The type of temperament is an innate feature of the human nervous system. Basically, it remains unchanged throughout life (not to be confused with character). Knowing the type of temperament, we can say about the speed of occurrence and intensity of an individual’s mental processes, the strength of his emotions, and these are not all the characteristics.
Each temperament has its own capabilities - find out which activity suits you
To determine your temperament type, take the test. The accuracy of the result depends on how honest you are with yourself. A brief description of each type of temperament is below the test. When two types of temperament are combined, the test does not give an interpretation, read it yourself. So let's get started...
KEY TO THE TEST: TYPES OF TEMPERAMENT
Melancholic temperament type
Melancholic. You are the owner of a rich inner world. Externally they are calm, internally there is a seething ocean of passions. Vulnerable, suspicious and thoughtful. You have excellent taste, a creative nature, and a wonderful imagination. Often you experience causeless sadness and anxiety, but you hide your emotions and experiences well from others.
Having a sensitive nervous system, you subtly perceive the imperfections of this world. Sometimes you hide behind a mask of feigned optimism or pronounced pessimism. - why it is difficult to immediately determine your type of temperament. You avoid noisy companies and are very selective in your friendships, but the relationships are deep and trusting. In relationships with the opposite sex, do not try to show your feelings and expect activity from your partner. You like to feel someone else's care. You love stability both in relationships and in everyday life. You have excellent mental abilities - you easily master new material, but with the same ease you can forget it. You underestimate yourself and are often overly critical of yourself and the fruits of your creativity.
Sanguine temperament type
Sanguine. You are a walking generator! A source of fresh creative ideas and positivity. Looking at you, the question arises: “Where does a person get so much energy?”
Flexible and adaptive. A born leader, you always want to be the first in everything. Very sociable - easily make new contacts. But in communication, as in everything else, they are superficial - that’s why you have a huge number of acquaintances, but may not have real friends. You are friendly, easy-going and pleasant to talk to. Lightning fast - capable of moving mountains in a short period of time. Very sociable, sometimes even hyper-sociable. Excellent speakers, you won’t have to put your words into your pocket. Bright, artistic, your facial expressions and gestures are expressive. You are sensitive to the needs of others, but can sometimes fail to keep your promises. Love of freedom and an overly active lifestyle are sometimes an obstacle to marriage and starting a family. Disadvantages include inconsistency - once you get excited about an idea, you quickly lose interest in something.
Phlegmatic temperament type
Phlegmatic person. You are all calmness and self-control. Calm externally and internally. People around you have an opinion of you as a person who is always in a state of sadness or completely insensitive, but this opinion is wrong. You are capable of deep, strong feelings, but you will not show them
Restrained, avoid disputes and conflicts. It’s not easy to piss you off, but if this happens, the choleric person will “nervously smoke on the sidelines”...
In your contacts, you are selective and not proactive. You will always be the first to go to peace, because you don’t like conflicts and separations. They are slow, but in fact there are positive sides to this. Your slowness is compensated by thoroughness and perseverance.
Your behavior is patterned. Facial expressions and gestures are inexpressive compared to others. You need a lot of time to switch to a new task, to start learning something new. It always takes time to “build up”. You experience difficulties in a new business, but in an already familiar type of activity you act at a fairly fast pace.
Temperament and character
Temperament should not be confused with a person's personality. Personality is a combination of many human factors, while temperament is only one factor, albeit a very important one.
Temperament is not the same thing as character and has nothing to do with a person's personality type or level of maturity.
Our temperament
is a set of tendencies with which we are born, and it practically does not change throughout life. It depends on the characteristics of the nervous system, including mobility and balance.
Temperament governs our actions and reactions and is influenced by our character and personality.
Our character
is an acquired characteristic and can change over time. This is who we are when no one is around. Our character is influenced by life experiences, upbringing, nationality and other factors.
Our personality
– this is how we express ourselves, how we appear to other people (cheerful, angry, smiling). How others perceive us depends largely on what we allow others to see. Sometimes we behave like the person we would like to be, without being one ourselves.
Take the test now
Having passed the temperament test, your inner self will appear before you in a new light. You will determine what your character really is, and this will help you find the most successful path in your life. Knowing the temperament of your family and friends will help you feel calm with your family and surrounded by work colleagues.
Also, employers are increasingly offering to take a temperament test during the employment process to identify exactly the kind of future employee who will be able to better adapt and get along in the workforce.
Take the temperament test right now on our website! Thanks to saving test results and registration, you can always re-read the results and they will not be lost!
Famous test author
Hans Eysenck (HJ Eysenck)
- world-renowned scientist, psychologist and psychotherapist. In 1916 he was born in Berlin. He later left Germany due to disagreement with the Hitler regime.
Hans Eysenck's main areas of scientific research were in the field of personality theory, intelligence research, social attitudes, behaviorist genetics and behavioral psychotherapy. He treated the study and research of psychology as a natural science and criticized humanistic and psychodynamic approaches for their subjective nature.
His psychological test for extraversion, neuroticism and psychoticism, created by Hans Eysenck together with his wife Sibylla in 1968, became quite famous for his work.
Find out your temperament on our website
It is necessary to know your temperament type not just out of idle curiosity. For self-development and self-improvement, test results are simply a gift. Knowing your temperament, you have the opportunity to control your behavior, take your destiny into your own hands, using primarily your strengths, while suppressing your weaknesses.
Knowing your temperament, you will understand why it is easy for you to find a common language with some people, while others seem difficult, choosing interests and hobbies will no longer be a difficult task.
Register on our website, take the Eysenck test with the ability to save your results! You can also share the results with your friends on social networks.
Header image by Adi Constantin, Unsplash.
Characteristics of a choleric person
Strengths:
- Born leaders
- Dynamic and active
- Strong need for change
- Strong-willed and decisive
- Non-emotional
- They're hard to break
- Independent and self-sufficient
- Exude self-confidence
- They take on any task
Weak sides:
- They like to command
- Impatient
- Hot-tempered
- Can't relax
- Too impulsive
- They like to argue
- Don't give up even when you lose
- Lack of flexibility
- Unfriendly
- They do not like displays of sentimentality and emotion.
- Unresponsive
Choleric at work
- Purposeful
- Sees the big picture
- Organizes well
- Looking for a practical solution
- Moves quickly to action
- Distributes tasks
- Insists on his own
- Sets goals
- Stimulates activity
- Likes to argue
Most suitable professions
in the field of: management, technology, statistics, engineering, programming, business
Choleric friend:
- Doesn't need a large circle of friends
- Will lead and organize
- Always right
- Copes well with unexpected situations
Choleric child, teenager, adult
Infant
Pros:
decisive look, fearless, energetic, sociable, fast development
Minuses:
demanding, loud and noisy, throws things, sleeps poorly
Child
Pros:
natural leader, courageous and energetic, productive, goal-oriented, fast-moving, self-sufficient, competitive, self-confident
Minuses:
controls parents, tends to manipulate, is capricious, restless, insists on his own, likes to argue, stubborn, disobedient.
Teenager
Pros:
aggressive, competent, quickly organizes any business, takes leadership, solves problems, self-confident, stimulates others, knows how to act in a critical situation, good potential, responsible.
Minuses:
likes to command, controls his friends, believes that he knows everything, tends to look down on, becomes unpopular at times, decides for others, can offend, does not like to repent, blames others.
Adult
Emotional needs:
devotion of the crowd, sense of power, appreciation, gratitude for one's actions
Cause of depression:
life out of control, problems with money, work, spouse, children or health
How to get rid of stress:
work more, engage in physical activity, avoid difficult situations
Energy Level:
excess energy, needs to reboot
Characteristics of a melancholic person
Strengths:
- Deep and thoughtful
- Analytic mind
- Serious and focused
- Gifted
- Talented and creative
- Artistic and musical
- Ability for philosophy or poetry
- Connoisseur of beauty
- Sensitive to others
- Selfless
- Conscientious
- Idealist
Weak sides:
- Remembers negative moments
- Tendency to mood swings and depression
- Likes to be offended
- Head in the clouds
- Low self-esteem
- Selectively listens
- Concentrated on himself
- Closed
- Often feels guilty
- Prone to persecution mania
- Prone to hypochondria
Melancholic at work
- Sticks to schedule
- Perfectionist, sets high standards
- Pays attention to details
- Persistent and thorough
- Organized
- Careful
- Economical
- Sees problems
- Finds non-standard solutions
- Loves graphs and lists
Most suitable professions
and in the fields of: research, arts, science, administration, social work
Melancholic friend
- Makes friends with caution
- Prefers to stay in the shadows
- Tries not to attract attention to himself
- Devoted and faithful
- Ready to listen to complaints
- Can solve other people's problems
- Concerned about other people
- Looking for the perfect partner
Definition of temperament: where it all began
Predecessor test
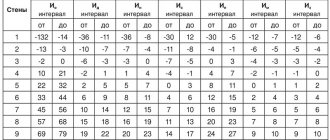
Scientists have been trying to correctly determine the type of temperament for a long time. The first questionnaire to identify temperament and its components, MMQ, was proposed by Hans Eysenck back in 1947. It consisted of 40 questions to which a person answered “yes” or “no.” Based on them, temperament was characterized by only one scale – “neuroticism”. In the process of continuing research on larger samples, the psychologist was able to identify a new scale - “extraversion-introversion”.
Modified techniques
In 1963, Eysenck created a new questionnaire, the EPI (Eysenck Personality Inventory), a test consisting of 57 items. Of these, 48 measure the “neuroticism” and “extraversion-introversion” scales, and 9 questions make up the “lie” scale, designed to help determine the degree of a person’s sincerity.
The EPI test exists in versions A and B, which are similar in meaning. All this is done to increase accuracy during repeated playthroughs.
In 1969, Hans Eysenck and his wife Sibylle proposed the EPQ (or PEN), a personality questionnaire that, in addition to the scales that make up the EPI, is capable of diagnosing psychoticism. This term is associated with the presence of special conditions that can lead to inappropriate behavior and non-standard mental reactions (psychosis). The test is relatively lengthy and is presented in the form of 101 questions. It was this option that became the classic test for determining temperament.
Today, the PEN test has become quite popular, although many foreign scientists believe that the results obtained on the psychoticism scale are often contradictory and not scientifically substantiated.