History of the study and researchers
The direction of psychocorrection is based on two specializations - defectology and psychology. The first scientist who proposed the use of complex therapy to work with children who have developmental delays and pronounced mental retardation was E. Seguin. The next researcher who developed original methods of psychological correction is Peter Troshin.
The basic theoretical concepts of psychocorrection techniques were proposed later. At this stage, the scientist M. Montessori became famous. She created several correctional techniques that were designed to develop cognitive processes in children. Another researcher who made a great contribution to the development of psychological correction is A. N. Graborov. He proposed a number of techniques aimed at developing memory. V.P. Kashchenko developed a system of pedagogical correction methods.
L. S. Vygotsky made a huge contribution to the development of psychocorrection.
Classification
Scientists classify methods of psychological correction according to various criteria. The choice of method depends on the patient’s condition and the desired result.
By task type
Classification by type of task:
- gaming techniques;
- family correction;
- ways for personal growth;
- neuropsychological techniques.
By nature of direction
Depending on the nature of the direction:
- Symptomatic is one of the types of psychocorrection with which psychologists relieve acute emotional stress and help during periods of nervous breakdowns and acute developmental deviations.
- Casual - psychological correction aimed at resolving the causes and main developmental problems.
By method of influence
Depending on the methods of influence:
- direct;
- indirect.
According to the form of organization
Types of psychological correction depending on the form of organization:
- Special - a set of techniques for working with one child or a group. The goal is to resolve one or a number of psychological problems.
- Private - a variety of psychological and pedagogical influences used to improve educational processes.
- General - methods of general pedagogical nature. Designed to regulate emotional stress and the social environment in which the child develops.
How to write a term paper on speech therapy
07.09.2010 179883
These guidelines are compiled to help students gain an understanding of the content and structure of coursework in speech therapy.
Logopedia of pedagogical science that studies anomalies of speech development with normal hearing, explores the manifestations, nature and mechanisms of speech disorders, develops the scientific basis for overcoming and preventing them means of special training and education.
The subject of speech therapy as a science is speech disorders and the process of training and education of persons with speech disorders.
The object of study is a person suffering from a speech disorder.
The main task of speech therapy as a science is the study, prevention and elimination of various types of speech disorders.
Coursework in speech therapy is a student's scientific and experimental research. This type of educational activity, provided for by the educational and professional program and curriculum, contributes to the acquisition of skills in working with literature, analyzing and summarizing literary sources in order to determine the range of insufficiently studied problems, determining the content and methods of experimental research, processing skills and qualitative analysis of the results obtained. The need to complete coursework in speech therapy is due to the updating of knowledge concerning the content, organization, principles, methods and techniques of speech therapy work.
As a rule, during their studies, students must write two term papers - theoretical and practical.
The first course work should be devoted to the analysis and synthesis of general and specialized literature on the chosen topic. Based on this analysis, it is necessary to justify and develop a method of ascertaining (diagnostic) experiment.
In the second course work, it is necessary to provide an analysis of the results obtained during the ascertaining experiment, as well as determine the directions and content of speech therapy work, and select adequate methods and techniques of correction.
So, let’s present the general requirements for the content and design of coursework in speech therapy.
The initial and most important stage of working on a course project is the choice of a topic, which is either proposed by the supervisor or chosen by the student independently from a list of topics that are consistent with the areas of scientific research of the department.
Each topic can be modified, considered in different aspects, but taking into account a theoretical and practical approach. Having chosen a topic, the student needs to think through in detail its specific content, areas of work, practical material, etc., which should be reflected both in the formulation of the topic and in the further construction of the study. It should be recalled that the chosen topic may not only have a purely theoretical orientation, for example: “Dysarthria. Characteristics of the defect”, “Classification of dysgraphia”, but also take into account the practical significance of the problem under consideration, for example: “Speech therapy work on speech correction for dysarthria”. It should also be taken into account that when formulating a topic, excessive detail should be avoided, for example: “Formation of prosodic components of speech in preschoolers of the sixth year of life attending a preschool institution for children with severe speech impairments.”
The course work includes such mandatory parts as: introduction, three chapters, conclusion, bibliography and appendix.
The text of the term paper begins with the title page . An example of its design can be seen here.
Then the content of the work is given, in which the names of chapters, paragraphs, and sections are formulated in strict accordance with the content of the thesis. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the text, each subsequent chapter and paragraph begins on a new page. At the end of each chapter, the materials are summarized and conclusions are formulated.
The introduction reveals the relevance of the problem under consideration in general and the topic being studied in particular; the problem, subject, object, and purpose of the study are defined. In accordance with the goal and hypothesis, objectives and a set of research methods aimed at achieving the objectives must be defined.
The relevance of the topic lies in reflecting the current level of pedagogical science and practice, meeting the requirements of novelty and usefulness.
When defining the research problem, it is important to indicate what practical tasks it will help to implement in training and educating people with speech pathology.
The object of research is understood as certain aspects of pedagogical reality, perceived through a system of theoretical and practical knowledge. The ultimate goal of any research is to improve this object.
The subject of research is some part, property, element of an object, i.e. the subject of research always indicates a specific aspect of the object that is to be studied and about which the researcher wants to gain new knowledge. An object is a part of an object.
You can give an example of the formulation of the object, subject and problem of research:
– The object of the study is the speech activity of preschool children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The subject of the study is the features of intonation speech of children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The research problem is to determine effective directions for speech therapy work on the formation of intonation expressiveness of speech in the system of correctional intervention.
The purpose of the study contributes to the specification of the object being studied. The goal of any research is to solve a specific problem. The goal is specified in tasks taking into account the subject of research.
The research objectives are formulated in a certain sequence, which determines the logic of the research. The research objectives are set on the basis of a theoretical analysis of the problem and an assessment of the state of its solution in practice.
The first chapter is an analysis of literary sources, which examines the state of this problem in historical and modern aspects, and presents the most important theoretical principles that formed the basis of the study.
When writing the first chapter, you should pay attention to the fact that the text of the course work must be written in a scientific style. When presenting scientific material, it is necessary to comply with the following requirements:
– Specificity – a review of only those sources that are necessary to disclose only a given topic or solve only a given problem;
– Clarity – which is characterized by semantic coherence and integrity of individual parts of the text;
– Logicality – which provides for a certain structure of presentation of the material;
– Reasoning – evidence of thoughts (why this and not otherwise);
– Precision of wording, excluding ambiguous interpretation of the authors’ statements.
A literary review of the state of the problem being studied should not be reduced to a consistent presentation of literary sources. It should present a generalized description of the literature: highlight the main directions (currents, concepts, points of view), analyze in detail and evaluate the most fundamental works of representatives of these directions.
When writing a work, the student must correctly use literary materials, make references to the authors and sources from which the results of scientific research are borrowed. Failure to provide required references will reduce your coursework grade.
As a rule, in coursework on speech therapy, references to literary sources are formatted as follows: the number of the cited source in the general list of references is placed in square brackets. For example: General speech underdevelopment is a speech pathology in which there is a persistent lag in the formation of all components of the language system: phonetics, vocabulary and grammar [17].
When using quotations, in square brackets, in addition to indicating the source number, the page number from which this excerpt is taken is indicated, for example: Speech rhythm is based on a physiological and intellectual basis, since, firstly, it is directly related to the rhythm of breathing. Secondly, being an element that performs a communicative function, “correlates with meaning, i.e. controlled intellectually” [23, P.40].
However, course work should not be of a purely abstract nature, so you should not abuse the unreasonable abundance of citations. Quoting should be logically justified, convincing and used only when really necessary.
In the second chapter , devoted to experimental research, the organization should be described and the program of the ascertaining experiment should be presented. The survey methodology, as a rule, consists of a description of several series of tasks, with detailed instructions, visual and lexical material, the procedure for completing tasks by experiment participants, and scoring criteria. This chapter also provides a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the results obtained.
When analyzing the results of an experiment, it is necessary to use a scoring system. Examples of various criteria for quantitative and qualitative assessment are presented in the following works:
– Glukhov V.P. Formation of coherent speech in preschool children with general speech underdevelopment. - M.: Arkti, 2002. - 144 p.
– Fotekova T.A. Test methodology for diagnosing oral speech of primary schoolchildren. - M.: Arkti, 2000. - 56 p.
– Levchenko I.Yu. Pathopsychology: Theory and practice. - M.: Academy, 2000. - 232 p.
In order to visually present the results obtained during the experimental study, it is recommended to use tables, graphs, diagrams, etc. Histograms can be used in a variety of ways - columnar, cylindrical, planar, volumetric, etc. An example of the design of tables, figures, and histograms can be found here.
The third chapter provides a rationale for the proposed methods and techniques and reveals the content of the main stages of correctional work.
The conclusion contains a summary of the material presented and the main conclusions formulated by the author.
The bibliography must contain at least 25 sources. The list includes bibliographic information about the sources used in preparing the work. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the application you can present bulky tables or illustrations, examination protocols, observation records, products of activity (drawings, written works of children), notes from speech therapy classes, etc.
The volume of one course work must be at least 30 pages of typewritten text.
In general, coursework in speech therapy is the basis for a future thesis, in which the study of the begun problem can be continued, but from the standpoint of a different approach or a comparative analysis of the disorders being studied in different age categories of people with different types of speech disorders.
The content and format of theses in speech therapy can be found here.
Literature:
1. How to write a term paper on speech therapy: Methodological recommendations. Educational and methodological manual / Comp. Artemova E.E., Tishina L.A. / Ed. Orlova O.S. – M.: MGOPU, 2008. – 35 p.
2. Research work of students in the system of higher professional pedagogical education (specialty 031800 - Speech therapy). Methodological recommendations for completing the thesis / Compiled by. L.V. Lopatina, V.I. Lipakova, G.G. Golubeva. - St. Petersburg: Publishing house of the Russian State Pedagogical University named after. A. I. Herzen, 2002. - 140 p.
Indications and contraindications
Individual psychological correction is prescribed when a number of problems are identified:
- severe developmental retardation;
- loss of goals, meaning of life;
- misunderstanding oneself;
- unreasonable, childhood fears that inhibit development;
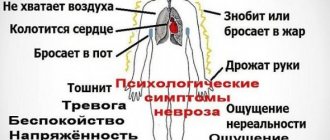
- severe anxiety;
- lack of interaction with society (a person cannot work in a group).
Psychocorrection is needed when the patient is prescribed powerful methods of psychological influence, his condition is constantly changing and requires control.
There are few contraindications to psychocorrection. Before prescribing it, specialists must diagnose the patient in order to identify the exact developmental disorders. One of the contraindications is serious mental disorders, which must be corrected comprehensively.
Basic principles
Basic principles of psychocorrection:
- Normative development. Before prescribing methods of psychological correction, it is necessary to study the individual characteristics of the individual, social status, and level of development of the main activity.
- Unity of correction and diagnostics. The success of using psychocorrection depends on the depth and thoroughness of diagnostic procedures.
- Correction from top to bottom. For correctional activities to be effective, psychologists must create a “proximal comfort zone.”
- Operating principle. Correct corrective action provokes a person to be active and directs his energy in the necessary direction. This promotes positive changes in the psyche.
Chapter 1 Theoretical and methodological foundations of psychological correction
COMPETENCIES OF A PSYCHOLOGIST:
Know
Personal development in various types of activities. Personal growth problems. Diversity of conceptual approaches in the correctional activities of psychologists. Formation of personality as a developing system. Identify and differentiate personality traits; strong-willed qualities.
Be able to
Explain any defense mechanism (rationalization, denial, regression, repression, projection, introjection, replacement, sublimation, etc.).
Own.
To teach a behavioral model in the face of a person’s confrontation with difficult life situations, increasing the individual’s self-esteem.
Requirements for a psychologist and the developed program
There are a number of requirements that a psychologist must follow when developing psychocorrectional methods:
- Theoretical knowledge of psychological effects on people.
- Practical skills in using psychocorrectional techniques.
- Personal readiness. Before starting to work with patients, specialists must deal with personal problems and anxieties.
The psychologist should not be biased towards the patient. Otherwise, the results will either not give the desired effect or will harm it.
Techniques
There are different correction methods. Each of them has certain characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses. When working psychologically with children, all methods must be turned into games, the main principle of which is the creation of leading activity and its knowledge.
Puppet therapy
Using this technique you can:
- relieve emotional stress;
- weaken negative emotions, aggression;
- activate cognitive processes;
- develop hand motor skills;
- increase self-confidence.
Stages:
- Making a doll from any materials. The patient chooses the size and shape independently. The doll can be decorated with various decorative elements.
- Revitalization of the figure. The child must come up with a name for the doll, tell who she can be friends with, and what she does every day.
- Playing out life situations.
At stage 3, you can find out what worries the child, what barriers stand in front of him, preventing him from actively developing.
Psychodrama
Psychocorrectional technique used to work with a group of people. To reveal the inner world of the participants, various dramatic situations are simulated. Objectives of psychodrama:
- formation of new behavior that will be adequate;
- rethinking problems, internal conflicts;
- developing adequate self-understanding;
- overcoming incorrect behavior patterns.
The procedure consists of 5 elements:
- The protagonist is the first player who plays the role of the main character. He performs dramatic scenes.
- The director is an experienced psychologist who identifies disorders and mental problems and helps to deal with them. He creates dramatic scenes and gives commands to the protagonist.
- Auxiliary selves are clients who enhance the functions of the psychologist. They can play the role of people who are close to the main character.
- Spectators are members of a pre-selected group. They analyze the scene after it's completed and discuss it. They themselves do not participate in the experiment.
The stage is the place where the main actions take place.
Holding therapy
The method was developed for psychological assistance to children. When conducting the procedure, the psychologist must:
- encourage and inspire the mother of the child;
- analyze the family situation;
- restrain the mother's despair and anger;
- observe the development of the situation, record or videotape what is happening.
The principle of the technique is to force the mother to attract the child to her. After that, she must hug him and not let him go under any conditions. The mother should try to establish contact with the child, not pay attention to crying, blows, psychosis.
Imago method
An effective method of psychocorrection, in which the patient trains to reproduce different images in order to get rid of internal barriers and fears.
At the first stage, the person acts as a listener or storyteller, at the second stage the dramatization of the story is included, at the third stage dramatic performances are performed in front of the patient.
Psycho-gymnastics
A psychocorrection method in which all participants exchange information without words. Thanks to this procedure, fine motor skills of the hands actively develop and interhemispheric interaction is activated.
Play therapy
A method of psychological correction that is suitable for children and adolescents. Through the game you can get rid of negative emotions and experiences. It is important that the roles of individual participants in the game are special for the main character or all participants, and that the plot is similar to unpleasant life situations.
Art therapy
A set of techniques whose main goal is to influence the human psyche through creativity and art. The psychologist must teach the patient to express his emotions and feelings in paintings and drawings. After this, the specialist analyzes the images, disassembles the details, and prepares conclusions.
Music therapy
It is used to correct emotional disorders in children of different ages. The technique helps:
- increase aesthetic needs;
- develop communication skills;
- activate emotional processes.
Music therapy can be receptive or active. Active is needed to start productive activity, receptive is needed for psychocorrection.
Bibliotherapy
A method of psychological correction in which a psychologist conducts a survey on a topic of interest, selects specific literature for the patient, and reads it. Using this method, you can distract a person from worries, stress, and depression. Additionally, mental balance is restored.
Dance therapy
A psychotherapy technique that helps:
- establish connections between thoughts, feelings, movements;
- develop social skills;
- become aware of your own body, capabilities, features.
The practice of the technique is prohibited for people with increased aggression or diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Fairy tale therapy
Designed to correct psychological disorders in children. With its help, you can correct the child’s consciousness and behavior. It is necessary to select fairy tales that describe the experiences and problems of children.
PSYCHOLOGICAL CORRECTION AND ITS TYPES
⇐ PreviousPage 2 of 11Next ⇒Psychological culture is taking care of your mental health, the ability to get out of psychological crises yourself and help loved ones.
three main in psychological culture :
1. Self-knowledge and self-esteem.
2. Knowing other people.
3. The ability to manage your behavior, emotions, communication.
Psychological assistance includes: psychodiagnostics, psychocorrection, psychotherapy, psychological counseling, career guidance, etc.
According to R.S. Nemova, the difference between the concepts of “psychotherapy” and “psychocorrection” is as follows:
psychotherapy is a system of medical and psychological means used by a doctor
for the treatment of various diseases,
psychocorrection - a set of psychological techniques used by a psychologist
to correct shortcomings in the psychology or behavior of a mentally healthy person.
The term "correction" literally means "correction."
Psychocorrection is a system of measures aimed at correcting shortcomings in psychology or human behavior using special means of psychological influence.
V. Dubrovina considers psychocorrection as a form of psychological and pedagogical activity aimed at correcting tendencies in mental development that do not correspond to the hypothetical optimal model of normal development
Psychocorrection is subject to shortcomings that do not have an organic basis and do not represent such stable qualities that are formed quite early and practically do not change in the future.
According to A.S. Spivakovskaya, psychocorrection is intended both for healthy people who have problems, and for people who are in a borderline state, i.e. people with maladaptive behavior and emerging neurotic reactions.
The purpose of psychological correction is to eliminate deficiencies in personality development. Psychological correction differs from psychological counseling and psychotherapy in that it is not aimed at changing views, the inner world of the individual and can be carried out even when the client is not aware of his problems and the psychological content of correctional exercises.
When specifying correction goals, you must be guided by the following rules:
1. Correction goals should be formulated in a positive, not negative form. Defining the goals of correction should not begin with the word “not” and should not be of a prohibitive nature, limiting the possibilities of personal development and manifestation of the client’s initiative.
The negative form of determining the goals of correction is a description of the behavior of the activity, personal characteristics that must be eliminated, a description of what should not exist.
The positive form of presenting correctional goals, on the contrary, includes a description of those forms of behavior, activities, personality structures and cognitive abilities that should be formed in the client. The positive form of defining correction goals meaningfully sets guidelines for an individual’s growth points, opens up a field for productive self-expression of the individual, and thereby creates conditions for the individual to set self-development goals in the future.
2. The goals of correction must be realistic and correlated with the duration of correctional work and the client’s ability to transfer new positive experiences and methods of action learned in correctional classes into the real practice of life relationships. If the goals are far from reality, then the psychocorrectional program is a greater evil than its absence, since the danger is that it creates the impression that something useful is being done, and therefore replaces more significant efforts.
3 . When setting common goals
correction must take into account the long-term and short-term perspective of personality development and plan both specific indicators of the client’s personal and intellectual development by the end of the correction program, and the possibility of reflecting these indicators in the characteristics of the client’s activities and communication at subsequent stages of his development.
4. It must be remembered that the effects
correctional work manifest themselves over a fairly long time interval: in the process of correctional work; by the time of its completion; and finally, about six months later, we can finally talk about the consolidation or loss by the client of the positive effects of correctional work.
Psychocorrection is also considered as a process of expanding the range of a client’s response to certain stimuli, developing skills that make his behavior more flexible and increase the adaptive capabilities of his personality.
Onishchenko , summarizing these approaches, notes that psychological correction is a tactful intervention in the processes of mental and personal development of a person in order to correct deviations in these processes and often affects not only the individual, but also his environment, the organization of his life
Specific features are identified that distinguish it from psychotherapy.
— Psychocorrection is aimed at clinically healthy people who have psychological difficulties, problems, and neurotic complaints in everyday life, as well as people who feel good, but want to change their lives or have a goal of personal development.
— Correction focuses on healthy aspects of the personality, regardless of the degree of impairment.
— In psychocorrection, they often focus on the present and future of clients.
— Psychocorrection is usually focused on medium-term assistance (as opposed to short-term - up to 15 meetings - assistance with counseling and long-term - up to several years - assistance with psychotherapy).
— In psychocorrection, the value contribution of the psychologist is emphasized, although the imposition of certain values on the client is rejected.
— Psychocorrectional influences are aimed at changing the behavior and developing the client’s personality.
The difference between psychotherapy and psychocorrection is that psychotherapy deals with various types of disorders in people suffering from various types of somatic or mental illnesses (disorders). Many anomalies in the psyche and behavior of people that manifest themselves in diseases are similar to those that a psychologist dealing with psychocorrection deals with. However, people who seek help from a psychotherapist are usually called patients or patients, and those who need only correctional help are called clients.
A client is a normal, physically and mentally healthy person who has experienced psychological or behavioral problems in his life. He is not able to resolve them on his own and therefore needs outside help.
The main difference between psychocorrection and influences aimed at the psychological development of a person is that psychocorrection deals with already formed personality qualities or types of behavior and is aimed at remaking them,
while the main task
of development
is to
form
the necessary psychological qualities in a person in the absence or insufficient development.
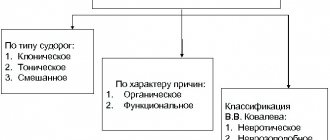
In the practice of correctional work, there are various models for explaining the causes of developmental difficulties.
Biological model -
explains the etiology of developmental deviations by a decrease in the rate of organic maturation.
Medical model-
brings problems, difficulties and developmental deviations into the area of abnormal development.
Interactionist model -
emphasizes the significance of failures and disturbances in the interaction between the individual and the environment for the occurrence of developmental problems and, in particular, due to the deficiency of the environment, sensory and social deprivation of the child.
Pedagogical model -
sees the causes of deviations in the phenomena of social and pedagogical neglect of the child.
Activity model -
puts the emphasis on the immaturity of the leading type of activity and other types of activity typical for a given age stage.
objects of correctional influence can be an individual, a family or a group.
Psychocorrection is characterized by the following features:
— Discreteness (means the psychologist’s influence on the relatively independent specific components of a person’s inner world);
— Focus on age norms (i.e. focus on a certain contingent of correctional interventions - children, adolescents, etc., or on the use of appropriate techniques).
The task of psychocorrection is formulated depending on:
— the addressee (a child with abnormal development or a person who has deviations and difficulties within the psychological norm),
— content of correctional work (correction of mental or emotional development, correction and prevention of neurotic conditions and neuroses).
⇐ Previous2Next ⇒