Kinds
Stuttering that occurs in adults manifests itself only in communication with others, if the disorder is not associated with organic damage to the brain.
Logoneurosis is divided into 2 types:
- Stuttering of a neurotic nature. The reason is a stressful situation.
- Organic disorder or logoneurosis of neuron-like form. Occurs under the influence of mechanical damage to the brain. This occurs due to birth trauma, tumors, strokes, oxygen starvation or ongoing inflammatory processes. The symptoms of stuttering in this case in a person do not depend on his emotional state. Stuttering in this case is accompanied by convulsive twitching of the facial muscles and various body movements.
In medicine, according to the characteristics of convulsive movements, 3 types of stuttering are distinguished:
- Clonic. In this case, spasms of the muscles that are involved in pronouncing sounds contribute to the involuntary duplication of consonants, individual syllables or words.
- Tonic. Prolonged contraction of the muscles of the mouth and throat leads to a delay in speech, lengthens pauses between words, a person constantly repeats vowels and some voiced consonants.
- Mixed type. It combines movements of types 1 and 2.
Logoneurosis in adults (treatment is much more difficult than in children) in many cases has childhood roots. Whatever the root cause, neurotic or organic, the disease does not go away on its own with age, but becomes persistent, which greatly complicates treatment. Treatment should begin at the first sign of stuttering, even in childhood.
What is logoneurosis in adults
Nervous speech disorder implies the inability to speak smoothly, with a relaxed speech apparatus, while the patient has no organic reasons for this condition. A person may repeat syllables and words many times, experience throat spasms, nervous twitching of facial muscles, and sudden shortness of breath. In connection with these symptoms, logophobia arises - the fear of speaking. In ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision), logoneurosis has code F98.5.
Stuttering in adults can be explained by the difficulty of self-expression, self-doubt, fear of humiliation, public “shame,” excessive thoughts about how a person looks from the outside and how people perceive him. Often a person does not consider himself worthy to communicate on equal terms, to express himself freely and boldly, he sees himself as uninteresting and “worse than others.” Like all existing neuroses, logoneurosis almost always occurs in sensitive people with high demands on themselves and complexes.
If stuttering haunts an adult throughout his life, one can add to the prerequisites demanding and authoritarian parents, often neurotic, who cut off the child’s attempts to express his individuality.
Stages and degrees
Stuttering can be permanent or temporary. Symptoms intensify when a person is nervous or worried.
According to the nature of the course of the disease, the following stages are distinguished:
- Constant. Once a speech disorder occurs, stuttering is present in all situations involving the need to communicate through speech.
- Intermittent. Speech problems sometimes disappear and reappear. This is due to emotions and stress.
- Periodic. Stuttering may disappear for a certain period of time, a person will forget about it, and then it returns again under the influence of unfavorable factors.
Neurotic form of stuttering - about the causes, manifestations, course
The neurotic form of stuttering appears suddenly at the age of 2-6 years. These are children born at term, without intrauterine infection, without complications during childbirth. They grow and develop normally according to their age, motor development is not delayed - the child crawled on time and walked on time.
Most children, before the onset of stuttering, already have certain personality characteristics - mood swings, fear of dark rooms, tearfulness, excitability, nocturnal enuresis. In an unfamiliar environment, such children become frightened, afraid of change, and adapt to kindergarten for a long time and have difficulty.
The neurotic form of stuttering in children occurs as a result of acute or chronic mental trauma. Acute mental trauma is a sudden fear, chronic is an unfavorable climate in the family, scandals. Neurotic stuttering develops in children with the active introduction of a second language, with bilingualism in the family, or with parents’ enthusiasm for methods of early child development. In this case, learning a second language is accompanied by great nervous tension, which the child cannot always bear.
The course of the neurotic form of stuttering can be favorable when, after changing the environment and carrying out therapeutic measures, a rapid reverse dynamics is observed - the child’s speech is completely restored. An unfavorable course is typical for children with a hereditary predisposition to stuttering (mom or dad stutters), against the backdrop of a persistent conflict mood in the home.
Neurosis-like stuttering begins to appear in children 3–4 years old without any visible prerequisites. Deviations are observed in psychomotor function. Hyperactivity syndrome often manifests itself. The pregnancy history includes difficult gestation, toxicosis in the last trimester, and birth asphyxia. Children are quick-tempered, difficult to discipline, fussy, and restless.
All these symptoms are combined into a cerebral syndrome. Speech development is delayed. Speech pathologies are clearly expressed. Vocabulary is slowly accumulating. The child cannot structure his speech consistently. Many sounds are pronounced with a delay. Over the course of 1–6 months, stuttering occurs in waves, but there are practically no periods of speech without stuttering.
Clinical examination reveals mild organic damage to the brain centers responsible for motor skills. A speech therapy study shows that the speech apparatus is normal, but its movements are limited. Characteristic symptoms are insufficient mobility of the tongue, impaired coordination, and difficulties in finding articulatory forms.
In the neurotic form of stuttering, there is no dysfunction of the brain centers. Symptoms worsen under stress. If speech pathology does not disappear by a certain age, logophobia develops, which is reflected in behavioral deviations:
- patients refuse new acquaintances;
- patients try to talk less;
- Those suffering from neurosis use various tricks and cunning in their speech, and draw out their words.
Information is poorly absorbed, and persistent neurosis is observed. Symptoms depend on the neurotic form of stuttering. When fixed, additional symptoms are observed: sleep disorders, depression, neurasthenia, hypochondria, asthenic syndrome.
Symptoms
Noticeable signs of stuttering: frequent hiccups before speaking, reluctance to continue a conversation, lack of self-confidence during a conversation. Often people try to avoid conversation by nodding their heads, simply assenting, or avoiding public speaking.
Visible symptoms of logoneurosis:
- lengthening of sounds in words, unusual for ordinary speech;
- repeated repetition of individual sounds, syllables or even words;
- tense expression of muscles and entire face;
- difficulty breathing, lack of air;
- reluctance to start a conversation;
- neurotic state before the conversation begins.
Psychological causes of stuttering in children with different vectors of development
So, if a child with an oral vector of development (talker) in childhood receives good listeners in the person of his parents, when he can think in speaking, then he can grow into an outstanding speaker (teacher, etc.).
Such a child thinks out loud, and since children are constantly thinking about something, reflecting on everything they see around them, such a child constantly speaks without stopping. He likes to be listened to, so sometimes he starts making up tall tales.
But often parents cannot stand it and begin to make their own demands. And if the child also likes to embellish his stories, then they often hit him on the lips (“so that he doesn’t lie anymore”).
For an oral child, such a blow to the lips is a severe shock and trauma. His nature requires speaking, but an obstacle arises in the form of parental punishment. If this situation is repeated often, then such a child begins to stutter, and his speech begins to be distorted (lisp, burr, whistling, etc.).
It is known that a child with an anal vector of development (slow) is characterized by such characteristics as: slow but thorough learning (both everyday and other actions), asking again until he understands, indecisiveness, obedience, etc. He likes to get things done.
At the same time, an anal child enjoys recognition of his achievements and well-deserved praise from his parents, so he loves to study and please his parents (with behavior, order in the room, studies).
If such a child receives the necessary conditions for development, then he can grow up to be a very competent specialist, a professional in his field, or an outstanding scientist.
However, if parents constantly rush such a child, pull him back, interrupt him (speaks slowly), and do not allow him to finish speaking, then he begins to develop a speech disorder - stuttering.
Psychologists note that a child with a visual vector of development is the most impressionable and sensitive, and he experiences emotions with maximum strength.
Normal developmental conditions (a strong emotional connection with the mother, which gives a feeling of security and safety) allow this fearful child to grow up to be a fearless and compassionate person, capable of all-encompassing love for people. Therefore, such children often become medical workers, social workers, cultural workers, or do charity work.
The emotionality and sensitivity of a visual child contribute to the fact that fear received in childhood or severe emotional stress leads to a violation of his speech.
The stuttering of such a child is characterized by confusion, as if he is overwhelmed by emotions that do not allow him to pronounce words normally.
Reasons for appearance
Logorneurosis in adults (treatment depends on the cause of the disorder) has slightly different consequences than in children. If children experience only psychological discomfort when communicating, then stuttering in an adult affects his social life. Speech disorder is very often an obstacle to building a career, starting a family and living comfort.
The main factor that influences the development of stuttering in adults has not yet been sufficiently studied. In medicine, there are various theories explaining the pathogenesis of this disorder. Many are inclined to believe that several factors are involved in its development. This makes it difficult to determine the exact cause of stuttering.
19% of patients with this disorder had a genetic predisposition to it.
And yet the main reasons have been identified:
- Organic brain damage. Diseases of the head, central nervous system, and brain injuries cause stuttering due to abnormal nerve impulses. This form of the disorder is characterized by convulsive contractions of the facial and respiratory muscles. When talking, patients, in addition to facial muscle contractions, perform motor activity with their hands and head.
- Causes of a neurotic nature. Stress, difficult situations experienced in youth, and emotional experiences leave an imprint on speech. Logoneurosis often manifests itself before public speaking or competitions. In this case, stuttering has a short period of action.
- Incorrect or incomplete treatment of logoneurosis in childhood. Incomplete therapeutic actions aimed at eradicating stuttering in children lead to the disorder becoming chronic. In this case, treatment in adults will take longer and be more difficult.
- Hereditary factor. This category includes brain diseases that are genetic in nature, physiological characteristics of a person, or hereditary predisposition.
In adults, the causes of logoneurosis often affect the duration of its treatment.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, logoneurosis develops in childhood or adolescence. The set of reasons that led to its occurrence is very individual. Experts identify both neurological and genetic factors.
The prerequisites for the occurrence of logoneurosis include:
- children's age period from 2 to 6 years, when rapid accumulation of vocabulary occurs;
- on the contrary, existing other speech disorders (delayed speech development, general underdevelopment of speech, alalia, dyslalia, rhinolalia and others);
- certain properties of the nervous system (impressionability, vulnerability, increased excitability, emotional lability);
- pathological upbringing, violation of family roles;
- parents who stutter and their characteristic character traits;
- adolescence (15-17 years), when the child’s stress load increases due to the need to defend his social significance, as well as due to hormonal changes in the body;
- infectious lesion of the central nervous system;
- cerebral palsy (sometimes logoneurosis manifests itself in cerebral palsy as a concomitant disease);
- endocrine disorders.
In the presence of one or more of these factors, the disease can occur under conditions of acute stress (conflict in the family, sudden fear, etc.). Logoneurosis in adults occurs much less frequently than in childhood, but can also be triggered by a traumatic situation.
Treatment of logoneurosis should begin as early as possible, before the corresponding symptoms have time to take hold.
Logoneurosis in children involves complex therapy, and necessarily work with a family and child psychologist who will help the family develop a harmonious parenting style and create a comfortable psychological microclimate in the family.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of stuttering is not made immediately. Small pauses between words, rare repetition of words and syllables are not always an indicator of the presence of a disorder. Minor speech disturbances may indicate strong excitement, haste, or, conversely, thoughtfulness.
Some aspects of speech (singing, long pauses between words) may be distinctive features of a race or geographic region. Temperament may also contribute to changes in speech characteristics.
Moreover, it is not enough to diagnose “stuttering”; it is necessary to determine what neurotic type this speech disorder belongs to, since this will determine the correctness and effectiveness of the chosen treatment methods.
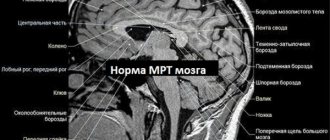
The specialist can prescribe various tests (blood and urine), as well as instrumental diagnostics, which can reveal organic brain damage at different stages. Instrumental methods in this case include MRI (tomography) of the brain and electroencephalogram (EEG).
All adults have many differences. It is necessary to determine the cause of the speech disorder in order to understand which treatment methods will be most effective.
This differential diagnosis with the participation of a speech therapist, psychologist, neurologist, psychiatrist based on a complete medical history, using the results of instrumental and laboratory studies can lead to a complete picture of the disease, establish or refute a hereditary predisposition to develop a plan for the effective control of this pathology.
Treatment of logoneurosis in adults
Let's talk about how to treat stuttering. First of all, the disease is treated by restoring the harmony of the nervous system through effects on the body. This goal can be achieved by a variety of methods - reflexology, physiotherapy, herbal medicine and the prescription of a medicine such as glycine or novopassit. The direction of treatment is chosen by the neurologist after examining the patient. Often several treatment methods are prescribed - for example, taking sedative herbs and acupuncture, or osteopathy and acupressure, or physiotherapy and manual therapy.
With the help of these methods, the emotional background is leveled, the transmission of nerve impulses is improved, the body's stability is increased, the excitation of the autonomic nervous system is reduced, and, as a result, symptoms are alleviated. In addition, quality sleep returns, mood becomes good, the overall tone of the body increases, and depressive states disappear.
Typically, integral therapy methods are prescribed in combination with speech therapy treatment. A speech therapist helps a person get rid of fear and constraint by repeatedly pronouncing problematic sounds. A speech therapist can also teach the patient breathing exercises and proper breathing. With mild forms of logoneurosis, patients completely get rid of unpleasant symptoms and regain the joy of communication.
If the problem goes away only temporarily or not completely, more serious treatment for logoneurosis is needed. This means that the reasons are deeper than a simple “nerve disorder” from fatigue and overexertion. A psychotherapist teaches a person auto-training and relaxation techniques, analyzes the causes of stuttering, helps eliminate the fear of speaking and increase self-confidence. We are also working with psychological trauma. Psychologists use the following techniques:
- Gestalt therapy;
- cognitive behavioral therapy;
- autogenic training;
- group therapy.
In some cases, the psychotherapist prescribes nootropic drugs - for example, piracetam, phenotropil, gopantam, anvifen, noofen, phenibut or pantogam. The most popular nootropics are the last two, they are prescribed most often. Pantogam has an anticonvulsant effect. Both phenibut and pantogam contain hopantenic acid, which stimulates brain function, reduces its sensitivity to stress factors and has a mild sedative effect. Which drug is better? Only your doctor can answer this question.
When to see a doctor
You can first make or disprove the diagnosis of stuttering by performing a couple of tests:
- Count the number of unnecessary pauses when speaking a text of 100 words. Up to 7 breaks is the norm. More than 10 pauses - a high probability of developing speech pathology.
- Watch your facial expression. If your facial muscles look tense during a conversation, there is a possibility of speech impediment. This is evidenced by the presence of pauses between words lasting from 1 to 30 seconds.
These tests are not accurate research methods, but are only a reason to begin a more thorough professional diagnosis.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
Speech therapists treat various speech disorders. A correct diagnosis is important for timely and effective correction of defects. At the onset of the disease, stuttering is sometimes confused with tachylalia, which is similar in appearance to logoneurosis. Tachylalia manifests itself in a pathologically fast pace of speech, incorrect phrase construction (battarism), stumbling, hesitating, and pauses (poltern).
- imitation of the speech of the child’s adult environment;
- lack of attention during speech formation;
- unclear, blurry articulation.
You can distinguish tachylalia from neurotic stuttering by comparing a number of factors.
Tahilalia:
- there is no awareness of the defect;
- the speech act becomes better under tension;
- focusing attention improves speech;
- requiring accurate answers improves speech;
- reading familiar text impairs speech;
- reading unfamiliar text improves speech;
- the writing is repetitive, hasty, the handwriting is unclear;
- indifferent attitude towards one’s speech;
- psychological experience delayed.
Neurotic stuttering:
- awareness of the defect is present;
- the speech act becomes worse under tension;
- focusing attention impairs speech;
- demanding precise answers impairs speech;
- reading familiar text improves speech;
- writing is slow, tense;
- attitude towards one’s speech with expressed timidity;
- anticipatory psychological experience.
Diagnosis of logoneurosis is carried out with the participation of a speech therapist and neurologist
It is important to identify the patient’s history of acute or chronic stressful situations. A diagnostic examination of speech determines a violation of its tempo, rhythm and smoothness, the presence of hesitations, stretching of individual sounds, repetitions of syllables
A neurological examination does not reveal significant abnormalities in the neurological status. There may be some revival of reflexes and signs of autonomic dysfunction.
It is necessary to differentiate neurotic stuttering from neurosis-like stuttering. The latter occurs as a result of TBI or various diseases of the central nervous system (ischemic stroke, intracerebral tumor, hydrocephalus, previous encephalitis), gradually progresses, and is not accompanied by logophobia and the patient’s attempts to hide the speech defect. As a rule, with a neurosis-like form of stuttering, organic personality changes are observed: difficulty switching, a predominantly euphoric mood, inertia. To completely exclude the organic nature of stuttering, additional studies should be performed: EEG, Echo-EG, REG, MRI or CT scan of the brain.
Logoneurosis and so-called stumbling should be differentiated. The latter is a consequence of early organic cerebral pathology and includes slurred speech due to articulation disorders, disturbances in the rhythm and speed of speech (choking speech, tachylalia), monotonous speech, rearrangement of semantic stress, difficulty selecting words, etc. Neurotic stuttering can be a concomitant disorder with some mental illnesses (schizophrenia, oligophrenia, psychopathy). In such cases, the patient is prescribed a consultation with a psychiatrist.
Treatment methods
Logoneurosis in adults (treatment depends on the severity) has several aspects related to the physiology, socialization and mental state of a person. And only comprehensive treatment that covers all these aspects can give good results.
The choice of treatment methods for stuttering in adults depends on whether the speech disorder is of a neurotic or organic type. Treatment for the organic type of stuttering comes down to fighting the problem that gave rise to it.
And since the cause of this stuttering is serious disorders in the functioning of the brain, often complicated by a genetic factor, the treatment of stuttering and its root cause can take months and years.
Neurotic stuttering in adults can be treated much easier and more successfully. An integrated approach is provided for it, including medication and alternative treatment prescribed by a neurologist, as well as systematic work with a speech therapist, psychologist and psychotherapist who will help the patient restore the normal rhythm of speech, overcome fears, join the normal rhythm of life, and establish communication.
Medications
The method of treatment with drugs is aimed at eliminating the convulsive syndrome and stabilizing the functioning of the central nervous system, which is responsible for the occurrence of various nervous reactions.
Medicines prescribed in this case can be divided into 3 groups:
- nootropics, which improve brain function;
- sedatives, relieving nervous tension;
- antispasmodics, which have an anticonvulsant effect.
| A drug | Action | Purpose | Dosage | Contraindications | Price, in rub. |
| Nootropics | |||||
| Phenibut | Analgesic, psychostimulating effect, prevents the formation of clots in the vessels of the brain, destruction of body cells and promotes their regeneration. | This medicine can be prescribed by a doctor as a medicine for a neurotic disease, which is expressed as a fear of communication. | Phenibut tablets can be taken at any time of the day, preferably after meals, swallowing the tablet whole. | pregnancy and lactation, liver failure, hypersensitivity to a component of the drug. The drug has virtually no side effects. You may feel drowsy when you start taking the tablet. The same symptom, especially in combination with nausea and vomiting, may indicate an overdose of the drug. | 260 |
| Sedatives | |||||
| Afobazole | A non-addictive tranquilizer. | Its action is aimed at eliminating anxiety, fear, and associated nervous, muscular and respiratory reactions. | It is recommended to take the drug after meals in the amount of 1-2 tablets (10 mg) three times a day. Typically, the course of treatment lasts 14-28 days, but if necessary, the doctor can increase the dosage (up to 60 mg per day) and the course duration up to 3 months. | Pregnancy and breastfeeding, individual intolerance to the drug or its individual components, as well as age less than 18 years. | 400 |
| Novopassit | A preparation based on a rich collection of plants (valerian, lemon balm, St. John's wort, hawthorn) | It has a good sedative and calming (anxiolytic) effect. Available in the form of tablets or solution (syrup). | The usual single dose is 1 tablet or teaspoon of syrup (5 ml), pure or diluted in water. The drug is taken 3 times a day before meals. If the drug causes depression, the morning and evening doses are halved, and the daily dose remains unchanged. | Age under 12 years, myasthenia gravis (genetic neuromuscular disease), individual intolerance to the drug or its components. Side effects: discomfort in the digestive tract (changes in density, stool), less often dizziness and drowsiness, as well as allergic manifestations and weakness. | 250 |
| Antispasmodics | |||||
| Magnerot | An anticonvulsant drug replenishes magnesium deficiency in the body, which causes seizures and increased excitability | Among antispasmodics for stuttering in adults, doctors usually prescribe Mydocalm, Magnerot and Finlepsin in combination with vitamin B preparations. | Taking the drug can be divided into 2 stages: 7-day course: 2 tablets 3 times a day. In week 2: 1 tablet 2-3 times a day. The full course of treatment lasts from 2 to 4 weeks, sometimes more. The tablets are taken with a small amount of water before meals. | Kidney and liver diseases, bladder stones, lactose intolerance and lactase deficiency, age under 18 years, as well as individual intolerance to the drug. Side effects: common ones include changes in the frequency and quality of stool and the reaction of the immune system. | 400 |
Many drugs have contraindications, such as kidney and liver diseases, bladder stones, lactose intolerance and lactase deficiency, age under 18 years, as well as individual intolerance.
Traditional methods
Many patients, and most often their relatives, tend to treat stuttering at home. But at home there is no way to implement an integrated approach to treatment. But it is possible to train at home if you first study some elements of self-help, such as self-study, self-hypnosis, breathing exercises, for example, according to Strelnikova’s method, and the use of yoga elements.
Various breathing exercises for adults, in accordance with Strelnikova’s system, should be based on proper breathing during movements: a sharp inhalation and a long, calm, quiet exhalation, the active participation of the diaphragm during the breathing process. All active movements (squats, head turns, body bends) are performed only by inspiration.
Speech gymnastics at home helps develop proper breathing during a conversation.
Examples of tongue twisters for training speech and breathing:
- There is grass in the yard, there is firewood on the grass: one firewood, two firewood - don’t cut wood on the grass of the yard.
- Advertising for grips has seams with coverage, but potholders without coverage have been snatched up.
- Our head overtook your head, overdid it.
Aromatherapy has a positive effect. All the esters that are present in essential oils can ease nervous tension and calm fears. These include oils of bergamot and pine, rose and sandalwood, rosemary and basil, sage and geranium, and lavender. The inhalation procedure should be repeated 3 times a day.
Aromatic oils mixed with kefir can be used for bathing. To do this, take 100 g of fermented milk product and add 5-6 drops of any of the above essential oils. The oil-kefir mixture is added to a bath of warm water.
Logoneurosis in adults (treatment also includes herbal remedies) can be stopped with herbs in the form of decoctions and infusions.
Here are some of them:
- Take 5 g of aromatic rue, chop, add 2 glasses of water and boil for 5 minutes.
- Filter and cool slightly. Hold the hot broth in your mouth until it cools completely. The procedure is repeated very often (at least 6 times a day).
- Prepare a herbal mixture of chamomile, mint, nettle and valerian, taking 0.5 g of each herb.
- Pour a glass of boiling water over the herbal mixture and simmer for 15 minutes. Drink ½ glass of infusion 2 times a day.
Other methods
In addition to drug treatment, patients with logoneurosis are treated with hypnosis and acupuncture. One of the methods of therapy is the help of a speech therapist, who either corrects existing speech skills or instills new, correct ones. About half an hour after these exercises, massage treatments are prescribed.
Massage for stuttering in adults is presented in the form of reflexology (acupressure) and osteopathy (the effect of gentle massage on the muscles), which have a positive effect on the articulatory vocal apparatus and the respiratory system.
At the third stage of stuttering treatment in adults, therapeutic exercises, a swimming pool and a sauna are indicated.
There are many different methods of complex impact on the problem using various speech training systems, starting with visual communication and ending with public speaking in a team (a group of patients with the same problem).
Physiotherapeutic treatment of stuttering, in addition to reflexology and osteopathy, includes:
- Darsonvalization of the muscles of the face and neck is the effect on the muscles of alternating current of high frequency and voltage, but with low strength and short-term exposure to sinusoidal currents on the larynx.
- Procedures for restoring and optimizing the functions of the central nervous system (electrotherapy, therapeutic baths and massage, franklinization, alpha massage, various types of relaxation).
Traditional treatment of the disease
Neurologists have extensively studied the causes of stuttering in adults. Treatment options are tailored to each individual case. The longer a person stutters, the more effort and time it will take to rid him of the problem. If your speech skills are not formed correctly, you need to persistently practice. In an atmosphere of stress, overcoming stuttering is impossible. If you are exhausted by endless quarrels with neighbors or nagging from your superiors, you should distance yourself from the irritant.
Time-tested methods will help you get rid of stuttering forever:
- breathing exercises by A. Strelnikova;
- speech therapy classes.
Speech therapy session is an auxiliary method of stuttering treatment
Gymnastics Strelnikova
It is worth mentioning the principles of Strelnikova’s breathing exercises:
- the patient takes short, sharp and noisy breaths through the nose: simultaneously with each breath, he needs to perform movements that compress the chest;
- the patient does not think about exhalation; exhalation should be passive;
- load volume: 300 movements in 45 minutes;
- there is no pain in the patient’s muscles, there is no excessive stress;
- exercises developed by the author of the method involve all parts of the body;
- each breath is carried out on turns and tilts - these exercises involve the diaphragm;
- in 2 weeks of intensive training according to the Strelnikova system, the patient’s respiratory muscles are strengthened; this achievement is the first step leading you to getting rid of long-term stuttering;
- a person’s lungs are used to their full “power”, all organs, including the brain, are saturated with oxygen;
- Strelnikova’s gymnastics program includes sound exercises: their goal is to correctly position the patient’s voice.
How to control yourself when stuttering: a big advantage of gymnastic breathing exercises is that their conscientious implementation guarantees a person an increase in overall vitality.
If a patient in childhood faced several unsuccessful attempts to eliminate the disease, he subconsciously does not trust doctors and does not believe in healing. The work of a psychotherapist can help you cope with long-standing fears and doubts. It will be much easier to say goodbye to stuttering if you stop being afraid of “problem” words and begin to practice pronouncing individual phrases and large texts. When the patient ceases to be tormented by verbophobia (fear of speaking), therapeutic techniques for the treatment of stuttering soon bring the desired effect.
Competent help from a speech therapist
To make convulsive speech and awkward stutters a thing of the past, you should resort to speech therapy technologies for stuttering correction. A speech therapist will teach you correct speech techniques and help you adjust the pace and speed of your speech so that you don’t stumble or draw out sounds. The specialist will suggest that you accompany the pronunciation of words with rhythmic finger movements. When a person's motor and speech centers are engaged simultaneously, the patient can control stuttering.
According to doctors, singing is an excellent workout that promotes intelligible pronunciation of words and sentences, which is why speech therapists often use vocal techniques to treat stuttering. Vocal therapy helps relieve stress and promotes the development of good speaking habits. Most patients suffering from logoneurosis stop stuttering while singing songs. During normal conversation, the illness manifests itself again, but not as strongly as before. At the initial stage of “vocal therapy,” what is noticeable is not the elimination of stuttering, but a decrease in its intensity.
While singing, one word flows into another, there are almost no pauses. The main obstacle that prevents the patient from pronouncing words correctly is eliminated: the pronunciation of the first sound. There is an imperceptible correction of stuttering.
Singing helps correct stuttering
The human vocal apparatus changes slowly. If you are faced with the task of learning to speak without stuttering, a speech therapist will warn you that you should not expect instant changes. Hard work and self-confidence will help you achieve fluent speech.
Speech therapists have at their disposal many ways to harmonize convulsive speech: from eliminating “problems” in the operation of the articulatory apparatus with the help of regular exercises to complex speech-psychocorrection techniques. Logopsychocorrection technologies for eliminating stuttering are based on the idea being instilled in the patient: he can easily pronounce any phrases.
In recent years, psychotherapists, speech therapists, neurologists and even neurosurgeons have been developing an integrated approach to eliminating the prerequisites for stuttering. Knowing that you have a hereditary tendency for the disease, you can visit a neurology center to consult with a doctor.
Possible complications
Stuttering can lead to problems:
- Difficulty communicating with other people.
- Constantly avoiding situations that require speech.
- Loss of social or work participation in production, career ladder.
- Receiving ridicule and ridicule from other people.
- Low self-esteem.
If treatment is not started on time, stuttering can take a chronic form, when a person develops stereotypes of behavior and speech skills, and over time develops a fear of communication, causing severe anxiety. Verbal disturbances may be accompanied by nervous reactions of the face and body, self-doubt, rapid fatigue from talking, worsening mood, and decreased comfort in life.
A visible positive result can be obtained only if the patient has a strong desire to get rid of the rhythmic speech defect. Relatives and friends can provide significant psychological support and assistance in the treatment of logoneurosis. Treatment for an adult can be long, and he must be prepared for this, be patient and activate his willpower.
How to treat logoneurosis
Due to the fact that logoneurosis is one of the types of neuroses, the pathological condition must be differentiated from other disorders of the speech apparatus.
Clinical therapy
The problem under consideration is based on nervous disorders, therefore treatment of logoneurosis in adults and children is carried out with the help of sedatives that calm the nervous system:
- "Afobazole";
- "Glycine";
- "Grandaxin".
To eliminate spasms of the speech muscles, Mydocalm, Magnerot and other antispasmodic drugs are used. Additionally, in the treatment of the pathological condition, drugs that improve cerebral circulation are used.
Principles of psychotherapy
For logoneurosis, treatment based on psychotherapeutic techniques involves sessions:
- Rational psychotherapy. The method allows you to eliminate negative thoughts about yourself and the environment, as well as form a positive outlook on the problem.
- Suggestive psychotherapy. This approach involves a hypnotic effect on the patient’s psyche.
- Auto-trainings. This method helps the patient learn to control his own speech.
At the end of psychotherapeutic treatment, the patient should get rid of stuttering.
Speech therapy classes
Classes with a speech therapist give the most noticeable effect in the treatment of logoneurosis if combined with taking sedatives and visiting a psychotherapist.
The speech therapist works to establish the correct pronunciation of individual sounds or syllables. Moreover, in the case of stuttering that occurs at an early age, speech therapy treatment forms the basis of therapy for the pathological condition.
Physiotherapy
Treatment through exercise therapy, like other forms of therapy, is aimed at normalizing the state of the nervous system. A similar goal can be achieved by visiting a chiropractor.
Breathing exercises
Breathing exercises, like exercise therapy, belong to the practice of yoga. This method of treatment allows you to restore the state of the nervous system, get rid of anxiety and fear. Breathing exercises are effective in stressful situations. The procedure and rules for performing such activities should be clarified with your doctor.
Types of stuttering
To determine the type and severity of speech disorders, various classifications are used.
Types of pathologies:
- Evolutionary - the disease occurs at 2-4 years of age, weakens in adolescence, and can be neurotic or neurosis-like.
- Reactive – has a psychogenic nature, occurs in adolescents as a reaction to unfavorable events.
- Symptomatic - the secondary form of the disease develops as a consequence of damage to the central nervous system of an organic nature. It is diagnosed with tumors, poor circulation, and encephalitis.
- The severity of the disease is mild, moderate and severe.
The occurrence of neurotic stuttering is preceded by severe stress and nervous shock. This form of pathology can occur in children aged 2-6 years with normal development. Clinical convulsions are sometimes observed, which intensify during nervous tension at the beginning of speech. This type of disease is called logoneurosis.
Neurotic stuttering is divided into 3 types, depending on the characteristics of speech. The clonic form manifests itself in the repeated repetition of certain sounds, syllables, and words. Tonic stuttering is diagnosed when there are long pauses, excessive prolongation and drawn-out words. There is also a mixed type, when different types of pathology alternate.
Neurosis-like stuttering indicates the presence of various brain disorders and occurs at 3-4 years of age during intensive speech development. Children with this pathology quickly get tired, they are irritable, and sometimes psychiatric abnormalities are observed.
With a mild degree of stuttering, minor hesitations occur that practically do not interfere with communication, but you need to consult a specialist so that the pathology does not become chronic. Moderate degree of the disease - hesitations are quite long, the person often stops in the middle of a sentence.
What degree of stuttering is associated with embolophrasia? Emboli or parasitic words at the beginning of each phrase are a sign of a severe chronic form of the disease. Other pathologies may be added - logophobia (fear of speaking) and voluntary, involuntary accompanying movements.
Logoneurosis and non-eurosis-like stuttering - table of differences
| Characteristic | Logoneurosis | Stuttering |
| Form | Psychogenic disease, mainly affecting speech functions | Physiological disease |
| Causes | Adverse psychological factors | Organic brain lesions |
| Degree of manifestation of the disease | In a calm environment, there are practically no signs of the disease | Appears constantly |
| Presence of concomitant diseases | Logophobia, facial tics, muscle tension, frequent trembling of the eyelids, lips, enuresis. | Strong gestures, tongue-tiedness, high speech activity, no logophobia |
| At what age does it appear | At 2-5 years of age, at older ages the risk of developing the disease is no more than 1% | Most often at 3-4 years of age, but due to tumors or brain injuries it can occur at any age |
Treatment
If a child, and especially an adult, sometimes stutters a little, stammers, or begins to stutter severely, treatment for logoneurosis is necessary. Recommendations for treating childhood stuttering:
- The very first and most important step is to show the child to a good speech therapist; if you see that the child is not making any progress in getting rid of stammering, then try to show him to another specialist.
- Don't worry your child or put pressure on him. Accept his pathology adequately. Stuttering is a common disease among preschool children. And its treatment is not too complicated. Explain this to your child so that he is not afraid of anything.
- Treatment at home is just as important as with a speech therapist. Do not ignore this disease; the whole family, without exception, must fight against it. Don’t stop communicating with your child, take this more responsibly. A lot depends on the family. Do speech exercises and breathing exercises.
- After your child gets rid of the disease, do not stop going to the speech therapist! There is always a risk that the speech disorder may return suddenly.
Methods for treating speech disorders in adults include speech therapy, psychotherapy and medication:
- Speech therapy: working on speech with a speech therapist.
- Psychotherapeutic: work on the patient’s attitude to speech neurosis in the form of conversations with a specialist.
- Medication: taking special anticonvulsants and sedatives. Prescribed individually by a doctor.
Etiology and pathogenesis of neurotic stuttering
The main reason for the development of the neurotic form of stuttering is a psychotraumatic situation:
- fright;
- tantrum;
- long-term stress;
- conflict situation;
- separation from a loved one for a long time.
Speech pathology can be short-term. In most cases, the symptoms are clearly expressed and reach transient mutational forms in children and adolescents. Chronic deviations are characterized by the consolidation of speech pathologies and additional neurotic disorders.
60% of cases of childhood neurotic stuttering are provoked by an unfavorable speech therapy environment in the family circle:
- heredity;
- bilingualism;
- boosting the child’s speech skills;
- placing high demands on the child regarding speech;
- excess information.
The pathogenesis of the disease has not been studied enough to speak with confidence about the causes of development. In a stressful situation, the pathology progresses due to disruption of the transmission of conditioned reflex impulses. Pathology is established in adults due to the automation of motor reactions. Children exhibit a natural hesitation in speech patterns, characteristic of the development of speech functions.
The leading cause of logoneurosis is a psychotraumatic situation. This can be acute mental trauma (severe fright or other sudden shock, an attack of anger) or chronic stress (separation from loved ones, family conflict, troubles at work). In the first case, neurotic stuttering can be short-term, although often its symptoms reach significant severity, up to transient mutism (especially in children). In the chronic course of a psychotraumatic situation, speech pathology is consolidated, and other neurotic disorders may be added.
In children, about 60% of cases of the disease are associated with an unfavorable speech climate in the family. This includes attempts by relatives to speed up the child’s speech development, excessive demands on speech, information overload, bilingualism in the family, a sharp increase in demands on the child’s speech abilities, etc. In some children, neurotic stuttering can develop when imitating the speech of a stuttering person, if such a person is in their close environment. In such cases, stuttering becomes fixed according to the type of neurotic fixation.
Hereditary predisposition plays a certain role in the occurrence of the neurotic form of stuttering. It may consist of a genetically determined functional deficiency of the apparatus that provides speech motor skills.
The pathogenesis of logoneuroses has not been sufficiently studied. In acute stressful situations, neurotic stuttering presumably develops due to the emergence of a stable pathological conditioned reflex connection, and its consolidation is facilitated by the formation of motor automatism. When stuttering develops at the age of 2-4 years, it can be assumed that it is based on a pathological fixation of natural hesitations in speech, typical for the period of formation of speech function.
Symptoms of logoneurosis
Stuttering is expressed as a disturbance in the rate of speech and breathing caused by spasms of the organs of the speech apparatus. Spasms of the muscles of the larynx are vocal, spasms of the tongue and lips are articulatory. With respiratory spasms, breathing is interrupted, and there is a feeling of lack of air. Stuttering can appear suddenly and intensify, for example, with severe anxiety. The speech of a person who stutters is characterized by forced stops and involuntary repetition of individual syllables and sounds.
According to the type of seizures, three types of logoneurosis are distinguished:
- tonic - involuntary pauses in speech and prolonged inability to overcome tension
- clonic - most doctors describe this type as “obsessive repetition of individual syllables or sounds, especially at the beginning of a word,” in my experience it is more likely a desire to say the entire word, without hesitation. At a certain moment a spasm occurs and there is no way to speak further and I started the phrase over and over again, why? All stutterers are extremely embarrassed by their stuttering and subconsciously choose behavior in order to look less like a stutterer. I caught myself doing this many times, well, I couldn’t stand with a crooked face, a trembling jaw and squeeze out a word, it’s much easier to repeat the word, it worked 5-10 times.
- mixed - a combination of both types.
Logoneurosis, as a disease of a neurogenic nature, has 3 groups of symptoms:
- the main symptoms of logoneurosis are the well-known signs of stuttering described above;
- general neurological symptoms (emotional stress, feelings of inferiority, anxiety, fears, loss of appetite, insomnia, excessive sweating);
- accompanying neurotic symptoms (muscle tension, facial tics, respiratory spasms).