Article last updated 09/15/2018
Anxiety-phobia disorder is a neurotic condition in which obsessive fears (phobias), thoughts, and memories arise. All these obsessions (obsessions) are unpleasant and alien to patients, but they cannot get rid of them on their own.
Anxiety-phobic disorder, obsessive-phobic disorder, obsessional neurosis, obsessive-phobic neurosis are all different names for the same disease. Let's take a closer look at the causes of the development of this disease, its manifestations, and its treatment.
Description of the syndrome
OFS is characterized not only by the emergence of obsessive thoughts and ideas, pathological fears, but also by their development. The patient himself understands the meaninglessness of his actions, but cannot cope with the symptoms of the disease on his own. When they appear, you need to start treatment under the guidance of an experienced psychotherapist.
The main causes of neuroses are fears of various origins. For example, the prevailing fear of contracting a serious illness (cardiophobia, cancerophobia, syphilophobia, speedophobia, etc.).
People with neurotic phobic disorders try not to find themselves in situations where they are faced with a far-fetched problem: patients with claustrophobia do not use the elevator, and those suffering from agoraphobia avoid large crowds of people. Less commonly, this disease manifests itself through the occurrence of obsessive thoughts, which are difficult for patients to get rid of.
The dynamics of neuroses consists of three stages:
- the occurrence of fear in a person only when he is afraid of something;
- the emergence of fear when thinking about this situation;
- the emergence of obsessive fear when a conditionally pathogenic stimulus occurs (words associated with a phobia, an image, etc.).
A characteristic feature of neuroses in some patients is the manifestation of panic attacks. They provoke an attack of fear, which is accompanied by shortness of breath, loss of consciousness, rapid heartbeat, etc.
Such patients have a fear of recurrence of attacks, and they avoid going out unaccompanied. Symptoms may appear due to stress or overwork. In a psychiatric clinic, the above manifestations are described as diencephalic syndrome. The development of neuroses is protracted, turning into a neurotic formation of the patient.
Learn more about your problem by phone
If you are interested in more detailed information on the problem, leave your contact phone number, and the specialist on duty will call you back shortly and answer any questions.
I have read the Personal Data Privacy Policy and agree to the processing of personal data
Fear of “serious illness” is common:
- mental
- oncological
- cardiological
- or some other, unclear but frightening
Fear is accompanied by an obsessive search for signs of this disease.
Long-term anxiety can lead to panic attacks. Often, panic attacks and anxiety coexist with a fear of open or, conversely, too cramped space. There may be a fear of being in an awkward position in crowded places, for example: fainting, committing a senseless act.
Signs and causes of the disorder
The disease often begins after psychological trauma or as a result of a prolonged state of psychological discomfort. The disease can be identified by specific signs.
There are several causes of this disease:
- biological;
- psychological;
- social-public.
Experts attribute the following factors to the biological causes of obsessive syndrome:
- disorders in the autonomic nervous system;
- features of the functioning of electronic brain impulses;
- disruptions in the functioning of neurons, metabolic processes in nerve cells of the brain;
- consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- infection with viral infections;
- the predisposition is hereditary.
The psychological and social causes of nervous disorders include the following factors:
- traumatic family and social relationships;
- features of strict or religious upbringing;
- stress situations in the family and at work;
- fear and anxiety due to a situation experienced that really threatened life.
Manifestations of panic fear can arise as a result of imposition by society or as a result of personal traumatic experience. For example, a person has watched crime news and is haunted by obsessive thoughts about being attacked by criminals.
If a person cannot overcome such obsessions on his own, and he again performs control rituals (looks back every few steps, checks whether the door is closed, etc.), you need to turn to specialists.
The sooner psychotherapeutic treatment of such an illness is started, the greater the chance of protecting the human psyche from neurosis, which without the necessary treatment can turn into a paranoid syndrome.
The following criteria will help recognize the presence of neurosis:
- constant occurrence of obsessive thoughts and actions that cause anxiety;
- regular occurrence of obsessive grievances and thoughts in situations that do not involve their occurrence;
- frequent attempts to ignore obsessive experiences and thoughts, replacing them with others, switching to other useless actions;
- obsessive anxieties have nothing to do with reality, a person understands this, but continues to be in a restless state;
- there is an acute feeling of an irresistible desire to perform certain ritual actions in order to avoid the occurrence of any event, but the person is aware of the illogicality of his actions.
If you notice similar behavioral deviations in yourself or your loved ones, psychiatric help is needed to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe comprehensive treatment for phobic neurosis.
Forms of manifestations
Obsessive-phobic neurosis can manifest itself in several forms.
- Figurative.
- Distracted.
A characteristic feature of the figurative form is obsessive pictures of past events, accompanied by vivid memories, doubts, and apprehension. Abstract includes constant attempts to remember facts, names, surnames, faces, accounts, as well as replaying imperfect actions in the head.
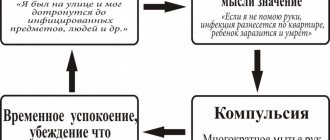
An obsessive state is manifested by compulsion in the motor-physical aspect, phobia in the emotional aspect and obsession in the intellectual aspect. All these components are closely connected and alternately trigger each other.
A striking example: patients with severe forms of neurosis develop ritual actions that allow them to find peace for a while.
Experiences usually appear during mental activity and provoke a return to the same thought and repeated actions in order to double-check the work. Endless repetition leads to fatigue. Doubts cause a persistent need to perform the same actions, at a time when reality is of less interest.
Treatment of the disorder
Diseases associated with various kinds of neuroses can sometimes occur in completely healthy children and adults. You need to be attentive to your body in order to recognize the onset of the disease in time.
In the initial stages, it is always easier to defeat a disease than to deal with its chronic manifestations. You must analyze the current situation with hysterical phobias and other symptoms of obsessive disorder, try to develop a strategy for your behavior to protect yourself from the disease.
Learn about obsessive-compulsive disorder. Read in detail about the causes, course and treatment of the disease. Compare the symptoms with your behavior by writing them down on a piece of paper. Having spoiled each detected manifestation, draw up an action plan to overcome it. This will help you cope if the alarming situation arises again.
An outside assessment will help you understand the current situation more deeply. A visit to a specialist doctor will help you understand the symptoms, analyze the course of the disease and develop a strategic plan to protect yourself from neurosis.
Look your phobias in the eye. People suffering from neuropsychiatric disorders realize that their fears are fictitious and born only of their imagination. As soon as a new desire arises to once again check whether the door, windows, etc. are locked, just remind yourself that this is a useless ritual and interrupt yourself at the stage of thinking. This method will help get rid of nervousness, you will learn to soberly assess the situation.
Praise yourself constantly. This method will put you in a positive mood. Rejoice at every successful step you take on the road to recovery. Praise yourself even for small victories, and you will feel yourself becoming stronger than the obsessive state. By gaining control over the situation, you will completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease.
When a person does not have enough of his own will to overcome nervous symptoms, it is imperative to organize a trip to a psychologist.
When do you need to use a course treatment program?
You are recommended to undergo the “Not Scary at All” treatment and rehabilitation program if you discover the following symptoms.
- Irritability, fear or anxiety, quickly developing into panic.
- Expectation of trouble or misfortune. Nervous tension. Physical stress. Headache.
- Intestinal dysfunction, diarrhea. Nausea and vomiting. Muscle pain.
- Decreased performance. Insomnia. Sexual disorders.
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), shortness of breath (rapid breathing, lack of air).
- Fear of going crazy or losing control of yourself. A feeling of unreality of the surrounding world, a feeling of time slowing down.
- Fear of “disappearing.” Prostration. Decreased vitality and motivation for life, the perception of the environment is “flat”, “in gray colors”.
- With severe panic disorder, there is a fear that another panic attack will occur spontaneously, “in public.”
Methods of psychology in solving problems
In modern psychology, this syndrome is most effectively treated through psychotherapeutic sessions. The medical arsenal includes several methods of getting rid of such a disease.
The method of cognitive-behavioral therapy of neurosis is a method aimed at counteracting the syndrome by reducing compulsions to minimal manifestations, and then completely eliminating them.
The technique involves step-by-step instructions, after which the patient fully understands his disorder and analyzes the causes of its occurrence. He takes decisive steps, after which he gets rid of obsessive syndrome forever.
The founder of this technique is the famous psychiatrist Jeffrey Schwartz. With the help of his technique, people are healed from psychological trauma, stressful situations and constant anxiety. It consists of four steps that are successfully used in the treatment of psychoneurological conditions by modern psychologists around the world.
Joseph Wolpe's technique is for a patient with a psychonervous disorder to look at the problematic situation from the outside. The patient recalls the stressful situation he experienced, and immediately after the onset of the obsessive state, the doctor introduces the principle of stopping thought.
The patient begins to be asked certain questions that help the specialist conduct an in-depth analysis of the patient’s behavior in a stressful situation. The patient is able to photograph the analyzed situation and examine it in detail from all angles. The comparative technique helps to restore control over emotions and remove anxious experiences.
There are many other methods for treating neurological conditions, but only the doctor chooses which one to use in each specific case.
Features of obsessions
An obsession is a series of obsessive thoughts and associations that arise involuntarily at a certain time interval. A person loses the ability to concentrate on his main work because he is unable to get rid of them by willpower.
Obsessions are classified as symptoms of intrapsychic activity, i.e., disorders of the central part of the psyche. They are classified as a subgroup of thought disorders. Of the 9 productive circles of damage, obsession belongs to the 3rd, i.e., it can be easily stopped with timely treatment.
Regarding pathogenesis, 2 groups of obsessions are distinguished.
- Elementary - observed immediately after the appearance of a super-strong psychogenic stimulus. The reasons for obsessive thoughts are clear to the patient.
- Cryptogenic - occurs spontaneously, the reasons are unclear. Misunderstanding of the process of formation of obsession is due to the body’s defensive reaction when it hides in the nooks and crannies of consciousness some traumatic facts from the life of an individual.
Healing with medicines
Cases where medication is used to treat obsessive-compulsive syndrome are called severe. Metabolic disorders affect the functionality of neurons, and this leads to a lack of serotonin in nerve cells.
To recover, the patient is prescribed drugs that slow down the reuptake of serotonin by neurons. Among the drugs that have a slowing effect, several effective drugs can be identified: Fluvoxamine, Escitalopram, tricyclic antidepressants, Paroxetine, etc.
A number of studies in the field of neurology have discovered the therapeutic effect of the following drugs: Memantine, Riluzole, Lamotrigine, Gabapentin, N-acetylcysteine, etc.
In the chronic form of obsessive-compulsive syndrome, the patient is prescribed atypical antipsychotic therapy. The combination of drug treatment with psychotherapy enhances the effect several times, and the patient successfully passes the stages of treatment.
Psychoprophylaxis as relapse prevention
There are many preventive methods to prevent relapses of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
To protect against the syndrome, you must:
- change the patient’s attitude towards stressful situations through personal conversations, suggestion, self-hypnosis, etc.;
- consult a doctor on time when an exacerbation of neuroses occurs and undergo regular medical examinations;
- increase the brightness of daylight indoors, conduct light therapy sessions; such procedures promote the production of serotonin;
- use vitamin therapy, walks in the fresh air, ensure proper sleep;
- provide adequate nutrition, including foods that contain tryptophan: amino acids can form serotonin; dates, figs, dark chocolate, and dairy products are rich in them;
- monitor all body functions, and in case of violations, treat them; special attention should be paid to the endocrine and cardiovascular systems;
- exclude the use of alcoholic beverages, narcotic and toxic drugs.
Features of compulsion
Compulsion - obsessive rituals - behavioral reactions that occur after a certain period of time. The patient feels that he is obliged to perform some action. If he refuses or cannot do this, anxiety increases and obsessions arise.
Compulsions vary in type of manifestation, but have similar features. The main problem is that they cannot be abandoned. If initially it is enough to perform the action once, then over time it is necessary to perform the ritual several times. The demands of the subconscious become more stringent every time. Thus, a disorder accompanied by a feeling of dirt on the hands requires more thorough washing.