Currently, psychogenic disorders have become a fairly common disease, and there is a logical explanation for this. Neurosis is a psychogenic disorder that occurs under the influence of external factors (prolonged stress, constant overwork and insufficient sleep, severe somatic illnesses).
In modern life, it is difficult to find a person who is not exposed to the aggression of one or more risk factors for the development of neuroses, since the rhythm of life requires constant overexertion, and rapidly changing political and economic conditions do not allow one to feel stability and security. But the disease does not develop in everyone, but only in people with a certain hereditary predisposition of the psyche.
Stress and psychological trauma contribute to the emergence of neurosis
Neurosis is not an organic mental illness; it is a borderline condition, and it is completely curable even in its advanced form. The disease has diverse manifestations and symptoms, despite this, there are certain signs by which a diagnosis can be made.
Mandatory signs:
- Reversibility of pathological manifestations at any stage of the disease.
- No personality changes or dementia.
- The ability to adequately assess one’s condition is retained.
- The disease is painful for the patient, unlike mental disorders.
What is neurosis?
Neurosis is a disease in which a person loses the ability to cope with stressful situations . The body’s defenses and the formed psychological adaptation “break down” in this state, leading to exhaustion of the nervous system. This disease affects not only the psyche and the nervous system; a person often notices a malfunction of an internal organ or prolonged pain.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
Strong neurosis does not go unnoticed from the outside either. People around note increased irritability and deterioration in the physical condition of a person suffering from this disease.
What to do if your legs are weak?
During and after an anxiety-panic attack, if possible, it is better to lie down or sit down and allow the body to completely calm down and recover.
The tips below will help you get rid of this unpleasant symptom:
- Move more, walk, take walks every day.
- Do any sport that trains your muscles.
- Massage your legs to help relax cramped muscles.
- Wear comfortable shoes.
- Use tonic foot creams.
- Take contrast baths for the lower extremities (for VSD, a contrast shower for the whole body is useful).
- When working sedentarily, get up from your chair every hour and do a warm-up for 10 minutes.
Of course, the main prevention of weakness in the legs with vegetative-vascular dystonia and neurosis is strengthening the nervous system. The less often you worry, get nervous, experience groundless fear and panic, the less unpleasant sensations you will have.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. Thank you for your attentiveness and help!
Causes of the disease
- An interesting fact is that not only situations associated with the loss of something close can lead to neurosis. The cause of the disease can also be a bright, joyful event , for example, the birth of a child, a wedding, or the start of studies at the desired college or university.
- Neurosis often occurs in melancholic and choleric people. These types of temperament are characterized by emotional instability, so typical melancholic and choleric people have a more difficult time experiencing traumatic situations.
- Physical and psycho-emotional stress ultimately lead to this nervous pathology. If a person constantly works or studies and does not have enough time for relaxation and rest, he is at risk. Especially with accompanying problems in your personal life, the development of neurosis cannot be avoided.
- With long-term or intense somatic illnesses, psychological problems associated with the inability to finish the work started, symptoms of severe neurosis also appear.
How does this disease manifest itself?
A neurotic disorder of the nervous system necessarily leads to detrimental consequences for the body and social activity of a person. It can cause neurosis, nausea, dizziness, constant headaches, increased conflict, irritability, and disability. That is why, when neurosis manifests itself, you need to solve the problem, and not hope for its independent disappearance .
The main manifestations of the disease include:
- headaches of various types;
- numbness of the limbs;
- dizziness;
- various types of sleep disorders;
- a person cannot relax if he wants to;
- increased irritability;
- the patient does not feel joy and happiness, he is constantly depressed;
- restlessness, anxiety;
- decrease in cognitive functions, intellectual abilities;
- fast fatiguability;
- pain in internal organs, in the limbs, without obvious reasons;
- decreased labor productivity;
- mood swings;
- tearfulness;
- touchiness;
- “getting stuck” in a stressful situation;
- the body's sensitivity to temperature changes and bright light;
- disorders of the autonomic nervous system: sweating, rapid heartbeat, fluctuations in blood pressure, problems with the stomach;
- decreased sex drive;
- decrease in the intensity of volitional impulses;
- dyspnea;
- dark spots when closing or opening the eyes, the condition is accompanied by dizziness;
- decreased appetite, inability to form a bolus due to insufficient amount of saliva in the mouth;
- the appearance of a feeling of fear without a threatening factor.
Reduced severity of physiological symptoms
The listed signs manifest themselves differently in each patient. For some, neurosis is accompanied by only a few symptoms of the listed manifestations, and some note almost all of the listed changes in their body. Among the common symptoms, patients note headache, nausea, dizziness, tension in the body and head.
Tension in the body
This is the main companion of the disease. Neurotic disorders are almost always accompanied by muscle tension. This phenomenon occurs for both physiological and psychological reasons. In the human body, an uneven distribution of muscle load occurs, and dystonic reactions appear.
Some researchers argue that tension in any part of the body is associated with specific psychological problems. For example:
- Feelings of hostility towards others lead to tense arm muscles.
- Increased muscle tone in the thighs and pelvis in adulthood is caused by sexual problems.
- Tension in the head during neurosis is caused by deep emotions, unresolved conflicts, and low self-esteem of a person.
Psychological problems are very closely related to somatic manifestations. That is why it is necessary to get rid of this symptom as part of a set of measures to overcome a neurotic disorder.
With neurosis, constant tension in the body is treated not only with medications, but also with active use of physical exercises. They are prescribed depending on which muscles cannot relax. The following would be appropriate here:
- relaxation massages;
- various water treatments;
- medications for severe symptoms;
- working with a psychologist, psychotherapist to solve the cause of muscle tightness.
Nausea with neurosis
Not all doctors associate this symptom with psychological problems. Only experienced gastroenterologists or therapists refer the patient for a consultation with a psychotherapist or neurologist when experiencing nausea. Nausea with neurosis can last from several hours to several days. And it should not be associated with low-quality food and take sorbents or bacteria for the intestinal flora - there will be absolutely no result.
Constant nausea in neurosis is often observed with a feeling of disgust towards an object, person or activity, if the patient has accumulated grievances, he is dissatisfied with his life, his health or appearance. Constantly interacting with what a person considers unworthy or bad, neurosis will manifest itself through the main symptom - nausea.
There are two treatment options:
- reducing the severity of symptoms, short-term techniques using antipsychotics or antidepressants;
- long-term psychotherapy aimed at eliminating not only the symptom, but also the causes of neurosis.
Dizziness with this disease
It is enough to associate this phenomenon with the pathology of the nervous system, since dizziness during neurosis is not always accompanied by problems with internal organs. A person may complain of weakness and dizziness, although when tested, all results will be within the normal range; blood pressure measurements will also not show any pathology. In this case, we can safely say that the symptom is caused by psychogenic causes.
Dizziness occurs with depression, panic attacks, vegetative-vascular dystonia, phobias, and anxiety. It is complemented by noise in the head, increased irritability and sleep disorders. With dizziness of a psychogenic nature, it is impossible to cure a person of them without the use of psychotherapeutic techniques.
If dizziness is accompanied by hearing problems and gait disturbances, then we may be talking about disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. In this case, an ENT doctor provides assistance. With changes in blood tests and examinations of the cardiovascular system, dizziness is caused by neurological or vascular diseases. A doctor working with a patient cannot immediately diagnose psychogenic dizziness, so first a negative diagnosis should be made - eliminating the physiological causes of the symptom.
In the treatment of dizziness due to neurosis, medications, special gymnastics and breathing exercises, as well as psychotherapeutic techniques are used.
Weakness in the arms and legs with depression and neurosis
Subjective feelings of patients with VSD about drowsiness are often very vivid and strong, which makes them suspect that they have a serious and incurable disease. In fact, VSD is a completely reversible benign disease. At the same time, young people can “wind up” themselves and become so immersed in imaginary drowsiness that they forget about everything in the world and focus only on their weakness.
There is even such a serious disease that appears against the background of manifestations of VSD. This disease sometimes appears in teenage children who have “outgrown” their age and are an order of magnitude taller than their peers. This disease is known as “Dissociative Conversion Disorder” or “Cerebral Angiodystonia Syndrome.” A completely healthy child feels drowsy and feels weak in the legs and throughout the body almost constantly. Basically, such children stop moving and crawl. The teenager withdraws into himself and rarely goes outside. Parents have to purchase a wheelchair so that the child can somehow go outside. There is usually no cure for this condition. Doctors say drowsiness and muscle weakness should go away on their own when the growth and riot of hormones stops (at 9 years old, the hormone levels in such children are much higher than in adults). There is practically no information about treatment.
If you complain of muscle weakness and drowsiness, it is better to first contact your family doctor/general practitioner. He will listen to you and explain what tests you need to take if you are weak. In most cases, a patient complaining of drowsiness will need to undergo the full range of possible tests, such as a complete blood count, biochemical analysis, and sugar test. A hematologist interprets blood tests. If blood problems are detected, the therapist refers the patient to be examined by a specialist. If no problems were identified, the therapist may refer you to a psychotherapist or neurologist. But in most cases, taking general strengthening medications and vitamins can overcome the problem of weakness and drowsiness during VSD.
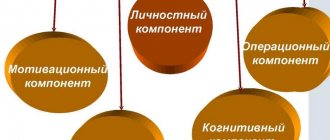
Neuroses (neuroses; Greek neuron nerve + -ōsis) are reversible borderline mental disorders, recognized by patients, caused by exposure to traumatic factors and occurring with emotional and somatovegetative disorders. The main cause of neuroses is mental trauma, but premorbid personality characteristics are also important. It is customary to distinguish three main clinical forms of neuroses: neurasthenia, hysterical neurosis, obsessive-compulsive neurosis and neurotic depression (depressive neurosis).
Neurasthenia is manifested by increased excitability and irritability in combination with rapid fatigue and exhaustion of mental activity. Conventionally, there are two variants of neurasthenia: exhaustion neurosis , the cause of which is excessively large, mainly intellectual, loads, and reactive neurasthenia , caused by prolonged psychotraumatic situations; Usually there is a combination of several etiological factors.
Hysterical neurosis is characterized by increased suggestibility and self-hypnosis of the patient. This explains the diversity and variability of hysterical disorders; they resemble manifestations of a wide variety of diseases. With hysterical neurosis, there is also a sequence in the development of symptoms - from autonomic and sensorimotor disorders to emotional and ideational ones.
Neurotic depression often develops in individuals with such character traits as straightforwardness, rigidity, and uncompromisingness. They are characterized by emotional intensity of experiences with the desire to retain external manifestations of feelings. There are two types of traumatic situations leading to neurotic depression. In the first option, the patient develops unfavorable relationships (“the patient’s whole life is unsuccessful”); in the second option, the patient is forced to live in a situation of “ emotional deprivation ” (long separation, lack of emotional contact with loved ones, etc.).
Obsessive-compulsive neurosis is characterized by the appearance of obsessions of varying content and form.
With the development of neuroses, a certain sequence of symptoms appears. Disorders with neurasthenia are expressed in the inability to concentrate, increased distractibility, exhaustion of intellectual activity, and inability to assimilate the necessary material; in hysterical neurosis - in emotional logic, when actions, assessments and conclusions are based on an emotional assessment of the environment, and not an adequate analysis of events; with obsessive-compulsive neurosis - in the complication of obsessions, joining “mental chewing gum” to phobias, obsessive doubts.
Neurasthenia. At the first stage of development of the disease, autonomic disorders are most pronounced: patients with any physical or emotional stress experience palpitations , increased sweating, cold extremities, disturbed sleep and appetite. Motor impairments manifest themselves in the fact that it becomes difficult for the patient to perform small precise movements , maintain a monotonous posture , wait for an extremely painfully long time get upset for an insignificant reason cry, often get offended, irritated, but quickly calm down. The mood is often lowered. Intellectual activity is difficult. Patients cannot concentrate for more or less long periods of time.
Instead of those described earlier in hysterical neurosis , numbness of the extremities, tingling, burning, and sometimes decreased sensitivity are usually noted instead of paralysis - weakness in the legs and arms, staggering when walking. Emotional disorders are characterized by lability of emotions, rapid mood swings , and a tendency to violent affective reactions (for example, crying that turns into sobbing). With a long course of hysterical neurosis in patients, features of emotional logic appear in their assessment of ongoing events, behavior becomes demonstrative, theatrical , a desire to attract attention and egocentrism arises.
Neurotic depression. Negative emotions caused by traumatic situations are suppressed. In these cases, at the first stage of neurotic depression, vegetative-somatic disorders occur; fluctuations in blood pressure, heartbeat, dizziness, gastrointestinal dysfunction. Subsequently, low mood . A mild form of depression is usually manifested by complaints of sadness, loss of joy from everyday successes, and decreased activity. Constant sleep disturbances. Patients often “flee to work,” where they feel much better. The course of neurotic depression is wavy. As it increases, tearfulness appears. Patients begin to cry for any reason and often for no reason.
Obsessive-compulsive neurosis is characterized by the appearance of obsessions of varying content and form, which are usually accompanied by anxiety, apprehension, low mood, as well as various autonomic disorders - tachycardia, excessive sweating, chilliness, blood pressure fluctuations, vasomotor reactions.
Treatment should be carried out by a psychiatrist and psychotherapist. At the onset of the disease, it is advisable to be hospitalized in a special department for the treatment of patients with neuroses in psychiatric or somatic hospitals.
The complex of therapeutic measures includes general strengthening therapy (vitamins, nootropic drugs, a rational diet, walks, exercise, massage, etc.), the prescription of psychotropic drugs, as well as psychotherapy. For hysterical neurosis, neuroleptics such as thioridazine (sonapax), tizercin, neuleptil are used in small doses; for neurasthenia - tranquilizers (seduxen, tazepam, etc.); in cases of obsessive-compulsive disorder, a combination of antidepressants in small doses (amitriptyline, azaphene) with antipsychotics (haloperidol) or tranquilizers is recommended. For neurotic depression, antidepressants with a stimulating effect are indicated; for severe anxiety, antipsychotics in small doses are indicated.
The choice of psychotherapeutic intervention depends on the clinical form of neurosis. In case of hysterical neurosis, several sessions of hypnosis are performed to relieve monosymptoms (for example, blepharospasm, mutism). For neurasthenia , training in autogenic training techniques is recommended; for neurotic depression, psychotherapeutic conversations are conducted to identify the traumatic situation and the patient’s attitude towards it. The purpose of such conversations is to create a new life attitude in the patient.
The prognosis for life is favorable. Restoring working capacity and social adaptation requires a long time, but with proper organization of complex treatment, complete recovery can occur.
To cope with nervousness, first of all change your sleep pattern , gradually increasing its duration - only two hours. is quite helpful in treating neuroses . To relax before bed, take a warm shower or a soothing fragrant bath with milk (or cream) and the addition of essential oils of rose, ylang-ylang, sandalwood and rosemary. The aroma of geranium, tangerine and mint calms the nervous system. A mixture of 1 drop of juniper and 2 drops of rosewood will have a tonic effect.
Previously, as a treatment for neurosis, the doctor prescribed a trip to the water. Now this may make you smile, but in fact the method is reasonable and effective. If we slightly change the outdated wording, then the advice sounds like this: change the situation . Light stress that accompanies change and travel, new acquaintances, the opportunity to look at your problems from a different point of view - often this is exactly what you need to break out of the vicious circle of habitual worries, hateful actions and seemingly insoluble problems.
Yoga can be a good help for those who want to increase their self-discipline, improve concentration and memory. For young people, yoga is a great way to maintain flexibility and mobility for many years to come. Yoga will help teenagers gain inner strength and cope with stress and negative peer influences.
Weakness with VSD is one of the most common signs, occurring in 95% of cases. This is precisely the basis for doctors to consider it one of the most striking symptoms for diagnosing the disease. How does it manifest itself? Is it possible to overcome it? How is dystonia diagnosed?
Vegetovascular dystonia (abbreviated VSD) makes itself felt not only by debilitating weakness. With this syndrome, almost all organs are affected: the heart aches, the head is dizzy, the heart is pounding or slows down. A person loses strength in a matter of hours, and with it the desire to think positively disappears, despondency sets in, which often leads people with dystonia syndrome to severe attacks of panic attacks, anxiety and even prolonged depression. Are you seeing these signs in yourself? It's worth getting tested.
Most often, patients note disturbances in the functioning of the heart and coordination system, when everything around begins to spin and it becomes difficult to maintain balance. Some even faint from time to time.
- Arrhythmia.
Drowsiness.
Many people ask: can VSD cause weakness in the arms and legs? It turns out yes. It is in the limbs that the feeling of weakness is localized when they temporarily lose their functionality. It becomes difficult to raise your arms, they become leaden, and your legs turn into cotton. The first reaction of any person is a feeling of helplessness, a desire to lie down and give up on everything. What can cause changes in well-being?
One of the most important reasons for the appearance of the syndrome is considered to be heredity. Simply put, a person is already born with a predisposition to the disease and, as soon as unfavorable provoking factors arise, it quickly worsens.
- In case of hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, menopause.
- About the reason for the surge of hormones in adolescence.
- Against the backdrop of severe stress due to the loss of a loved one.
- In case of disruption of the endocrine system.
- If you are very tired due to mental stress, for example after exams.
It is important to know! Women are at risk: after all, they more often experience hormonal shocks and worry even about little things. Also, VSD can “mow down” adolescents and people with excess body weight: excess weight is always an additional burden on a person, which means the cardiovascular system is overloaded.
Because dystonia is always a complex health problem, diagnosing it can be difficult. And with all these unpleasant manifestations, vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD) is not recognized by many doctors as a separate disease. They consider this a syndrome that is accompanied by numerous unpleasant symptoms and affects several systems and organs of human life.
Sometimes doctors advise you to get enough sleep, take vitamins, hoping that your general condition will return to normal. Doctors often turn out to be fair, but it happens that VSD is delayed and then consultation with several specialists may be required: a therapist, a cardiologist, a neurologist, an endocrinologist, and even a psychotherapist.
For a correct diagnosis and subsequent effective fight against muscle weakness, for VSD it is better to undergo:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Rheovasography (study of blood circulation in the upper and lower extremities of a person).
- Rheoencephalography (study of cerebral vessels).
- Echocardiography.
At the appointment, the doctor will definitely clarify whether there have been similar cases in the family, because, as already mentioned, very often the disease is hereditary.
How to explain the mechanism of muscle weakness during VSD? The reason lies in carbohydrate metabolism. It is no secret that carbohydrates are one of the main sources of energy that the body “draws” from nutrition. The supply of this valuable substance is constantly stored in the human liver and muscles in the form of glycogen and is consumed as needed.
To get energy from muscles, a person must move: biochemical processes are designed in such a way that glucose is released from glycogen only during physical activity, and in a passive position it practically does not arrive.
That is why doctors are sure that the feeling can be expelled by performing active, intense movements. Do you feel exhausted, exhausted by weakness in your legs due to VSD? Do five minutes of exercise. Are you tempted to give in to laziness? Stretch your arms in different directions, bend to the side, or simply dance to your favorite tune.
What is the secret of physical inactivity? Movement is the biggest “enemy” of dystonia. The whole point is that the contraction and relaxation of muscles that occurs during movement contributes to the production of energy, and life returns to the person: muscle tone returns, and helplessness leaves.
How to overcome severe weakness with VSD? The most important thing is to start moving. Physical activity (even the most moderate) will help get rid of it in a short time.
- Start eating right, adhering to the principles of a healthy lifestyle. To do this, keep sausages, smoked meats, sausages, lemonades, fast food, industrial juices, and white bread to a minimum. It is advisable to eat porridge, omelet or dairy products in the morning, and lean meat, vegetables and fruits in the afternoon. You need to eat in small portions 5 times a day, not forgetting about healthy snacks. At the same time, such a diet will allow you to lose excess weight, which means it will help you look better and feel lighter.
- Give up instant coffee and replace it with ground coffee: the aroma of freshly ground coffee invigorates you.
- Introduce bananas into your diet - they promote the release of the hormone of joy - endorphins.
- Set a goal that will motivate you. For example, start walking outside the city (in parks, forests, embankments), each time choosing a scenic route. Gradually increase your mileage. You can come up with any new hobby, as long as it requires useful activity from you: cycling, eco-tourism, swimming, gardening.
- Stop watching TV (or limit it to one hour a day). It's much better to start reading more. This will not only enrich your vocabulary and broaden your horizons, but will also minimize the risk of panic attacks that often plague VSD sufferers after watching TV shows.
- Try to travel more often if possible. Changing your impressions will have a positive effect on your mood and improve your body’s sensitivity to climate change.
- Find your doctor. He may recommend you vitamin complexes or other medications that relieve or alleviate the symptoms of VSD.
Many patients believe that constant weakness, drowsiness, and loss of vitality are inevitable accompaniments of dystonia and try to “lie down.” But doctors are confident that this path is a common mistake, which only aggravates the condition. It is important to act actively even when you have to do it through force.
And one more important and obligatory condition for getting rid of a painful illness, including severe weakness with VSD, is to believe in the best and not to lose heart. Then you won’t have to think: what to do, how to get rid of the problem. The syndrome will quickly give way to optimism, vigor and return the taste for life.
Headache due to neurosis, causes
Headache is a faithful companion of neurasthenia and hysteria; it is practically not observed in obsessive-compulsive neurosis. This symptom does not occur immediately after a stressful situation, but after a certain period of time, after the development of other symptoms, for example, sleep or appetite disorders.
Headache with neurosis manifests itself in different ways, depending on the location of pain and the human organs involved. It develops due to:
- Muscle “clamps”.
- Disturbances in the functioning of cerebral vessels.
- Without disruption of muscles and blood vessels.
As a result of this classification, the symptoms of headaches with neurosis will be slightly different.
Neuromuscular pain is accompanied by:
- feeling of squeezing of the head;
- numbness of some parts of the surface of the head;
- sensation of pain on the skin surface of this part of the body;
- a person feels constant tension in the head, which interferes with mental processes: it is difficult to remember something, concentrate attention, or decide.
The neurovascular nature of pain will be expressed through the following symptoms:
- throbbing pain in the head;
- pulsation constantly focuses a person’s attention on pain, he cannot perform any complex mental work;
- often localized in the temporal region, occipital and frontal;
- accompanied by nausea and weakness.
Headache without muscle tension and pulsation in a neurotic disorder occurs after overwork. It does not have a clear localization, and it is difficult to understand the nature of the pain. Its occurrence is associated with psycho-emotional experiences, so it is classified as neurotic symptoms.
How to get rid of neurotic headaches?
It is important for patients with a neurotic disorder to know how to relieve tension and pain in the head during neurosis, because their livelihoods depend on it. When treating this symptom, an integrated approach is used that helps reduce its intensity and remove the cause of the neurotic disorder. To achieve this, several types of patient assistance are used.
Subscribe to our VIBER channel!
Medication assistance
With neuroses, pain in the head can be simply unbearable. A constant feeling of heaviness, constriction and increased severity of pain leads to a deterioration in the patient’s psycho-emotional state. He becomes irritable, gets tired quickly, and does not want to use anything for food, since the chewing process also causes pain. To solve this problem, it is necessary to use medications to get rid of headaches. To do this, the doctor prescribes:
- sedative herbal preparations (Valerian, Peony Tincture, preparations with motherwort, Nervo-Vit);
- painkillers that relieve muscle or vascular spasm (Spazmolgon, Riabal, Novigan, various analgesics and others);
- vitamins to support the functioning of the heart and nervous system (various vitamin complexes with vitamins C, group B, magnesium, iron and other microelements);
- nootropics and anti-anxiety drugs (Glycised, Glycine, Nootropil, Pantogam), they have a good effect on brain function and normalize sleep, but the dosage and course of administration are determined only by a doctor.
Psychotherapeutic assistance
Psychological techniques are used not only to treat headaches, but also to get rid of the causes of neurosis. Cognitive behavioral therapy is actively used, hypnosis is an effective assistant, and it is also important to use positive therapy methods to restore a person’s psycho-emotional sphere. Long-term work with a psychologist or psychotherapist is required.
Psychotherapeutic treatment
Treatment of neurasthenic headaches should begin by using the principles of psychotherapy. There are several methods of such influence. Persuasion treatment involves instilling information that can change the perception of a traumatic factor. Another effective method is treatment by suggestion. Unlike the first method, information is entered independently of consciousness, i.e. it is not subjected to critical analysis, but is perceived as a signal to action.
The psychological impact of neurosis can be direct or indirect. With the direct method, the psychotherapist directly acts on the receptors through suggestion. The essence of the indirect technique is the use of an additional stimulus. Hypnotic sleep and self-hypnosis sessions are widespread. In any case, during psychotherapeutic sessions it is not the pain syndrome that is treated, but the immediate cause - the neurosis itself.