Home Articles Internal and external motivation of personnel
Business management
Sales department motivation
Motivation is an integral part of any work activity. Proper stimulation of employees by top management fully allows each person to realize their abilities and fulfill their work plans. Naturally, any manager knows that there are different types of motivation, as well as external and internal incentives to work, but not all bosses know what it specifically means and how to correctly introduce motivation into business. Every manager wants to increase staff productivity and sales growth. Proper incentives for employees can direct a person in the right direction and bring profit to the company. If you can find one for each sales manager, then it is possible to build long-term and fruitful relationships with the team.
Conduct an express audit of the sales department yourself using 23 criteria and identify points of sales growth!
What is motivation
Psychology views motivation from the perspective of a need for something. Need, the feeling of discomfort associated with it, depends entirely on the situation - environment, mood. The state of “yesterday I wanted to, but today I don’t really want to” hardly motivates action.
Motivation is the thought of how good it would be if. In fact, it's a dream, but not every dream motivates you to get off the couch. This is the dream that makes her achieve it. Turns a person into a scientist who has created a hypothesis of his own satisfaction if certain conditions are achieved.
Any real scientist begins to think through a plan of action, conduct experiments, and move towards the goal step by step.
The starting point in motivation becomes internal discomfort, the discrepancy between the real and the desired. Motivation is what forces two factors to be correlated:
- I can or I can’t (opportunities);
- I want or don’t want (intentions).
A person’s capabilities depend on abilities, equipment and knowledge – competencies. This is how motivation can stimulate the internal development of abilities, learning, to lead to a goal. However, the absence of one of the elements will lead to the fact that volitional effort will not be formed, and lack of will will lead to disappointment and stress.
How to apply this theory in practice?
- First of all, correct and change the company's bureaucratic policies. Make sure your human resources are in line with what other organizations offer and that they know what management expects. Taking both into account, create rules that are win-win for everyone.
- Make sure your managers are also mentors and not just bosses. Every employee should be respected and supported.
- Organizational culture plays a very important role here. There are no stamps here.
- Ensure compensation, benefits and bonuses meet market standards. If you don't pay your employees well, why should they be interested in any initiatives?
- To increase job satisfaction, make sure that workplaces are designed well and that employees find their work meaningful.
- Delegate your employees' responsibilities to make them feel valued. Respect their individuality, take their feedback seriously, and take action when necessary.
Main characteristics
Motivation consists of two parts:
- a person’s internal psychological attitude towards action or inaction;
- the ability to effectively correlate opportunities and abilities to achieve a goal.
It comes to a person in the form of specific experiences that are associated with positive emotions from achieving an object or realizing an idea. But the motive is realized only when it coincides with the ideals and cultural values of a person and society at a given moment in time.
The motif has several characteristics:
- gives energy for activity;
- directs actions to achieve goals;
- causes selectivity of attention;
- prepares for typical reaction scenarios.
The motive also necessarily includes the activity itself to achieve the goal. Motivation is not only how much a person wants to achieve a goal, but how much effort he is willing to put into it.
McClelland's acquired needs
The main idea of the method is that one should not be distracted by lower-level interests that have already been satisfied, but should pay attention to high-level needs acquired through life experience. There are three such needs - the need for achievement, participation and power:
- The desire to work much more efficiently than before. Such people take full responsibility and also rely only on themselves. They are very persistent, stubborn and strong-willed;
- The need for participation presupposes the need to communicate with people, the willingness to always listen to them. Such a person will not care what they say about him in society. Therefore, the main success is a high social position and positive opinion;
- The desire to rule is the willingness to take control of everything that happens around, all processes and phenomena. This is a “double-edged sword”: either constant and strict control over everything, or unwillingness to take responsibility and avoid any authority.
So, it is difficult to combine these needs into separate groups or indicate the direction of their satisfaction. However, knowledge of these will help in organizing the work of company employees. It is also important to consider how these motivational needs interact and influence each other. Remember that they are not mutually exclusive.
Types of motivation
A person goes towards something or leaves something.
In the first case, it is a positive motivation – movement “towards a goal”, in the second – a negative one – “from dissatisfaction (fear/poverty/poor self-esteem). But usually positive and negative motives are combined: if I quit smoking, I will become healthier, I will be able to play sports and earn more. “I’ll quit” in the context of a smoker is a negative attitude, but the ultimate goal is positive. Motivation makes you become better! External motivation is a call to action that can bring money, approval, or promotion.
Doing something interesting for satisfaction and self-realization is internal motivation. External - can be determined by a motive from the inside - a view of the situation, the internal state of a person. As a result, external and internal motivation have blurred boundaries. Motive is what affects a person’s consciousness and depends on his picture of the world. Therefore, the need for movement necessarily includes characteristics of internal and external motives: by taking action, a person changes the world around him and his attitude towards it.
Need, action, result
So, needs come first. In a practical sense, this factor can be simplified. The need can be: physiological, social and emotional.
With physiological needs everything is clear, it’s just eating, sleeping and sex. But this is elementary. Why do people buy red caviar? After all, with this money you can buy a whole range of other, no less tasty and healthy products. The fact is that red caviar and delicacies in general are not just food. This is already a social status. It is important for a person to gain a foothold in society. If a person wears simple clothes and eats sandwiches with inexpensive sausage, then in the public understanding he is ordinary, at least. And at most - a loser. It is important for people to be recognized, accepted, to have social status and rank.
What makes a person go to the movies or to football? Emotions. However, they concern not only entertainment. Many people experience real pleasure in solving a math problem, fixing a stool, or writing a program for personal use.
The result is that a person receives certain, as you can see, not only material benefits. Emotional satisfaction, for example, is generally difficult to measure.
Extrinsic versus intrinsic motivation: which is stronger?
One side of motivation supports the other. Praise, gratitude or feedback from a client evokes a sense of professionalism and competence, which increases internal motivation. Then, for the sake of approval from outside, you want to increase your skills, efficiency, and develop as a person. Falling in love with work and being inspired by the activity appears.
The relationship between internal and external is shown in the types of motivation that express the desire for success, popularity, recognition of significance, overcoming and self-overcoming (improvement), and vocation. These types are presented in the form of a ladder of human self-development. They show how a focus on external success creates people who are satisfied with their work.
Internal factors
Note 1
Through internal factors, it is taken into account that work is part of the life of any employee, associated with his emotions and feelings.
In this case, the employee should feel like part of a team (team) that is united by common goals and interests. The employee uses team support, interchangeability and group voluntary work.
These factors are internal in relation to the interests of the enterprise, since they are interconnected with life motives and the existence of personnel within the company. The emotional and psychological perception of an employee’s life is shifting towards work activity, while such factors of the motivational process may come to the fore as:
- Opportunities for self-expression;
- teamwork;
- career as an aspiration for leadership;
- management evaluation;
- the struggle for the attention and admiration of colleagues;
- pleasure from work and its results;
- pride of belonging to this enterprise.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
Factors that determine the level of motivation
The power of motivation consists of the factors that make it up:
- internal motive - the need for action, development, change forms the reason for movement. The goal or desired object (result of action) - must be so significant as to influence the picture of the world, capture consciousness and attention.
- The possibilities of satisfying a need are sometimes much smaller than the circumstances that have to be overcome. Therefore, a sober assessment of strengths and weaknesses is important.
- Ability to plan – a plan does not have to be on paper, but only in your head. To perform an action, you need to have knowledge and instructions for completing it. Lack of knowledge may be the reason for low levels of motivation.
- Self-control and implementation of the plan depends on what you have to sacrifice to achieve the goal. Insufficient reward can disappoint - that’s why motivation always consists of internal and external factors.
The vector of effort, the direction - it is important that a person is attracted to the external aspects of the process or result. It is the internal motive - the need for action, development, change that forms the reason for movement.
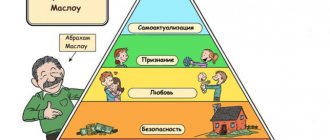
Maslow's gradation of needs
We feel different needs for something, which interact and influence each other, first at a lower level, then at a higher level. Needs are combined into groups, representing what an individual needs:
- sleep, food and rest - satisfy the basis of the creature’s life;
- stability and security;
- sociality – the need to communicate with others and loved ones;
- achieving certain goals and objectives;
- universal recognition of one's merits.
So, we have looked at all the steps of Maslow’s pyramid, placed in hierarchical order. Remember, without satisfying what we need, it will not be possible to move from a lower level to the implementation of high and sophisticated requests.
Methods (ways) of motivation
The methods of motivation depend on the object of effort. The term motivation is used to force a person to act in a certain way. To be more precise, motivation increases the effectiveness of a person’s activities in any field. Methods of exposure depend on the area of application.
Staff motivation
Personnel motivation refers to measures taken to increase labor efficiency. Depending on the goals and principles of management, the organization uses:
- financial incentives;
- organizational and administrative (fines, regulations, coercion, negative incentives);
- socio-psychological (addressed to internal motivation - involvement in something).
The choice of a motivational method in management depends on the manager’s skill and ability to find an individual approach to subordinates.
Student motivation
Teachers must take into account age-related characteristics of attention, thinking and memory in order to organize the cognitive activity of children of different ages. The most commonly used are classic
- verbal – a vivid, emotional story;
- visual and practical aids - cards with tasks, laboratory exercises that open up a desire to experiment in children;
- reproductive and search - methods of problem situations aimed at developing creative potential;
- independent work - preparing abstracts from a group or student, conducting observations that connect theory with practice.
The right choice of personnel incentives
It is important for any management to understand in a timely manner what incentives motivate this or that employee. Therefore, when building a motivation system, it is so important to navigate the team and understand each employee. The boss needs to study the reasons for the staff’s lack of interest in work using a questionnaire or survey. The results obtained will help to understand which bonus principles are suitable for stimulating these workers. Different goals and plans of people, level of education and aspirations of the employee determine the use of different types of personnel motivation:
- Material incentive;
- Non-material motivation of personnel;
- Motivating the team leader. \
The first thing you need to do is formulate a goal that may be slightly overestimated, but is quite achievable by the employee. In addition, there are now many books on the effectiveness of personnel management on store shelves. The specialized literature contains tips and methods that, after application, will bring about some changes in the company.
Scope of application of the concept
Motivation is a broad concept, but in general it reflects the reasons for human behavior. In various scientific fields, a person is an object of research in various directions. Therefore, different types of motivation are considered. In psychology, it is a carrier of consciousness; in economics, it is a subject of economic activity with needs; and in management, it is an employee whose activities are subordinated to the company’s goals. Teachers motivate by increasing the activity of cognitive activity in schoolchildren and students. The term is used in marketing when a person with needs, motives and judgments makes a decision to purchase a product.
In psychology
Psychology seeks answers to two questions:
- How does human behavior differ from that of animals?
- How can behavior be regulated to solve the problems of training, education, and activity management?
Therefore, in the broad sense of the word, motivation includes:
- psychological and physiological characteristics of a person;
- environmental factors influencing behavior.
In the narrow sense of the word, these are psychological changes that shape, direct and support human behavior. These are reasons that explain why a person did what he did in a particular situation. Why? For what purpose? For what?
Psychology of motivation studies three aspects:
- biological and physiological mechanisms associated with the satisfaction of basic needs;
- behavioral or non-psychological stimuli from the internal and external environment - conditioned reflexes;
- psychological – psychological factors are considered (unconscious, internal and external stimuli, social factors, humanistic – human consciousness).
There are various branches of psychology that have studied aspects of behavior.
In management
In management, motivation is the process of stimulating one or more people to activities that are aimed at achieving the goals of the enterprise. It's a way to get work done efficiently.
Hedonic motivational method
His supporter Jung found that people want to achieve maximum joy and minimum discomfort. Enjoyment is a fundamental factor that determines the active desire to work, the direction and organization of actions. Emotions drive behavior. If they are positive, the action is repeated, otherwise not.
Proponents of this method argue that emotions appear to be pleasure to some level that can be determined. After satiety comes the complete opposite - displeasure. In this method, two necessary factors are distinguished: the level of stimulation and hedonic tone, subjective pleasure depends on the latter.
Why do you need motivation?
Who needs it? Motivation is an instruction for behavior. When a person wants something, the brain independently finds clues to achieve success. A guy seeks a girl's attention, a child finds gifts from Santa Claus, a woman loses weight after giving birth. They are motivated because they know exactly what they want. The search for motivation is carried out by those who are not sure of the goal. A person who gets paid to work for survival will crawl to work. His ego will scream that it is better to sleep, but to sleep he will want to eat, and food is bought with money. And again we need to work!
Motivation is a struggle against one’s own habits and foundations. Therefore, trainers and motivators warn - get ready to change your life completely. Trying on someone else’s experience is being motivated by someone else’s success. This reveals the line between how external and internal motivation works - the difference between an imposed goal and determination.
What is the importance of motivating staff in an organization?
According to psychologists, self-realization is a very human thing. Our basic nature is to cherish something and see it flourish, and this applies to most things we do in everyday life. This is true for both social and societal space.
Motivation plays a very important role in a person's life. Whether it's improving ourselves or our organization. Motivated employees do not need to be told how to achieve results; they take initiative, are willing to take on additional responsibilities, are innovative and goal-oriented.
Motivated employees ensure the following:
- There is a positive atmosphere in the organization
- Colleagues are happy and feel safe at work
- Make sure customers are happy
- They always achieve better results than their colleagues
Thus, motivation is a very important factor and ensures that employees remain active and do their best for their organization. In addition, a high level of motivation reduces staff turnover. In the next section, you will learn about 5 simple ways to motivate your employees.
Practical advice
Motivation is needed by those who want to force a person to fulfill demands and obey. Therefore, they manage children, subordinates, consumers - buyers of goods and services. Even the desire to have a slim body is an imposed motive. To avoid needing motivation, you need:
- determine the type of activity you like;
- identify the goal that can be achieved in this activity;
- to have, as a result of achieving the goal, satisfaction of the financial and internal goals - gratitude, self-esteem, recognition of mastery.
That's when there will be no need for motivation. The purpose of the activity motivates itself.
Porter-Lowler model
Porter and Lauler created a method that incorporates elements of expectancy theory and equity theory. The developed model consists of the following points:
- effort made;
- perception;
- results achieved;
- reward;
- feeling of satisfaction.
According to the theory, the results directly depend on our qualities, efforts, and abilities, therefore, to determine the motivation of employees, it is enough to take them into account. High performance is achieved when work done is rewarded (material incentives). It follows that achieving good results becomes the reason for quality work. The cause, but not the effect.
Psychoanalytic motivational method
Freud created and developed the psychodynamic approach to the study of human behavior. It is based on the recognition that there are psychological forces that shape our actions, but are not always conscious of them. Freud believed that instincts drive our behavior. Eros is life. Thanatos – destruction and death. Source, goal, object and stimulus are the main instinctive parameters. An individual is understood as a community of three parts:
- “I” – knowledge of oneself and one’s “ego”;
- “Id” (it) – accumulates instincts and impulses;
- “Superego” (unconscious) – moral behavioral aspects.