still cannot accurately determine the range of reasons that provoke deviant behavior. The examples provide only a rough list. It looks like this:
- inconsistency between the goals set and the available means that can be used to achieve them;
- a decrease in the level of society's expectations from a particular individual, which gradually leads to marginalization;
- addiction to alcohol and drugs, deterioration of the genetic fund and other social pathologies;
- mental illnesses of various types;
- lack of clear motivation that would allow one to accurately determine adequate actions for a specific situation;
- social inequality and injustice that encourage aggression;
- armed conflicts, man-made disasters and natural disasters that disrupt the human psyche.
Characteristics of a deviant
Increasingly, in society one can encounter such a phenomenon as deviant behavior. Examples allow us to highlight a number of common features that are common to all people with this problem. Thus, deviants can be characterized as follows:
- cause a sharp negative reaction and condemnation from society;
- may cause physical or material harm to themselves or others;
- abnormal behavior is constantly repeated or has a permanent character;
- there is social maladjustment;
- behavioral deviations are fully consistent with individual personality characteristics;
- there is a desire to express one’s personal characteristics.
What is the norm?
A social norm regulates the behavior of people in society, their relationships with each other and with society as a whole.
There is an idea of normal behavior. This is a historically established option; it presupposes a kind of framework of permitted or obligatory behavior.
Norms can be divided into two groups: officially established (for example, norms of legal laws, various instructions, etc.) and actually established ones . These latter include traditions, norms of etiquette, morality, etc.
TOP 4 articles that are read along with this
- 1. Unemployment
- 2. Conflicts in society (8th grade)
- 3. Types of legal liability (table)
- 4. Dictionary of non-verbal means of communication
Officially established and actually established norms may not coincide. For example, everywhere in cities they ignore the rules for walking dogs only in special areas. This norm is official, but in fact not established.
Sometimes it happens that an officially created norm has a disorganizing effect, that is, it is abnormal. This is possible in the case where there is voluntarism of legislators. One can cite as an example the anti-alcohol campaign in the USSR in the 80s, which led to the creation of a mass of underground enterprises for the production of alcoholic beverages.
Examples of deviant behavior in society
Despite the fact that theoretical definitions clearly describe behavioral signs, they do not always fully reflect the essence of the phenomenon. However, if you look around, you will be surprised how often deviant behavior occurs in society. Real life examples are as follows:
- People without a fixed place of residence. Due to the prevailing circumstances, their behavior differs significantly from generally accepted norms.
- Begging may cause pity or negative reactions from others. In any case, in a society where the vast majority provides themselves with material resources through work, such behavior is perceived inadequately.
- Prostitutes are morally reprehensible.
- Drug addicts and alcoholics are recognized as deviants not only because of their dependence on the use of certain substances. When intoxicated, they can pose a real physical threat to others.
- Oddly enough, monks, from the point of view of society, are also considered deviants. Most people do not understand the desire to give up all public benefits and opportunities.
- Geniuses are also treated with caution, despite the fact that scientific and technological progress has firmly entered modern life. Nevertheless, the attitude towards people with a high level of intelligence cannot be called negative.
- Murderers, maniacs and other criminals are condemned not only by society. The legislation provides for severe punishment for them.
When considering deviant behavior, examples from life can be given for a very long time. So, for example, someone might include here people of art, parasites, informal people, and so on. In any case, if desired, a person can rid himself of such a characteristic (regardless of whether it is acquired or congenital).
Prevention
Early age-related prevention of deviant behavior will help to effectively increase personal control over negative manifestations.
It is necessary to clearly understand that children already have signs indicating the onset of deviation:
- manifestations of outbursts of anger that are unusual for the child’s age (frequent and poorly controlled);
- using intentional behavior to annoy an adult;
- active refusals to comply with the demands of adults, violation of the rules established by them;
- frequent confrontation with adults in the form of arguments;
- manifestation of anger and vindictiveness;
- the child often becomes the instigator of a fight;
- deliberate destruction of someone else's property (objects);
- causing harm to other people using dangerous objects (weapons).
A number of preventive measures implemented at all levels of society (national, regulatory, medical, sanitary, pedagogical, socio-psychological) have a positive effect on overcoming the prevalence of deviant behavior:
- Formation of a favorable social environment. With the help of social factors, an individual’s undesirable behavior with possible deviation is influenced - a negative background is created regarding any manifestations of deviant behavior.
- Information factors. Specially organized work to provide maximum information about deviations in order to activate the cognitive processes of each individual (conversations, lectures, creation of videos, blogs, etc.).
- Social skills training. It is carried out with the aim of improving adaptability to society: social deviation is prevented through training work to build resistance to abnormal social influence on the individual, increase self-confidence, and develop self-realization skills.
- Initiation of activities opposite to deviant behavior. Such forms of activity can be:
- testing oneself “for strength” (risky sports, mountain climbing),
- learning new things (travel, mastering complex professions),
- confidential communication (helping those who have “stumbled”),
- creation.
- Activation of personal resources. Personal development, starting from childhood and adolescence: involvement in sports, personal growth groups, self-actualization and self-expression.
An individual learns to be himself, to be able to defend his opinions and principles within the framework of generally accepted moral norms.
Only with the adequate formation of a person as a personality, an understanding of deviant behavior as an unacceptable and unacceptable form of interaction between the individual and society is created in his consciousness.
Examples of positive deviant behavior
Positive deviant behavior is actions aimed at changing outdated values and norms that hinder further social development. It can manifest itself in creativity, political activity, or simply personal protest. Despite the fact that at the initial stage society may have a negative attitude towards such phenomena, examples of positive deviant behavior prove the effectiveness of this model:
- G. Perelman is a brilliant mathematician who became famous for proving the Poincaré theorem (other scientists worked on this for more than 100 years). As a result, he was nominated for several prestigious awards. But Perelman categorically refused all awards, which is bad form in scientific circles. However, this behavior did not bring any harm to society. In addition, Perelman considered it unnecessary to belittle the contributions of other mathematicians and generally transfer science to a commercial plane.
- The next example is also quite interesting, but there is no evidence of its veracity. Thus, the original method of psychiatrist D. Rogers was recognized as a mockery of patients, for which he was sentenced to death. The idea was to bring the patient to an extreme form of hysteria, after which he would recover and continue to live a normal life. Only 50 years after the execution, the doctor’s deviant behavior was recognized as effective.
- Some examples of positive deviant behavior have had a significant impact on our lives today. So, in the late 60s, computers were the size of a living room or even a school gym. A real revolution in this area was made by Steve Jobs and Bill Gates. What many considered madness, they brought to life. Today, almost everyone has a compact and functional computer.
Suicide and delinquency
The intention to take one's own life or try to intimidate others in this way are also features of deviant behavior. The most dangerous age for young people is 16–19 years old: at this time, disappointment in life usually sets in due to a failed first love, the inability to find a job or continue education. Social status, conflicts with society and stress are also powerful impetus for suicide. For people with suicidal tendencies, psychological help services and helplines are organized. Preventive work is also important: raising a child to be a cheerful optimist, demonstrating by example that life is wonderful, and the black stripes that are found in almost everyone only add variety and tart zest to it.
Offenses are a form of antisocial behavior that is directed against citizens, society, and the way of life. Teenagers have different motivations: from ordinary mischief to unmotivated aggression. In order to protect the growing generation from the influence of the criminal world, it is necessary to conduct lessons on relevant topics in schools. Parents, for their part, are obliged to explain that breaking the law is bad, causing harm or hurting others is unacceptable, and deviant behavior is punishable in any case.
Examples of situations of deviant behavior
Without even thinking about it, every day we encounter situations of deviant behavior. An example might be:
- A physically healthy young man enters public transport and takes an empty seat. There is nothing wrong with this, but at the next stop an elderly man gets on. Not wanting to give up his seat, the young man begins to pretend that he is sleeping and does not notice the old man. In most cases, this deviation is due not only to personal qualities, but also to improper upbringing.
- The student constantly violates discipline in the classroom, disturbing the teacher and his peers. Unfortunately, such manifestations of deviant behavior often cause a sharp reaction from teachers, which generates even greater resistance. As a rule, indiscipline among schoolchildren is a direct reflection of the psycho-emotional state and problems in the family.
- Social inequality and financial difficulties, in theory, should encourage people to take active action to overcome this situation. However, not everyone has the willpower to do this. Some people start using alcohol or drugs to escape reality, which inevitably causes social condemnation.
- People strive for the benefits of life, but the ways of obtaining them are different for everyone. For example, many, not feeling the desire or strength to earn money on their own, resort to theft.
Literary examples
If you are interested in examples of deviant behavior, you can learn a lot of interesting things from the literature. Here are the most striking of them:
- Raskolnikov from Dostoevsky’s “Crime and Punishment” demonstrates an example of deviant behavior. For the sake of material gain, he decides to kill.
- Chatsky’s behavior in the play “Woe from Wit” by Griboyedov. This character is sometimes hot-tempered and completely tactless. He acts as an exposer of other people's vices, as well as a strict judge of moral principles.
- In Tolstoy's novel Anna Karenina, the main character can also be cited as an example of deviant behavior. Adultery, extramarital affairs, and suicide are the clearest signs.
- In Makarenko’s “Pedagogical Poem,” almost all the orphanage students in one way or another personify deviant behavior. This work is interesting primarily because the talented teacher managed to correct the situation.
- The hero of Balzac's "Gobsek" is a rather interesting example of deviant behavior. A greedy moneylender has a pathological tendency to accumulate. As a result, in his closet they find a huge amount of material assets, as well as food that has simply spoiled.
Behavior of children and adolescents
Children and adolescents may be characterized by forms of deviant behavior of all groups: theft, fighting, begging, substance abuse and computer addiction, suicidal acts, etc.
In childhood and adolescence, the reason for such behavior is usually following group values. There are various methods for diagnosing the tendency of children and adolescents to deviant behavior and are widely used. Their main goal is to identify addiction tendencies.
Based on these techniques, various correction methods are used to protect children from the possible consequences of a tendency towards deviant behavior, teach them to interact with society, instill the ability to smooth out conflicts, and respect the norms of behavior accepted in society.
Examples from history
If you are interested in such a question as examples of deviant behavior, you can find quite a lot of interesting situations in history:
- One of the most striking examples of deviant behavior is the arson of the Temple of Artemis by a local resident of Ephesus, Herostratus. During torture, the man had to admit that he did this to glorify his name, so that his descendants would talk about him. Herostratus was not only sentenced to death, but also forbidden to mention him. Nevertheless, the historian Theopompus considered it necessary to talk about the crime of Herostratus, and therefore his goal was achieved.
- Adolf Hitler's behavior is also considered deviant. The particular danger was that he had strong leadership qualities and had power. The sad result is known to everyone.
- Another example of deviant behavior can be seen in the 1917 revolution. Then V.I. Lenin and his comrades decided to oppose the power of the tsar. The result was the formation of a fundamentally new state.
- There is a lot of evidence about how the deviant behavior of soldiers during the Great Patriotic War contributed to victory in battles. Thus, soldiers often sacrificed themselves by throwing themselves under the tracks of tanks with grenades. In this way they paved the way for their army. This is one of many examples of deviant behavior, which as a result are called a feat.
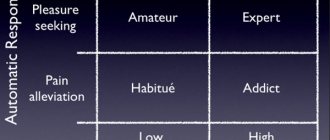
Positive deviance: what is it?
In modern science, the definition of deviation is most often correlated with negative mental manifestations of a person.
But there is also a downside: deviance can be positive, that is, one that is not destructive. The greatest interest today is caused by such a deviant personality trait as its genius, which may be unbridled and not perceived as normal behavior. Millions of people around the world are engaged in independent creativity, as well as the creation of works of art, but only a few take this to a qualitatively new level and create completely new objects. Such people are characterized by a different way of thinking, which helps them look at the world around them from other sides and, accordingly, not succumb to the influence of everyday life, and think differently. Few also reach the pinnacle of mastery: some lack professionalism, while others only need one idea, and they do not want to develop further. But there are people who find themselves at the pinnacle of success, and they are called naturally gifted, geniuses, child prodigies.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Positive deviant behavior 490 rub.
- Abstract Positive deviant behavior 270 rub.
- Test work Positive deviant behavior 250 rub.
Get completed work or advice from a specialist on your educational project Find out the cost
Such individuals devote their entire lives to either art, science, or the invention of new things, which subsequently penetrate into everyday human life, making it more interesting, richer, and at the same time much more easier. However, their way of life is not always correctly assessed by others; in principle, it may not be entirely understandable to the masses. Such a person has the following traits:
- He refuses to start a family in order to devote his entire life to inventions;
- He refuses the banal comfort of everyday life, devoting himself entirely to his work, forgetting about basic human needs;
- It is rather impractical in everyday affairs, since it is initially tuned to solving complex and controversial “high” problems. He is simply not equipped to resolve everyday issues, and therefore faces serious difficulties.
Note 1
In addition, people who are geniuses are quite capricious, they are perfectionists, and therefore cannot allow things to look wrong or events to not go the way they themselves planned. They are very picky about any little things, and this can irritate others, since their behavior sometimes reaches the point of absurdity, which is why other people do not understand them.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
Often the deviance of creative and gifted people is reflected in works of art. They can also have a specific form and content, and not everyone can understand them. However, we should not forget that art can be interpreted in its own way, and in any work a person can find something of his own, he begins to like it, and through these processes he realizes that the artist is not a strange person: he, like everyone else, has his own unique view of things, and this does not carry any negative connotations.
Children's deviant behavior
Unfortunately, deviant behavior in children is not uncommon. Examples that are most common are verbal aggression (foul language, rudeness and rudeness) and physical attack (hitting, biting or pushing). This phenomenon has specific reasons, the main ones being the following:
- Genetic predisposition to aggression, which is transmitted from close relatives. It is worth paying special attention to diseases associated with hearing and vision impairment, delayed mental and physical development, and mental disorders.
- The influence of external stimuli on the child’s psyche. This may be due to a tense situation in the family, conflicts with peers, or biased attitudes on the part of teachers.
- Physiological defects (speech or physical) often cause ridicule and negativity from others, and especially from children. This causes the child to feel inferior, which becomes one of the main causes of aggression.
To prevent and correct deviant behavior in children, the following measures can be taken:
- the task of adults is to arouse in the child a keen interest in communicating with peers, as well as teachers, psychologists and other adults who can help in solving the problem;
- formation of knowledge about the culture of behavior in society and skills of live communication with others;
- assistance in developing an adequate assessment of one’s own personality, as well as training in self-control techniques that will help stop attacks of aggression;
- independent or shared reading of fiction that contains positive examples of correct social behavior;
- organizing situational games during which children will independently model ways to resolve conflicts;
- rejection of habitual censures and prohibitions in favor of constructive dialogue, which is aimed at explaining to the child why deviant behavior is unacceptable.
Help
How can we pull teenagers out of the asocial abyss in which they are mired? Sociologists say: firstly, a special government program will help. The deviant behavior of children must be taken under control; this is the task of specialists. Favorable conditions must also be created for the opening of rehabilitation centers of various directions, in which experienced specialists could rid young people of addictions and direct their energy into productive and useful channels for society.
Secondly, invaluable help will be provided by hotlines operating in every city, nationwide helplines and regional family consultations with psychologists.
Thirdly, the study of the adaptation environment of adolescents should not stop for a day. Deviant behavior of schoolchildren requires constant adjustment, which must take place in full cooperation with the juvenile affairs inspectorate, doctors, police officers, and representatives of the guardianship authorities. If necessary, such children must be removed from the family if the cause of the deviation is precisely the influence of the parents.
Deviant behavior of adolescents
A pressing problem is the deviant behavior of adolescents, examples of which, unfortunately, are numerous. The first manifestations can be noticed around 12-13 years of age. This is the most dangerous age, when a child still has a child’s perception of the world, but at the same time there is an irresistible desire to show himself to adults. Even if children behave normally, it is extremely important not to miss this period. An alarming signal may be a change in preferences in music and clothing, as well as the first manifestations of rudeness. If educational measures are not taken in time, this can lead to the following consequences:
- running away from home and vagrancy;
- smoking, as well as alcohol and drug use;
- theft;
- association with “bad” companies;
- criminal activity;
- passion for extremist ideas;
- computer addiction;
- early sexual life;
- life-threatening hobbies.
There are known examples of negative and positive deviant behavior of adolescents. If everything is clear with the first, then many perceive the second as a normal manifestation. This may be about excessive effort in learning or physical development. Despite the fact that these actions have a positive connotation, it is important to ensure that the child does not withdraw into himself, so that hobbies do not replace communication with peers.
Deviant behavior: positive and negative
There is a variety of behavior in society that goes against expectations and cultural norms. Let's consider the following situations:
- Yesterday Maxim entered a 24-hour store and robbed the cashier.
- Anna was issued a fine for exceeding the speed limit by 15 km.
- Maria, who had just gotten married, decided to keep her maiden name instead of taking her husband's last name.
Which of these three people would have behavior that would be considered “deviant”? The correct answer would be all three. Both negative and positive deviant behavior is any action that is perceived as violating a cultural norm of a society or group. It is norms that dictate what is considered acceptable and unacceptable in different cultures.
One category of deviance is crime, which occurs when someone violates the formal laws of society. Criminal deviance covers a wide range of behavior, from minor traffic violations to arson or murder.
Maxim, who robbed a supermarket, and Anna, who ignored the speed limit, fit into this category. However, laws constitute just one set of a complex system of countless rules—formal, informal, written, implied, etc.—that we are expected to conform to. Any act of non-compliance with these rules is considered deviant.
Absolutely everyone commits small violations: someone forgot to return a library book on time, someone ran across the road at a red light, someone skipped several lessons at school, someone did not give up their seat to their grandmother on the bus. Non-conformity is not always a negative example of rule-breaking.
Whatever deviant actions are, negative or positive, they have a common feature - difference from the norm. What does positive deviant behavior look like? Maria's example shows that even if a girl does not commit a crime by choosing to keep her maiden name, she is still performing a deviant act, since taking her husband's surname is the norm in our society.