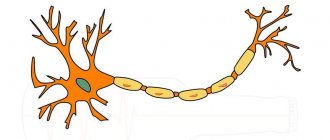
Polyneuropathy is a rather dangerous disease, which is a lesion of the peripheral nervous system, the basis of which is trophic disorders, sensitivity disorders, vegetative-vascular dysfunctions, flaccid paralysis, observed primarily in the distal segments of the limbs. This disease is usually classified according to the etiological factor, pathomorphology of the pathological focus and the nature of the course.
Polyneuropathy of the extremities is considered a fairly common pathology, usually affecting the distal parts with gradual involvement of the proximal parts.
What is polyneuropathy of the lower extremities
The name of the disease is translated from Greek as “disease of many nerves,” and this translation fully conveys the essence of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities. In this case, almost all endings of the peripheral nervous system are affected.
There are several forms of the disease:
- Sensory polyneuropathy of the lower extremities. It manifests itself to a greater extent as a sensitivity disorder in the affected area, for example, numbness, a tingling or pins and needles sensation, a burning sensation. Treatment consists of controlling sensory symptoms with medications. Distal sensory polyneuropathy of the lower extremities brings a lot of inconvenience to the victim, since initially suspecting the disease is quite problematic, but the longer treatment is delayed, the more difficult it will be.
- Motor. The main symptom is muscle weakness to the point of complete inability to move arms or legs. This can very quickly lead to muscle atrophy.
- Sensorimotor. Combines symptoms of sensory and motor polyneuropathy. In most cases, this form is diagnosed.
- Vegetative. It differs in that in the foreground there are symptoms of damage to vegetative fibers. Direct symptoms include paleness of the skin, increased sweating, dizziness, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, constipation, and tachycardia. Autonomic disorders signal several problems at once, so it is imperative to consult a doctor.
- Mixed. This form is diagnosed if all of the above symptoms are observed.
Expert opinion
Author: Alexey Vladimirovich Vasiliev
Neurologist, Head of the Research Center for Motor Neuron Disease/ALS, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Polyneuropathy is a complex disease characterized by atrophy of nerve fibers as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the peripheral nervous system. The pathology affects the upper and lower extremities and is accompanied by impaired sensitivity of the integumentary tissues, muscle performance, and deterioration of blood circulation.
Polyneuropathy is divided into 2 types:
- Primary is deadly, can be observed in any healthy person, progresses very quickly, and often ends in Landry’s paralysis.
- Secondary develops as a result of metabolic disorders and is a consequence of diabetes mellitus, vitamin deficiency in the body, general intoxication, infections, and injuries.
Symptoms of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities are pronounced. Initially, a person feels weakness in the legs, a feeling of numbness of the feet appears, gradually spreading to the entire limb. Some patients complain of burning and pain, tingling in the legs; in advanced cases, there is an unsteady gait and dysfunction of motor skills. Depending on the severity of the condition, symptoms such as dark circles under the eyes, dizziness, weakness, and tremors may appear. Doctors at the Yusupov Clinic will examine the patient, based on comprehensive diagnostics, identify an accurate diagnosis, and prescribe treatment in accordance with the general condition and side symptoms of the disease.
Inflammatory polyneuropathies
The diphtheria form of the disease is characterized by the early appearance of oculomotor disorders (mydriasis, ptosis, diplopia, limited mobility of the eyeballs, paralysis of accommodation, decreased pupillary reactions to light) and bulbar symptoms (dysphonia, dysphagia, dysarthria). One to two weeks after the onset of the disease, paresis of the extremities, predominant in the legs, becomes evident in its clinical picture. All these symptoms are often accompanied by manifestations of intoxication of the body.
HIV-associated polyneuropathy is accompanied by distal symmetrical weakness in all extremities. Its early symptoms are mild leg pain and numbness. In more than half of cases, the following symptoms are observed:
- distal paresis in the lower extremities;
- loss or decreased Achilles reflexes;
- decreased vibration, pain or temperature sensitivity.
All these symptoms appear against the background of other signs of HIV infection - fever, weight loss, lymphadenopathy.
Lyme borreliosis polyneuropathies are considered a neurological complication of the disease. Their clinical picture is represented by severe pain and parasthesia of the limbs, which are then replaced by amyotrophies. The disease is characterized by more severe damage to the arms than to the legs. In patients, deep reflexes in the hands may completely disappear, but the Achilles and knee reflexes are preserved.
Causes of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities
The causes of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities of various types are similar. The following points may lead to development:
- Diabetes. It is the most common cause of the disease, as it disrupts the proper functioning of the vessels that feed the nerves, thereby causing a deviation in the myelin sheath of the nerve fibers. With diabetes, the legs are most often affected.
- Severe deficiency of any of the B vitamins. The work of the nervous system is based on them, and therefore their long-term lack can lead to the development of the disease.
- Exposure to toxic substances on the body. Toxins include chemical toxic substances, alcoholic beverages, as well as intoxication due to various infectious diseases: diphtheria, human immunodeficiency virus, herpes. When the body is poisoned with carbon monoxide or arsenic, distal polyneuropathy can develop in just a few days, and with alcoholism and infections a longer development is typical.
- Traumatization. Nerve fibers are damaged by injury or surgery. The first include compression of the nerves, which is characteristic of spinal diseases such as herniated intervertebral discs and osteochondrosis.
- Guillain-Barre syndrome. Autoimmune disease often develops in the human body after infectious pathologies.
- Hereditary predisposition. Researchers have proven that certain disorders in proper metabolism that lead to polyneuropathy are transmitted genetically.
In rare cases, pathology occurs in pregnant women who seem to be absolutely healthy. The disease can manifest itself at any time - both in the first and third trimester. Scientists agree that the cause is precisely a deficiency of B vitamins, prolonged toxicosis and an unpredictable reaction of the pregnant woman’s immune system to the fetus.
The first signs of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities
The first symptoms are found mostly on the distal parts of the legs. First of all, the foot disease is affected, and then the symptoms of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities gradually spread upward, so it is important to start treatment on time.
Initially, patients experience discomfort:
- burning;
- tingling;
- "goosebumps";
- numbness.
Then pain appears, and it is possible even from a light touch. Additionally, there may be a disturbance in sensitivity in the area of damage to the nerve fibers - it can either decrease or increase.
Symptoms are complicated by muscle weakness. In extremely rare situations, restless legs syndrome occurs.
Due to improved blood circulation in the affected areas, tropical and vascular disorders occur over time on the victim’s skin, which manifest themselves in:
- worsening or hyperpigmentation;
- peeling;
- cracks;
- ulcers.
Vascular type disorders include excessive pallor of the skin and a feeling of cold in areas prone to the disease. Symptoms of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities cannot be seen in the photo, so you should listen to your feelings.
Dynamics of manifestations
In patients suffering from sensory polyneuropathy of the lower extremities, positive sensory symptoms (burning sensations and other paresthesias) first appear in the feet, most often in the fingertips. Over time, negative sensory symptoms (numbness and decreased sensitivity) appear. As shorter and shorter nerve fibers are affected, they gradually spread proximally (to the lower leg and thigh).
After the symptoms in the legs rise to the middle of the legs, a violation of superficial sensitivity appears in the arms. This leads to the classic "socks and gloves" look. If the sensitivity disorder has risen to the middle of the thigh on the legs and to the level of the elbow on the arms, you can expect the appearance of an area of reduced sensitivity in the lower part of the anterior abdomen. It is caused by damage to the longest trunk nerves and has the shape of an irregular semicircle with the apex directed towards the sternum. In contrast to the level of damage in diseases of the spinal cord, sensory disturbances in sensory polyneuropathy are detected only on the anterior surface of the body and are absent on the back. Their upper border is curved rather than horizontal.
With porphyritic polyneuropathy, sensory disturbances are not detected on the feet and hands. And in the proximal parts of the limbs and on the trunk. If deep sensitivity fibers are involved in the pathological process, sensitive ataxia develops - a disorder of sensory perception of pressure, vibration and body position in space. It leads to incoordination and movement disorders. It manifests itself as a disorder of coordination and gait, decreased tone of skeletal muscles and distal limbs. Patients experience constant worm-like hyperkinesis of the upper extremities (slow movements of the fingers) with outstretched arms, which intensify with closed eyes.
Symptoms of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities
The causes of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities are different, but the symptoms are always similar. They are expressed as follows:
- muscle weakness;
- decreased sensitivity, which may disappear altogether;
- lack of reflexes;
- burning;
- swelling;
- trembling fingers;
- increased sweating;
- cardiopalmus;
- lack of coordination;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- difficulty with balance;
- slow healing of wounds.
Symptoms can vary in severity. Therefore, the disease can develop either over years or in a matter of days.
Diagnosis of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities
The presence of polyneuropathy can be determined without special tests, based on the symptoms and first signs. It is necessary to conduct special tests to identify the cause of the disease. Due to the abundance of symptoms, diagnosis can be difficult. In this case, a number of instrumental and laboratory studies will be required.
Initially, consultation with a neurologist is necessary. The doctor should examine the affected areas and check reflexes. If polyneuropathy is suspected, you must do the following:
- general blood analysis;
- check blood and urine sugar levels to rule out or confirm the presence of diabetes;
- biochemical analysis for indicators such as creatinine, urea, total protein, liver enzymes, vitamin B12 levels.
Sometimes a nerve biopsy may be necessary.
Electroneuromyography is also additionally prescribed. Neurophysiological research helps to find out how quickly the signal reaches the nerve endings. Carrying out is necessary regardless of clinical symptoms, as it helps to identify the speed of spread of excitation along the nerves. To assess the symmetry and level of the lesion, an EMG of the legs is required.
A history and physical examination can help determine the need for additional testing to determine the cause of the neuropathy.
Treatment of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities
A patient with polyneuropathy of the lower extremities needs to prepare for long and difficult complex treatment. Since it consists not only in relieving symptoms that poison life, but also in eradicating the root cause of the disease.
As a result, the nerve fiber is destroyed, and it will take a long time to restore it. The course of treatment begins with a direct impact on the factor that caused the polyneuropathy, that is, with the relief of the underlying disease or stabilization of the patient’s condition.
For example, if the cause of the disease is diabetes mellitus, then all efforts are initially aimed at reducing blood sugar levels; in case of an infectious type, drug therapy is aimed at fighting the infection, and if the root of the problem is hidden in a deficiency of B vitamins, then it is important to compensate for the deficiency in a timely manner. If the cause of polyneuropathy is disruption of the endocrine system, the doctor prescribes hormonal therapy. But vitamin therapy is more widely used in treatment.
Positive results are demonstrated by those drugs that are aimed at improving blood microcirculation, and therefore nourishing nerve fibers.
Physiotherapeutic techniques, such as electrophoresis, are actively used in treatment. If polyneuropathy of the lower extremities is accompanied by severe pain, the patient must be prescribed painkillers, locally and orally.
It is impossible to completely insure yourself against the disease. But you can try to prevent it using simple precautions. That is, when working with toxic substances, it is imperative to use appropriate protective equipment, take any medications only after consultation and prescription of a doctor, and do not let infectious diseases take their course, preventing them from going into a chronic inflammatory period, when it will no longer be possible to cure the disease and all that remains is to treat it. exacerbations and relieve symptoms. The simplest measures to prevent problems are a balanced diet rich in vitamins, constant physical activity, and avoidance of alcoholic beverages.
Initially, treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause, and then maintenance therapy continues. It is necessary to discontinue medications and eliminate the effects on the body of toxic substances that caused the disease, adjust the diet, supplementing it with the necessary vitamins. Considering that only these measures slow down the course of the disease and reduce complaints, recovery progresses extremely slowly and may be incomplete.
If the cause cannot be stopped, all treatment is reduced to minimizing pain and disability. A rehabilitation specialist and physical therapist will recommend special orthopedic devices.
Tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants are prescribed to relieve neuropathic pain such as burning or pins and needles. Medicines that affect the central nervous system are selected individually for each patient, depending on the state of the body and the patient’s psyche. It is strictly prohibited to prescribe medications on your own, so as not to cause even greater harm.
For demyelinating polyneuropathy of the legs, treatment based on immunomodulators is often used. Plasmapheresis or intravenous administration of immunoglobulins is recommended for acute inflammatory demyelination.
For chronic myelin dysfunction, plasma exchange or intravenous administration of immunoglobulin, corticosteroids or metabolic inhibitors is prescribed.
Of the entire list of vitamin preparations, preference is given to vitamins B1 and B12, which are also called thiamine and cyanocobalamin. The substances improve the level of transmission of excitation throughout the nerve fiber, which significantly reduces the manifestations of the disease, and also additionally protects the nerves from the effects of active radicals. They are prescribed over a long course in the form of injections administered intramuscularly.
Even if the treatment was successful and all or most of the nerve fibers were restored, it is too early to relax. It is necessary to carry out a long course of rehabilitation therapy, since with polyneuropathy, the muscles first suffer, losing tone. Therefore, long-term work aimed at restoring mobility is necessary; the help of several specialists may be required at once.
During rehabilitation after an illness, massage is mandatory. It repeatedly improves blood supply, restores mobility and elasticity to muscle tissue, and improves metabolic processes.
A similar effect is provided by various physiotherapeutic techniques. They also improve microcirculation, reduce pain and restore muscle cells. Physiotherapy for polyneuropathy of the lower extremities is most useful, so it is not recommended to neglect it.
In cases of severe injuries where complete recovery is not possible, the assistance of an occupational therapist may be required. Occupational therapy is action therapy. The specialist helps facilitate the patient’s process of adaptation to a state of limited movement, develops a new algorithm of movements necessary to perform everyday activities.
Due to the uniqueness of each case, the scheme of rehabilitation measures is developed individually and depends on the patient’s condition. Rehabilitation may include vitamin therapy, long-term work with psychologists, diet therapy and other techniques, depending on the specific situation.
Treatment of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities must begin immediately, without delay. As soon as alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor - without timely treatment, there is a high risk of complications in the form of paralysis, disruption of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Timely treatment will help reduce the likelihood of complications to a minimum and maintain full functionality. Don’t forget about restorative therapy, it is this that will consolidate the effect obtained from the treatment.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a way to correct mild symptoms of the initial stages of polyneuropathy. Such methods can be used independently if a disease occurs due to a lack of vitamins or vascular disorders.
In other cases, physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary method of treatment, and its leading function is to enhance the effect of the main therapy.
Let's consider all types of physiotherapeutic treatment, as well as their effect on nerve cells.
Electrophoresis
A weak pulse of electricity is an effective means of stimulating the activity of nerve impulses and enhancing metabolic processes in cells.
A little stress causes cells to begin functioning in an enhanced mode and use all internal reserves. Active self-healing processes are immediately launched, which is very important in the treatment of polyneuropathy.
Electric current also affects blood circulation in peripheral vessels. By stimulating them, it promotes active flow of blood and nutrients.
All these properties have a positive effect on the course of recovery and promote active healing of damaged membranes.
Magnetic therapy
Exposure to magnetic fields is carried out in case of damage to the peripheral parts of the nervous system . It acts locally, that is, it affects only the nervous tissue that was exposed to the waves from the device.
Magnetic waves influence biochemical processes in cell membranes, as well as the axons themselves (the core of the cell). Metabolism improves, the transmission of nerve impulses through membranes improves, and natural restoration of damaged areas begins.
They also have an effect on the cell core. Accelerated restoration of the fibers of the axon itself is triggered.
The method is used separately or in addition to main therapy, and can be combined with massage or physical therapy.
Massage
Massage is one of the most effective means of recovery for muscle fiber atrophy. It is performed by special health workers trained in professional massage techniques. There are also some complexes that are available to the patient at home. That is, you can do them yourself.
The procedure instantly improves blood supply to tissues, which is why it has such a strong effect.
Massage is indispensable for complete or partial atrophy, when it is not possible to even perform physical therapy complexes on your own.
Sometimes this is the only remedy that can raise an immobile patient to his feet.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is one of the most popular methods of treating polyneuropathy. Exercise therapy allows you to:
- Improve blood circulation (increase the effect of drugs aimed at this);
- Restore muscle strength;
- Regain the ability to walk.
Without additional physical activity, the effect of the medications will not be as effective when it comes to returning the ability to walk.
Prognosis of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities
The disease is very dangerous for humans, as it does not go away on its own. If you start polyneuropathy, the consequences will be sad.
It is worth remembering that prolonged muscle weakness often leads to a decrease in the tone of the body muscles and subsequently to complete muscle atrophy. In turn, this can lead to the appearance of ulcers on the skin.
In rare cases, polyneuropathy results in complete paralysis of the distal planes of the body and respiratory organs. This is deadly for humans. A progressive disease causes a lot of inconvenience to the victim, forcing him to build a new way of life, radically changing his usual way of life. Over time, patients lose the ability to move independently and care for themselves, which is fraught with feelings of increased anxiety and depression. In this case, the help of a qualified psychologist is urgently needed. Distal polyneuropathy of the lower extremities requires long-term rehabilitation even after recovery and relief of all symptoms.
Complications of polyneuropathies
Common complications associated with polyneuropathy include:
- Falls and Injuries
– Lack of balance and coordination, as well as muscle weakness, can lead to falls and injuries. - Burns and skin damage
. Numbness and the inability to feel pain or temperature changes can lead to accidental burns, cuts, and other skin injuries. - Infections
. Injuries, burns and cuts, especially on the legs and feet, can go undetected, increasing the risk of infection.
Prevention of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities
In order to prevent a disease such as polyneuropathy of the lower parts of the body, it is necessary to stop drinking alcohol, regularly monitor blood and urine sugar levels, and when working with hazardous and toxic substances, it is imperative to use special personal protective equipment.
To avoid pain after relieving the disease, it is recommended:
- wear loose shoes that do not pinch your feet;
- do not take long walks over long distances;
- do not stand still for a long time without changing position;
- wash your feet in cool water.
Do not forget about physical therapy, designed to keep muscles in constant tone, preventing atrophy. Regular physical therapy for polyneuropathy will strengthen the body. It is worth leading a calm lifestyle, avoiding emotional stress, which can negatively affect the nervous system, eating right and listening to the state of the body in order to prevent the disease from returning.
Author
Olga Vladimirovna Boyko
Neurologist, MD
Surgical interventions
Surgical intervention is used for paraneoplastic type of polyneuropathy. It develops with concomitant oncology, with a large tumor size.
The tumor compresses any part of the nervous system (nerve), which immediately disrupts the full flow of the nerve impulse, delays in transmission occur, and the peripheral part that was hit begins to suffer from a lack of sensitivity. Polyneuropathy is formed.
The only possible method of correcting the condition is to remove the tumor and relieve pressure from the area of the nervous system.
Surgical interventions are also used for the diabetic form of the disease.
Expert opinion
Filimoshin Oleg Alexandrovich
Neurologist, city clinic of Orenburg. Education: Orenburg State Medical Academy, Orenburg.
In this case, dead tissue or whole parts of the body are removed (if gangrene develops).
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Batueva E.A., Kaygorodova N.B., Karakulova Yu.V. The influence of neurotrophic therapy on neuropathic pain and the psycho-vegetative status of patients with diabetic neuropathy // Russian Journal of Pain. 2011. No. 2. P. 46.
- Boyko A.N., Batysheva T.T., Kostenko E.V., Pivovarchik E.M., Ganzhula P.A., Ismailov A.M., Lisinker L.N., Khozova A.A., Otcheskaya O .V., Kamchatnov P.R. Neurodiclovit: possibility of use in patients with back pain // Farmateka. 2010. No. 7. pp. 63–68.
- Morozova O.G. Polyneuropathy in somatic practice // Internal medicine. 2007. No. 4 (4). pp. 37–39.
Prognosis for polyneuropathy
Patients diagnosed with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy have a favorable health prognosis. The mortality rate of patients with this diagnosis is very low. However, it is impossible to completely cure the pathology, so treatment involves eliminating its symptoms. Immunosuppressive therapy can achieve remission of the disease in more than 90% of cases. However, it must be remembered that the disease polyneuropathy is accompanied by numerous complications.
Hereditary polyneuropathy progresses very slowly, making its treatment difficult and the prognosis for patients poor. However, many patients manage to adapt and learn to live with their illnesses. A favorable prognosis for diabetic polyneuropathy is possible only if it is treated in a timely manner. Usually doctors manage to normalize the patient's condition. Only in the later stages of polyneuropathy can the patient complain of severe pain. The prognosis for the life of a patient with uremic polyneuropathy depends on the severity of chronic renal failure.