General information
Borderline personality disorder (otherwise called ambulatory schizophrenia ) refers to emotionally unstable, deep and persistent psychopathy . This disorder is characterized by impulsivity, low self-control, emotional instability, an undeveloped sense of self, high levels of anxiety, and severe levels of desocialization. The condition is considered borderline - an intermediate phenomenon between neurosis and psychosis , since the failure of the organization is more pronounced than in a neurotic disorder, but less pronounced than a psychotic one. Some scientists consider this a way of coinciding with real life, a kind of adaptation developed in childhood.
However, unfortunately, such adaptive behavior of children does not allow them to find happiness in adulthood; it is difficult for them to separate from their parents and act independently as an adult. The most dangerous manifestation of a borderline neurosis-like pseudoneurotic disorder is self-harm, which is most often provoked by painful memories, feelings of emptiness and uselessness. Even minor, ordinary life situations and incidents can cause symptoms. Some researchers associate the development of pathology with substance abuse, depression , and eating problems. Approximately 10% of patients commit suicide.
Most often, young people suffer from borderline disorder - approximately 1.5%, women 3 times more often than men. Improvement with modern treatment methods can be achieved in approximately 10 years.
Psychology
The most common cause of borderline disorder is child abuse. A common case is that a girl is abused by an adult man (stepfather). He intimidates her, and she doesn't tell anyone about it for years. And such an emotional environment leads to borderline personality disorder in the future. But sometimes parents can create it too.
Sometimes a family looks outwardly prosperous, but in reality, its adult members experience borderline states when parents pelt each other with accusations. When children cannot predict these sudden outbursts, they prescribe crazy traits to themselves. Violence can be moral and invisible to others.
There are officially recorded cases where borderline disorder developed like this. The child lived with a believing grandmother, who carefully instilled in him a religious attitude. He began to treat every mistake as a sin and felt guilty everywhere.
Pathogenesis
A person’s temperament and personality are psychologically influenced by their immediate surroundings and external environment every day. The ability to respond “appropriately” and maintain normal cognitive and behavioral responses primarily depends on learned skills to deal with negative emotions and stress.
The manifestation of “painful” behavior occurs at a fairly young age. It begins with the development of affective instability, when a person has strong emotions in ordinary life situations and it takes a lot of time to achieve the initial normal state. For example, instead of embarrassment, people experience great guilt and shame, instead of irritation - rage, etc. In addition, they may experience euphoria and dysphoria , that is, causeless transient cheerfulness or, on the contrary, severe anxiety, mixed feelings of anger and sadness. They are characterized by depression, spiritual and emotional distress. The condition can also be considered an extension of post-traumatic stress .
In the future, the condition may worsen. To varying degrees, there will be a tendency towards self-destruction, victimization, separation or loss of identity. People with this disorder are increasingly making rash decisions, becoming addicted to psychotropic substances, leading a promiscuous sex life, committing crimes, especially in response to life shocks, thus trying to escape from the problem and “engaging” in self-destruction, getting rid of feelings, emptiness, boredom and pain. However, in the future they experience an even deeper feeling of guilt and remorse (but not always), but in order to get rid of it they return to impulsive actions and the circle closes. Moreover, in the future, thoughtless, impulsive actions become an automatic reaction to any emotional shock.
One of the ways people with borderline personality disorder cope with negative emotions is through self-harm and self-destruction. This may be due to self-punishment, problems of self-esteem, a way to express anger, distraction, or, on the contrary, a desire to return to normal sensations (as a response to dissociation). While the desire to end life is an urge to do better for others. For example, in adolescents, sexual violence becomes the impetus for suicide and self-destructive behavior.
Typically, people with borderline disorder find the world to be cruel and evil. In their relationships with loved ones, they tend to adopt a fearful, avoidant, ambivalent, and fearful pattern of devotion.
Biology
Doctors have discovered the presence of abnormalities in the brains of people suffering from this disease. The appearance of suicidal thoughts, anxiety and fear of loneliness is explained by the fact that there is little serotonin in the body. Its production is disrupted. Due to stress at an early age, the situation gets worse. Therefore, impulsive actions, weakness of will and self-discipline are not the result of promiscuity, but have a biological cause.
For specific biological reasons, patients are unable to control their own aggression. For example, in the brain of a person suffering from BPD, the amygdala, which is responsible for emotions, is over-activated. This provokes an error in the perception of the interlocutor’s facial expression, so he may look angry and unfriendly.
But experts noted that mental disorders can be both a consequence and a cause. That is, the more a person behaves impulsively, the less certain areas of the brain are used.
Also, every person with borderline personality disorder has increased activity in the production of stress hormones - cortisol. For this reason, they are always overly wary.
There is weak activity in the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for self-control. Therefore, it is difficult for them to look at themselves from the outside.
Many patients also noticed a small volume of the hippocampus, which affected their memory. It is difficult for them to realize the history of relationships with others.
The production of dopamine is impaired. Thus, in healthy people, this hormone causes pleasure from pleasant events and encourages them to look for pleasant things in the world around them. But for those suffering from BPD, it is produced from negative emotions in relationships. Therefore, they look for repetitions of negative relationship scenarios.
Classification
A borderline state, depending on the clinical manifestations, can be presented in the form of a psychosomatic, neurotic, neurosis-like and shallow affective syndrome or as an amorphous, variable, fluctuating symptom complex, which is characterized by a different mosaic of mildly expressed mental, neuroendocrine, neurovegetative-visceral and neuroimmune disorders.
In addition, in the borderline syndrome, mood disorders, cognitive, antisocial and narcissistic can be distinguished separately.
Causes
The etiology of borderline disorder is not fully understood, but factors contributing to its development include:
- irrational intake of high doses of psychotic substances;
- childhood psychological trauma (most often - verbal, emotional, physical or sexual abuse, incest, death of parents);
- depressive state;
- problems in eating behavior;
- increased levels of chronic stress;
- dissatisfaction and problems with a romantic partner, such as domestic violence and unwanted pregnancies;
- having close people with a similar disorder;
- difficult events in the world or personal life;
- genetic predisposition - due to gene polymorphism, the synthesis of serotonin and its activity in the brain are reduced and, as a result, aggressiveness increases.
It is less common to consider the influence of congenital brain damage, neurobiological factors, social instability and sleep abnormalities on the manifestation of a mental disorder.
Where do “psychopathic border guards” come from...
Until today, scientists cannot say with complete certainty the exact causes of borderline personality disorder; there are only theories:
- It is believed that the disease is caused by an imbalance of chemicals (neurotransmitters) in the patient's brain. They are responsible for the mood of the individual.
- Genetics (hereditary predisposition) also plays an important role As noted above, women are more often affected by the disease (more than two-thirds of all registered cases).
- The occurrence of the disease is also influenced by the nature of the . People with low levels of self-esteem, increased anxiety, and a pessimistic outlook on life and events can be conditionally classified as a risk group.
- Childhood is also of great importance . If a child has been sexually abused or has been exposed to physical and emotional abuse for a long time, or has experienced separation or loss of parents, all of this can trigger the development of a personality disorder. But even in quite prosperous families, there is a risk of a child developing a mental illness if the parents forbid him to express his feelings and emotions, or were overly demanding of him.
Symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder
Borderline personality disorder causes psychophysical discomfort and is accompanied by the development of a number of psychological and behavioral atypical reactions.
Symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder
The main symptoms that borderline syndrome includes:
- strong emotional reactions that last longer than usual and are experienced more deeply, for example, feelings of love, happiness, guilt, sadness, anxiety, anger, aggression;
- “split and weak Ego”, reasoning in a dichotomous (black and white) vein - patients tend to idealize, experience a feeling of adoration, or, on the contrary, change their minds and become very disappointed in loved ones, beginning to feel anger and disgust, devalue the value of a previously dear person, this also applies to attitude towards oneself, so to speak - “thinking in extremes”;
- emotional isolation, paranoid thoughts, self-harm and suicidal behavior - may be caused by fear of being alone, hypersensitivity to criticism, rejection, failure, or manifestations of anger, self-punishment;
- constant feelings of emptiness and loss, apathy can be caused by difficulties with self-perception - difficulties in determining goals and aspirations, tastes and values;
- problems with concentration and signs of dissociation, expressed in “switching off” attention;
- impulsive tempers, rash decisions and risky actions, for example, passion for alcohol, drugs, anorexia , bulimia or other eating disorders, promiscuous and unprotected sex life, thoughtless spending.
Types of spontaneous behavior addictions accompanying borderline mental disorders
Mental disorders of various types, including borderline ones, make a person more impulsive and spontaneous, increase the tendency to rash, risky, and in this case, self-destructive actions. Spontaneous actions lead to emotional chaos and can be divided into several types of addictions:
- passion for arson or pyromania - patients have a tendency to deliberately set fires, which brings them pleasure, and not material gain or a way to take revenge;
- unbridled desire to steal ( kleptomania ) - characterized by the patient’s inability to resist the impulse to steal something, and their financial viability allows them to pay for these purchases;
- trichotillomania – the desire to pull out hair from one’s own body and even eyebrows and eyelashes;
- Gambling addiction is a constant obsessive desire of people to participate in gambling, despite the consequences.
Characteristic manifestations
Basically, when talking about these types of disorders, they mean neuroses, sometimes neurotic reactions, psychopathy.
And if the latter are of a purely biological nature (organic failure), then social problems lead to neurotic reactions. A characteristic feature of neuroses is maintaining criticism of what is happening. Neurotic reactions last for a certain period of time, in which the beginning can be clearly identified. Meanwhile, the onset of psychopathy is difficult to establish; one can only find a situation that significantly influenced the development of psychopathy, which, as a rule, caused a conflict.
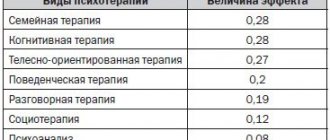
We recommend: Methods and types of psychotherapy
All other borderline states can be placed between a neurotic reaction and psychopathy. Gradually moving in the direction of psychopathy, we will observe that the importance of psychogenic factors decreases, and biological ones increase.
The bulk of neurotic disorders are divided into neurotic reactions, the neuroses themselves, as well as personality development, which can be called neurotic. Neuroses include neurasthenia (easily excitable and quickly exhausted), psychasthenia (mental weakness, the first signaling system is less manifested than the second, this causes a lot of indecision), obsessive states (thoughts, fears, desires that cannot be gotten rid of) and hysteria ( a very vivid perception of the world completely suppresses rationality).
One of the new borderline disorders is PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder). Its essence is that after experiencing severe stress (catastrophe, massacres, military operations, natural disasters), a person develops anxiety, scenes of the past can be constantly reproduced in memory, which is why there is increased aggressiveness, and avoidance of any mental stress.
Borderline disorders also include social stress disorders that arise in certain social, economic and political conditions. Social stress disorders are characterized by the fact that social disasters invade the mental life of a huge number of people. There is a high risk of developing social stress disorder in situations related to changes in the lifestyle adopted by the majority, religion or the basic idea of the state.
We recommend: What is anhedonia?
The study of psychopathy (sustained disharmonious changes in character in the absence of serious mental disorders) began already in the 18th century. By now, psychopathy has acquired a new name in science – personality disorder.
The main characteristics of personality disorder are the persistence of character changes, their totality and problems with social adaptation. Prevalence estimates range from 5 to 10%, with as many as a quarter of those in prison already having such disorders.
Presumably, disorders can only arise due to an innate predisposition, although there are other points of view. Their main signs are emotional-volitional disorders, loss of control over activities.
At different stages, each of the considered forms of borderline disorders is expressed differently. If we talk about the general form, the following violations can be compared to the forms:
- Adaptive reactions: asthenia, anxiety, sleep disorders.
- Neurotic reactions: anxiety and fear, neurotic disorders, decompensation.
- Neuroses: depression, neurasthenia, hypochondria, obsessions.
- Development of individuals with disabilities: Enduring personality changes.
- Reactive psychoses: fear, disorganization, confusion, uncriticality of one’s own condition.
Tests and diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, the psychoanalyst must thoroughly study the anamnesis, clinical picture and nature of the symptoms. Conversations and stories from patients about their experiences, actions and difficulties in social interaction help with this. Moreover, it is possible to exclude other diseases, for example, of organic origin, after undergoing a full comprehensive examination of the body.
It is often most difficult to distinguish a personality disorder from drug addiction and identity disorders, so it is important to:
- assess the amplitude of distress and emotional lability;
- study the state of working capacity and productivity;
- identify suicidal manifestations and a tendency to self-destruction (scars, burns, tattoos, etc.);
- detect a state of combination of 3 feelings - devotion, self-destruction and loss of control.
Thus, compliance with the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) criteria is assessed. At least 5 out of 9 must be completed, these include:
- uncertainty and disharmony of self-image, life positions, identification and behavior tactics;
- pathologically unstable interpersonal relationships and social maladjustment;
- affective and emotional instability;
- emptiness and obvious impulsive behavior of a chronic nature.
Borderline Personality Disorder Test
Today, for a personal express analysis of one’s mental abnormalities and to establish a tendency towards borderline personality disorder, a test for borderline disorder was developed by Lasovskaya, Yaichnikov, Sarycheva and Korolenko, which is available even to online users. The test is a 20-item questionnaire based on DSM-5 diagnostic criteria. If the test taker scores 25 or more points, then this is a clear signal to seek help from a specialist.
Diagnosis of BPD
Diagnostics is the first and main stage before prescribing a course of therapy. The specialist takes the following steps step by step:
- a detailed survey of relatives, work colleagues and friends, which helps to establish the exact time when signs of borderline personality disorder first appeared;
- studying family history - it is important to make sure that close relatives do not have similar diseases;
- collecting maximum information about the patient’s life;
- conversation with the patient and observation of him from the outside in order to identify characteristic symptoms of mental pathology;
- conducting psychological testing to obtain a complete picture of the internal state of a mentally ill person.
Diet for Borderline Personality Disorder
Diet for depression
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 1-3 months
- Dates: no data
- Cost of products: 1700-1800 rubles. in Week
Since eating problems are common among people with borderline disorder, it is very important to monitor your eating and keep a diary . It is best to choose a healthy, balanced diet. If you have problems with excess weight, then you can try a protein-vegetable diet for weight loss or another that is balanced and healthy, and most importantly, capable of providing the body with all the nutrients necessary for life.
Mental disorders and depression can be associated with depletion of neurotransmitters , insufficiency of joy hormones, vitamins and, in general, an imbalance of humoral and neuroregulation. To provide the body with all the plastic components it is recommended to add to the diet:
- fish and various seafood;
- eggs and poultry meat;
- cereals and whole grains found in healthy breads and pastas;
- dairy products;
- fresh bright and colorful fruits, vegetables and herbs;
- herbs and spices help stimulate appetite and improve mood and satisfaction from food;
- chocolate is a known source of dopamine ;
- Bananas also help achieve the usual daily feeling of “euphoria.”
History and reasons
For the first time, people started talking about borderline disorders in the context of neurotic ones already in the 16th century, trying to understand what nervousness is.
This was followed by a description of hysteria, and it was only in 1776 that the now widespread term “neurosis” was introduced by Cullen. He associated this condition with damage to the nervous system. Neurasthenia played a special role in the accumulation of knowledge about borderline states. It, hysteria and hypochondria became the main diseases considered by borderline psychiatry in the 20th century. Along with this, the doctrine of psychopathy developed, presenting descriptions of various deviations in the personality structure.
We recommend: Psychopathology is
As a result of lengthy discussions, many researchers and scientists agreed that borderline disorders develop against the background of organic problems, which include all factors leading to pathological disruption of the normal functioning of the body (including trauma, radiation, infections, etc.).
As Sommer established, the mental basis for the development of disorders is associated with a large gap between a person’s capabilities and the requirements of the environment. It would be more accurate to say, following Osipov, that the problem lies in emotional and affective disorders that lead to anxiety.
Neurotic reactions occur in response to severe stress and nervous exhaustion. Psychopathy is considered genetically determined, or at least explained by factors that acted in the first years of life.
Thanks to medications that reduce emotional stress, it is possible to achieve significant therapeutic effects. The effectiveness of the drugs partly proves the leading role of the constitutional characteristics of a particular person in the development of borderline disorder. Research data shows a relationship between borderline states and problems in the functioning of certain brain structures.
We recommend: Excitability: a concept in psychology
Much can also be explained by the social conditions of society. There are a number of reasons that are closely related to the development of borderline states. Among them, Aleksandrovsky names:
- Ecological distress.
- Natural disasters.
- Increasing number of refugees.
- Dangerous working conditions.