Logoneurosis is a speech disorder that is manifested by repetition of the same words, utterance of individual sounds, conversational pauses and interrupted speech. Logoneurosis according to ICD-10 has code F98.5 - this is stuttering/stammering. Logoneurosis and stuttering are synonymous concepts, but to understand the difference between them, it is worth paying attention to the causes of stuttering. If stuttering is neurotic in nature, then it is logoneurosis. In addition, there is also neurosis-like or organic stuttering associated with physiological reasons. Below we will talk specifically about neurotic stuttering. Logoneurosis prevents a person from living fully, so you need to start fighting it in childhood and as early as possible. The earlier a violation is identified, the easier it is to correct it and the fewer associated problems there are (self-doubt, low self-esteem, anxiety, fear of speaking - logophobia). Before you begin speech correction, you need to identify the causes of logoneurosis. According to statistics, logoneurosis appears in preschool age. Boys are three times more likely to stutter than girls. If logoneurosis is not cured, the person will continue to stutter into adulthood.
Treatment methods for stuttering in children
Logoneurosis in children is treated with speech therapy sessions, breathing exercises, special massages, computer programs and drug treatment.
Speech therapy classes involve complex exercises that are tailored to each child individually. After the doctor identifies the degree of logoneurosis, he chooses a set of activities for the patient that will help normalize speech.
Breathing exercises are performed with the patient, based on the methods of A. Strelnikova. While performing them, the child is allowed to sit or stand. Inhalations must be made sharply, exhalations smoothly and not quickly. These exercises include:
- Cat. Each squat is accompanied by body rotations. While straightening, the patient should want to inhale, while squatting, exhale.
- Pump. Deep and slow inhalations and exhalations with lips stretched out in the shape of a pipe.
- Ears. Tilt your head until your ear reaches your shoulder. While bending, inhale; while straightening, exhale.
- Palms. The arms are bent at the elbows with the palms facing the floor. While straightening your arms, exhale calmly, starting position, inhale quickly.
During acupressure massages aimed at treating logoneurosis in children, smooth and massaging movements with the hands occur, which affect the edges of the lips, areas of the nose, earlobes and chin. During the massage, relaxing music is turned on or good poems are recited.
Nowadays, such methods of treating childhood stuttering as the use of computer programs are popular. They are approved by many doctors from all over the world. They are used for home treatment of childhood logoneurosis. The following computer programs exist:
- Demosthenes.
- Dr. Flunz.
Medicines are used only as an auxiliary method of treating childhood stuttering. Their intake is necessary to normalize brain function, as well as to correct pathologies in the area of the central nervous system. Taking the drug without aspen treatment does not bring positive results.
The child may be prescribed medications such as:
- Anti-seizure medications.
- Homeopathic medicines.
- Calming.
- Tranquilizers.
- Nootropics.
Fighting methods
This condition is highly resistant to therapy, however, a number of researchers have found effective methods to combat it. Thus, treatment methods are used for adolescents that lead to a change in their thinking, leading to the commission of actions condemned by society. After undergoing this therapy, patients showed much less antisocial behavior.
And yet, most often, attempts to make adjustments to this condition are not crowned with success. Some treatments only made the situation worse. This is what happened with programs of the internally oriented approach used in the treatment of depression when they tried to work with patients with antisocial disorder.
The most positive effects were demonstrated by rigorous programs that taught patients new skills that could be applied in life regardless of the restrictions of society.
Medicines can only help in alleviating the conditions that accompany the disorder. So, if there are symptoms of depression accompanying antisocial disorder, antidepressants are taken. Aggressive patients are prescribed mood stabilizers that control symptoms of anger and impulsivity.
General characteristics, medical definition of the concept, ICD-10 code
In short, stuttering is a speech disorder that manifests itself in difficulty pronouncing sounds and syllables, a violation of the tempo-rhythmic organization of speech. It is accompanied by changes in sound timbre and leads to impaired speech fluency. There is also a definition of stuttering as a complex psychophysical disorder.
What is the scientific name for stuttering? Is it a disease? This pathology has other name options:
- logoneurosis;
- laloneurosis;
- Logoclony:
- battarism;
- balbucio.
What is the difference between stuttering and logoneurosis, what are their differences? All these pathological conditions (logoneurosis and others) belong to forms of stuttering, but they all manifest themselves differently.
For example, battarism is the same speech disorder, but in which words are pronounced blurry at a very fast pace and are not fully understood. Unlike ordinary stuttering, there are no convulsions and psychological uncertainty in public.
These terms are mainly used to refer to stuttering in medicine (neurology). Logoneurosis code according to ICD-10 - F98.5
Statistics on stuttering, what is the prevalence of the disease:
- Stuttering occurs more often in children aged 3-5 years. During this period, the human speech organization begins to develop.
- The pathology occurs approximately 3 times more in boys than in girls.
- The chance of developing this pathology is higher in orphanages than in kindergartens and primary classes.
- This disease affects 1-3% of the adult population.
History of creation and revisions of the ICD
Attempts to collect together the names of all diseases, organize them, and generalize them into groups were made back in the 18th century. A special contribution was made by François Bossier de Lacroix (France). The issue of generalizing diseases was given great attention by William Farr (England, 19th century), who described the principles of constructing a unified classification. The issue was discussed more actively, and understanding of the need for classification grew.
The first internationally applicable classification of causes of death was adopted in Paris in 1855 by the International Statistical Congress. It was built on the basis of two lists of diseases, compiled according to different principles, from Dr. William Farr and Dr. Marc d'Espin. In subsequent years (1864, 1874, 1880, 1886), the classification was revised - additions and changes were made.
In 1893, the Bertillon Classification was adopted in Chicago after Jacques Bertillon (France), who led the preparation of the classification. It was also called the International List of Causes of Death. It laid the foundation for the classification that is now known as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Since 1893, the classification has been revised approximately every 10 years. The current classification is the 10th revision. It was approved by the International Conference on the Tenth Revision of the ICD in 1989 and adopted in May 1990 by the Forty-third World Health Assembly. It has come into use in WHO member states since 1994, and since 1999 in Russia. The release of ICD-11 is delayed, but work on its preparation is ongoing. The adoption of the 11th revision of the ICD is expected in 2016-2017.
The preparation of the Russian version of ICD-10 consisted of drawing up a classification based on WHO clinical diagnostic terms, but adapted to the practice of medical institutions in Russia. The Moscow Center for the International Classification of Diseases, collaborating with WHO, took part in the adaptation of the international document. During the preparation, the work experience of specialists from large clinical institutes of the country was taken into account, and proposals were made by specialists from the Ministry of Health. The Russian paper version of ICD-10 is the result of the painstaking work of academicians, doctors and candidates of medical sciences.
Participated in the preparation
• Academicians of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences: I.I. Dedov, V.A. Nasonova, D.S. Sarkisov, Yu.K. Skripkin, E.I. Chazov, V.I. Chissov;
• Corresponding members of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences: G.I. Vorobyov, E.A. Luzhnikov, V.N. Serov, V.K. Ovcharov;
• Doctor of Medical Sciences: V.G. Goryunov, B.A. Kazakovtsev, N.V. Kornilov, V.S. Melentyev, A.A. Priymak, D.I. Tarasov, M.S. Turyanov, A.M. Yuzhakov, N.N. Yakhno, O.N. Baleva, P.V. Novikov;
• Candidates of Medical Sciences: O.N. Belova, M.D. Speransky, M.V. Maksimova.
The classification is a normative document that consists of three volumes. In the Russian edition of ICD-10, volume 1 consists of two parts.
Volume 1. Special lists for statistical development
Volume 2. Collection of instructions for use for ICD users
- Description of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems
- Rules and instructions for coding mortality and morbidity
- Presentation of statistical data
- History of the development of ICD
How to use the ICD
Volume 3. Alphabetical index to classification
- Preface to the Russian edition
- General index construction
- Conventions used in the index
- Section I. Alphabetical index of diseases and injuries by their nature
- Section II. External causes of injury
- Section III. Table of drugs and chemicals
Our website contains an online version of a fragment of the Russian edition of ICD-10, which includes a list of classes, blocks, three-digit headings, four-digit subcategories and their contents. You can also download an electronic version of the Russian edition of ICD-10 in different formats from our website.
Psychotherapeutic treatment
Working with a psychotherapist helps to cope with the effects of stress, increased anxiety, suspiciousness and other problems.
For this purpose use:
- Rational psychotherapy. Helps to form an adequate attitude of a person towards himself, his problem and ways to solve it.
- Suggestive psychotherapy. It includes work with a psychotherapist and hypnosis sessions, during which a specialist “loosens” muscle blocks and “removes” the causes of neurosis.
- Autotraining. The psychotherapist helps the patient choose and learn speech control methods that he can use independently.
Speech therapy treatment
The speech therapist teaches the patient methods and techniques for correct pronunciation of various sounds and words. Classes with a speech therapist are considered the main method of treating stuttering in children of preschool and school age.
Treatment at home
You can cope with logoneurosis at home.
- taking herbal sedatives: tinctures of valerian, motherwort, peony, hawthorn;
- normalization of sleep and rest patterns;
- rejection of bad habits;
- reduction of nervous and physical stress.
When treating stuttering in children, it is important not only to reduce psycho-emotional stress, but also to increase self-esteem in the child. In addition to general treatment methods at home, you can:
In addition to general treatment methods at home, you can:
- learn articulation gymnastics;
- learn breathing exercises;
- take special herbal teas.
You can learn the techniques of articulation and breathing exercises from specialists or on your own, using tutorials and programs on the Internet.
The following herbal remedies are also recommended at home:
- oregano decoction;
- decoction of fragrant rue;
- nettle decoction is dull.
These herbs have sedative effects and help reduce nervous tension.
Logoneurosis is a pathology that can lead to serious consequences. Often, children with stuttering develop various complexes, their socialization is disrupted, they have difficulty communicating with people and are not always successful in their future development. Therefore, timely treatment of stuttering in children is the most important condition for their further development.
Author of the article: psychiatrist Shaimerdenova Dana Serikovna
Definition
Logoneurosis (ICD-10 code F98.5) is a condition in which speech loses its fluency, becomes convulsive, protracted pronunciation, involuntary delays or repetitions of sounds, syllables or words appear.
This disease is classified as stuttering, which occurs as a result of neurosis.
Its manifestations are not permanent and are often combined with other neurotic disorders.
It is important to note that this type of stuttering appears only in moments of severe nervous tension and disappears after the end of the influence of the provoking factor. Also, a person who suffers from logoneurosis does not have problems pronouncing specific sounds or sound combinations
Also, a person who suffers from logoneurosis does not have problems pronouncing specific sounds or sound combinations.
Logoneurosis is often clearly associated with logophobia - the fear of speaking.
Causes of logoneurosis
Factors that influence the formation of a risk group:
- Disadvantages of the central nervous system associated with pathologies of intrauterine development, birth injuries and diseases suffered at an early age; Labile nervous system, which is expressed in tearfulness, anxiety, irritability;
- Individual characteristics of speech development (a more intense pace of development of phrasal speech can provoke the occurrence of stuttering, as well as the sudden introduction of a second language into use, while the child has not yet fully mastered his own);
- Genetic weakness of central speech mechanisms.
- To trigger logoneurosis in children, the causes and predisposing factors must be supported by the acute additional influence of a pathogenic external influence.
- Late development of speech in the child and disinhibition of the nervous system, as a result of which sounds are pronounced blurred or crumpled;
- Physical disabilities that can form a “black sheep” complex and a feeling of inferiority.
- Unjustifiably high demands made;
- An overly strict attitude towards the child, nagging, control, lack of a unified parenting strategy, conflicting demands;
- Lack of emotional contact, coldness in relationships with loved ones and relatives, lack of support and care;
- Mental trauma, chronic or acute stress. Features of the atmosphere and microclimate in which the child most often finds himself (traumatic situations in the family, chronic conflicts in the children's team).
Manifestations
People suffering from this disease behave destructively and aggressively, often leading to constant contact with law enforcement agencies. But not in all cases the pathological personality structure manifests itself in this way.
Some people with dissocial personality disorder, due to these same characteristics, achieve great success in business, where they often need to go against the grain and face public opinion. Impulsiveness in action, the ability to show indifference and an appetite for risk are valued in this field. Dissocial personality disorder is accompanied by "corporate" egocentrism, ambition and delusions of grandeur, which are combined with charming behavior, which also increases a person's chances of success.
The diagnosis is made by 1% of women and 3% of men. Antisocial disorder manifests itself in the inability to create warm relationships with people. Urban residents and people from low-income families are most often susceptible to it.
According to some studies, 75% of prisoners suffer from antisocial personality disorder. Nevertheless, many people with this pathology do not get involved with the criminal world, being satisfied with committing acts condemned by society.
How to treat logoneurosis?
To treat logoneurosis in children, the doctor may prescribe medications that have a calming effect on the child’s nervous system, however, as you understand, this will not be enough to eliminate speech problems. Logoneurosis is treated by specialists such as a psychotherapist and speech therapist. Psychotherapy is the key to successful treatment of logoneurosis, and speech therapy works by performing complex exercises. Speech training, self-control processing, intellectual development must be combined with psychotherapy to achieve a positive result. Herbal medicine is often used as an adjunct to primary treatment. There are many traditional medicines that have a calming effect on the child’s nervous system, and this is what is needed when treating logoneurosis in children.
Physiotherapy, exercise therapy, reflexology - all this, along with psychotherapy and speech therapy, helps eliminate speech defects in a child.
Treatment of logoneurosis is not an easy task; you will have to spend a lot of time and effort to achieve results, but it is possible and it is worth the result.
Parents need to try to change the tense situation in the family, if any, and also communicate with the child slowly, clearly pronounce the words and in no case scold the child for failures. Try not to show that the child is sick with something, otherwise this can lead to even more stress, isolation, and complexes.
Mechanism of logoneurosis
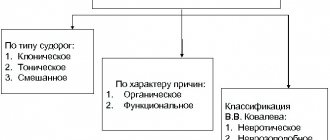
Logoneurosis is a neurotic form of stuttering that is not associated with organic disorders or pathology of the structure of the speech apparatus. Stuttering can be of a tonic nature, which is associated with tension in speech and the inability to overcome a forced pause, or clonic, which involves prolongation and repetition of sounds and syllables. There are mixed or tono-clonic stuttering, which are characterized by combinations of the two indicated variations.
In addition to stuttering, speech neurosis is accompanied by frequent blinking, jaw trembling, and facial muscle tension. In a child with stuttering, the rhythm, tempo, and smoothness of the voice and breathing are disrupted, the cause of which is the occurrence of convulsions of the speech apparatus (larynx, tongue and lips).
Stuttering intensifies as a result of fear of communication and expression of one’s thoughts. Over a certain period, its manifestations may be absent, but the child’s speech remains smooth. But at a moment of high emotional stress or in another situation that is psychologically difficult, logoneurosis worsens and the intensity of symptoms becomes more frequent. The more worried the child is, the higher the traumatic factor of the situation, the stronger the manifestations of stuttering will be, forming a persistent unconditional chain of logoneurosis: stuttering - fear - stuttering - fear.
What will happen if left untreated?
Patients suffering from this disease leave their negative mark on society in the form of mental suffering of the victims against whom they committed crimes. But sometimes a person with antisocial disorder can occupy a high position or be the leader of social groups. Then the consequences of its destructive impact are not so obvious until the moment when mass suicides occur. This has happened more than once in history. For example, this happened in Guyana in 1978 among the followers of Jim Jones.
People suffering from symptoms of the disorder are prone to using alcohol, drugs and committing crimes. Most often, they sooner or later end up in prison. They are susceptible to depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder and many other psychiatric diagnoses. They tend to self-harm themselves and others, often die as a result of murder or suicide, and often get into accidents.
The behavior of a person with a dissocial disorder can contribute to a change in the environment around him to a negative one. Often such people end their lives in psychiatric hospitals.
The risk of spending your life this way increases if the disorder is not treated. However, by the age of 50, many patients have the disease in remission.
Symptoms in children and adults
Symptoms vary depending on the types of stuttering. The main signs of a speech disorder are easy to recognize:
- Impaired speech fluency, changes in voice timbre and pitch.
- It's hard to start talking.
- The patient's facial expressions may change unnaturally when speaking, facial tics and slight twitching are possible.
- Having a fear of talking.
- Adding extra vowel sounds to your words.
Peculiarities of manifestation at different age periods
What does it mean to stutter, how does it manifest itself:
- Stuttering in children of junior and senior preschool age. The motor system is disrupted: when walking, running and playing, the elbow joints move tensely, the knee joints bend less often than their peers. This occurs due to convulsive speech reflexes that spread to other parts of the body.
- Stuttering in children of primary school age. The child fully learns to compare his breathing with the arrangement of words and phrases. He pronounces them in the exhalation phase. At school, there is a risk that a student with a stutter will be worried about his illness, which will aggravate his situation, causing convulsive stuttering.
- Logoneurosis in adolescents. A speech defect has a great impact on a person’s personal characteristics, since during this period the psychological aspect undergoes restructuring and formation. When stuttering, adolescents have a high risk of developing logophobia, fear of their own speech.
- Adults mostly suffer from neurotic stuttering. The psychological trauma that led to speech impairment could be very difficult. As a rule, this is the most difficult age for healing. This illness could develop due to a long-lived illness. For example, due to a stroke or encephalitis. It can also be a secondary disease (an adult could have stuttered in childhood or adolescence).
Betrayal
Most often, the roots of the disease lie in psychological trauma received in childhood. Future patients grow up in false relationships. This happens when parents deceive the child by pretending to love each other and him. Their behavior demonstrates love, but in reality the child feels deceived. In such conditions, he adopts the model of behavior he sees.
Growing up, he no longer has anything that would be valuable to him; any behavior patterns are normal for him.
All this leads to the fact that people cannot be in long-term relationships, since they do not value anything or anyone around them at all.
Often among such individuals there is a para-existential disorder, due to which they do not feel themselves and seek to achieve their goals. They are characterized by the thoughts “I will be nothing if I do not achieve success in my career, if I am not successful.”
In such a picture of the world, friends become means to an end, marriage is assessed in terms of the benefits it brings. All the people around are functional in nature. From the outside it may seem that the patient is living a meaningful life. However, he only moves away from existential meaning, striving for needs.
Antisocial disorder is similar to paraexistential disorder. They differ in that in the presence of the second, the patient’s behavior is more acceptable to society.
In any case, patients with both ailments only take advantage of the people around them.
Treatment
How to cure logoneurosis? Treatment of stuttering, especially in children, requires an integrated approach
It is important that young patients come to meetings with doctors accompanied by members of their families
Specialists from several areas are involved in the treatment of stuttering:
- psychotherapist.
Psychotherapy sessions will help eliminate manifestations of anxiety, help the patient acquire new skills and habits in communicating with people around him, and teach various relaxation methods; Hypnosis is considered one of the most effective psychotherapeutic methods in the treatment of logoneurosis. - neurologist. The participation of this specialist in the treatment of stuttering consists of prescribing nootropic and sedative drugs;
- physiotherapist. This doctor may prescribe massage or acupuncture, which will ensure normalization of the central nervous system;
- speech therapist. The work of this doctor is aimed directly at eliminating speech defects.
It is also effective to involve a family or child psychologist in the treatment of logoneurosis, who will help parents ensure a comfortable family climate, and also teach the nuances of raising a child who stutters.
Drug therapy:
- sedatives (“Afobazol”, “Glycine”, etc.);
- antispasmodic drugs (“Mydocalm”, “Magnerot”);
- nootropic drugs (“Piracetam”);
- peony tincture;
- Valerian tincture;
- hawthorn tincture.
The pharmacy chain has ready-made herbal preparations that have a sedative effect:
- Oregano (1 tbsp per 220 ml of boiling water, leave in a water bath for 15 minutes, then let it brew for 40 minutes, take 3 times a day);
- fragrant rue (1 dl per 220 ml of boiling water, cook in a water bath for 5 minutes, adults and adolescents are recommended to take 1 spoon 3 times a day, children - gargle);
- white ash (1 tbsp per 220 ml of boiling water, cover and let it brew for 30 minutes, take 1 tbsp 3 times a day, for small children - gargle).
Breathing exercises for logoneurosis help eliminate anxiety and fears and are effective in stressful situations.
Examples of exercises:
- Stand straight, bend and lower your elbows. The palms must be straightened and held with the back side facing up. As you inhale, you need to clench your hands into fists, and as you exhale, unclench your hands. The exercise must be repeated 3 sets of 10 times.
- While standing, turn your head left and right so that with each turn you can touch your chin to your shoulder. In this case, inhalations and exhalations should be rhythmic. Repeat the exercise 10 times.
One of the effective methods of treating logoneurosis is massage.
It helps reduce muscle tone, improve the functioning of the speech center, and generally strengthen the body.
There are two types of massage used in the treatment of stuttering:
- segmental, in which the massage therapist acts directly on the muscle responsible for speech;
- acupressure - has a relaxing effect, helps to minimize the excitability of the speech center and restore the speech centers of the nervous system.
The advantage of massage is that the child’s parents can master this technique under the guidance of a specialist and carry out treatment at home.
Dr. Komarovsky recommends including water procedures in the treatment of stuttering in children - a bath at least twice a day, games in water, long walks in the fresh air and meals that include in the child’s diet foods rich in microelements useful for the speech center (sea fish, dried fruits, dairy products).
Logoneurosis is an illness that, under unfavorable circumstances, can occur at any age and significantly worsen social adaptation and complicate the patient’s life.
However, this disease is curable, and with the right approach and following some simple recommendations, you can forget about stuttering.
Neurotic stuttering, logoneurosis, logophobia:
Our interesting VKontakte group:
Difference between dissocial disorder and psychopathy
Psychopathy is an unrecognized psychiatric disorder whose manifestations correspond to severe forms of dissocial disorder. The diagnosis of a psychopath is given to someone who has no sense of shame for their own behavior, demonstrating an open disregard for social rules. Only 15% of all patients suffering from antisocial disorder showed symptoms of psychopathy.
A psychopath is a more suspicious, paranoid person compared to other patients. This type of thinking leads to the fact that patients interpret all actions of others as aggressive towards them. Having a criminal record, they will see the injustice in their accusation. They will be sincerely confident that this is arbitrariness on the part of the court.
Disease prognosis
In the absence of therapy, the defect strengthens and progresses with age. Speech disorders are manifested not only by stuttering. The formation of pronunciation as a whole is disrupted. Sentences are devoid of meaning and logical sequence, basic speech skills are not consolidated.
By the age of 18, a mental response to one’s own defect is formed. Logophobia may develop. Although this pathological condition is more typical for neurotic stuttering.
Adequate speech therapy help prevents significant speech disorders and prevents the formation of mental defects. The effectiveness of exercise depends on the severity of the pathology.
Causes of stuttering
There are several causes of speech disorders:
- Organic brain damage due to strokes, injuries, contusions, as well as due to the development of tumors and infectious diseases of the central nervous system. In this case, it is not logoneurosis; stuttering is treated together with the underlying disease.
- Cervical osteochondrosis and pinched cervical nerve, subluxations of the vertebrae of the cervical spine.
- The development of neurosis after a strong psychological shock, emotional shock. For example, stuttering may appear after a sudden traumatic event - an attack, a hostage situation, etc. Or develop in connection with the loss of a loved one. Stuttering is not associated with physiological reasons, and occurs periodically, for example, when it is necessary to speak in front of an audience, or in the presence of a certain type of people - for example, women.
- Fear or anger. Temporary stuttering caused by anger or fear goes away with time and does not require treatment. Neurosis with such causes is called reactive or stressful. Despite its unexpressed form, it requires timely diagnosis and treatment, as there is a risk of perpetuating the disorders. Stress stuttering is usually accompanied by twitching or spasms of the facial muscles. It is the unpleasant experiences of one’s speech “inferiority” that can lead to the transition of stress stuttering into habitual stuttering.
- Genetic reasons. Sometimes stuttering develops in people whose parents also suffered from speech neuroses. In this case, the person cannot remember when he spoke without stuttering - the disturbances appeared in childhood, along with the first attempts to speak.
The second and third set of causes relate to logoneurosis. Treatment is carried out in accordance with the identified cause, and is fundamentally different in each case listed above. Correction of neurotic speech disorders in adults is impossible without psychotherapy.
Diagnostics
A neurologist diagnoses stuttering . Diagnostic measures include a detailed collection of family history, determination of the psychological climate within the patient’s family, and analysis of complaints.
Instrumental diagnostics are carried out using electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
These research methods make it possible to exclude such possible causes of the disease as volumetric and inflammatory processes in the brain.
If characteristic symptoms persist for three or more months, a diagnosis of logoneurosis is made.
Methods for treating stuttering at home
Logoneurosis, treatment at home which can give good results with regular exposure, is subject to correction methods:
Speech therapy treatment is aimed at relaxing speech during stuttering, establishing correct articulation and rhythmic tempo of speech, and cultivating fluency. Class assignments are first in the form of joint work with a speech therapist. The exercises become more difficult over time. The child must independently repeat the stories he has heard. The skills acquired in remedial classes are reinforced when communicating with others.
Part of the correctional work aimed at exercises for the diaphragm and vocal cords. Such exercises allow your voice and speech to become freer. Training the diaphragm helps make the vocal cords more elastic, allowing them to close tightly when speaking. The set of breathing exercises ends with relaxation tasks.
Methods of alternative medicine, in combination with other ways of corrective influence, can have a positive effect on logoneurosis in a child. With the help of regular courses of acupressure, which are determined by the characteristics and complexity of stuttering, it is possible to restore the nervous regulation of speech. Which helps to correct and eliminate its defects.
A specially developed set of computer programs makes it possible to achieve synchronization of the work of the auditory and speech centers. Treatment of logoneurosis using a computer is carried out as follows: the patient repeats words and sentences into the microphone, and the program delays his speech, playing it back a little later. Having heard his own voice, the child adapts to its sound. Constant training with computer programs can improve the pace of speech, make it smooth and continuous.
Causes
This pathological condition can occur at any period of human life, but each age has its own prerequisites for the occurrence of logoneurosis.
In the period from 2 to 4 years, the following reasons most often lead to stuttering in children:
- Features of the development of the speech apparatus. Parents’ attempts to teach their child several languages at an early age can lead to the development of an incorrect rate of speech in a child.
- Individual character traits. Suspicious, anxious, and nervous children are more prone to the occurrence of logoneuroses.
- Active accumulation of a large vocabulary in a short period of time.
- Heredity. Speech disorders often occur in children whose parents already suffer from some type of speech pathology.
- Disorders of the central nervous system caused by the pathological course of pregnancy or childbirth.
Infections during pregnancy, fetal hypoxia, trauma during childbirth. - The presence of any speech pathology in the child: alalia, dyslalia, rhinolalia.
In children over four years of age, stuttering occurs under the influence of other factors:
- Exposure to prolonged and severe stress. This may include frequent conflict situations within the family or problems with peers.
- Intense fear. Most often, the onset of the disease occurs when a child experiences severe fear against a background of nervous tension. Subsequently, when a similar situation arises, logoneurosis will manifest itself.
- Psychological trauma, such as pressure from adults, excessively high, impossible demands from parents.
- Physical or mental fatigue.
This cause of stuttering is more common in adolescents. The manifestations of such logoneurosis are short-lived. - Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Cerebral palsy. Sometimes stuttering is a concomitant disease in a child suffering from cerebral palsy.
Hormonal changes in the body, which is also more typical for teenagers.
Infectious diseases of the central nervous system. Mental disorders such as schizophrenia, neurasthenia, schizoaffective spectrum diseases.
In adults, stuttering is caused by:
- Various traumatic situations.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Infectious diseases in which the passage of impulses through the nervous tissue is disrupted.
- Pathology of the speech apparatus.
It should be noted that in adulthood, logoneuroses occur much less frequently than in childhood and adolescence.
Symptoms and clinical picture
In adults and children, stuttering manifests itself with the same symptoms. The development of these symptoms is associated with spasm of the muscles of the tongue, lips, larynx, and soft palate.
The main symptoms of logoneurosis:
- multiple repetitions of individual sounds, syllables, words;
- difficulty pronouncing words or syllables;
- articulatory spasms;
- involuntary pauses that occur during pronunciation;
- spasms of the speech apparatus;
- feeling of lack of air.
In addition, patients may present complaints indicating neurotic conditions:
- increased feeling of anxiety;
- the appearance of unmotivated fears;
- problems with self-esteem;
- increased sweating;
- sleep disturbances (insomnia or nightmares);
- state of mental stress;
- decreased appetite.
Logoneurosis will also be indicated by changes in facial expressions, tension in the facial muscles, tics, involuntary grimaces, twitching of the lips, and rapid blinking during speech.
The severity of the symptoms of the disease depends entirely on its stage:
- In the first stage of logoneurosis, the child begins to stutter only in moments of strong excitement, and at rest the speech is clear, separate and understandable, the symptoms of logoneurosis are completely absent.
- In the second stage, stuttering manifests itself constantly, the patient becomes withdrawn, complex, and taciturn.
- In the third stage of appearance, stuttering appears in public, and disappears when the person returns to a comfortable environment.
- The fourth stage of logoneurosis is characterized by obvious hesitations during the pronunciation of individual words.
How does adult stuttering differ from childhood stuttering?
If stuttering began after a shock, quick help in the form of sedatives can prevent the speech defect from becoming permanent. For example, you can offer a person hot tea, a mild sedative, sit him in a quiet place, and cover him with a blanket. However, if the defect appears once, you need to carefully monitor your condition - stuttering may appear in the next stressful situation, and then you will need to treat logoneurosis with a neurologist and psychologist.
Irina, a medical university student, says:
I started stuttering when I got my first C in my life on an exam. This put me under terrible stress, I cried all day, couldn’t eat or sleep, and during the next oral exam I noticed that I was stuttering. Fortunately, I soon got rid of this problem without doing anything special. The stress just went away. It was the penultimate exam of the winter session, and I had the opportunity to recover.
Psychologists note: logoneurosis in adults differs from childhood stuttering in that a person is able to speak normally in a calm state, but in a situation of stress begins to stutter. In addition, children often have repetition of syllables even in their thoughts, while in adults, internal speech remains free. The onset of stuttering in adulthood is much less common than in childhood. It is believed that “adult” stuttering is more treatable. But self-medication - self-prescription of drugs such as Pantogam or others - rarely contributes to a final cure.
Externally, logoneurosis in children and adults looks exactly the same. Spasms of the palate, lips, tongue, larynx, as well as respiratory spasms with a feeling of lack of air may be present. But at the mental level in adults, speech disorders often coexist with other neurotic symptoms - anxiety, unreasonable fear, a feeling of melancholy, a feeling of inferiority, poor sleep, sweating, appetite disturbances.