Symptoms of severe depression
Major depression has the following manifestations:
- apathy;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- depressed mood;
- lack of interest in people around you, work, hobbies, previous interests;
- increased anxiety, restlessness, internal tension;
- guilt, low self-esteem;
- memory impairment, decreased ability to concentrate;
- obsessive thoughts of suicide.
Prolonged depression entails not only mental disorders, but also health problems:
- sleep disturbance;
- sudden change in body weight;
- loss of appetite;
- anorexia or bulimia;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- muscle pain:
- disruption of the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- constipation;
- disorders in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- erectile dysfunction in men;
- menstrual disorder and anorgasmia in women;
- impairment of psychomotor functions (slow thinking, speech, motor coordination disorder).
Long-term depression often entails the development of alcoholism and drug addiction, which allow one to temporarily get rid of internal discomfort and depressing thoughts.
Severe depression is also manifested by a change in the patient’s behavioral model. A person strives for solitude, avoids communication with others, refuses walks and various types of entertainment, and his ability to work decreases.
Treatment of deep pathological conditions
Major depressive disorder responds to the same treatment methods as the usual syndrome, but takes longer. First, the psychotherapist must establish the causes of the pathology. Without eliminating them, it is impossible to return the patient to normal life. If necessary, the doctor prescribes medications.
The main attention is paid to the mental state of the patient, when all conflicts and problems are neutralized. Taking medications is necessary not only to neutralize the signs of a severe syndrome, but also to eliminate the physiological cause of its development.
Taking medications is necessary to neutralize the signs of severe syndrome
We get rid of dangerous symptoms with the help of antidepressants:
- selective inhibitors;
- tetracyclic;
- atypical and heterocyclic;
- with serotonergic, noradrenergic effects;
- NASA subgroup drugs;
- MAO inhibitors;
- dopaminergic and melatonergic medications.
Among the neuroleptics, the following drugs are recommended: Haloperidol, Risperidone, Quetiapine, Triftazin. Walking in the fresh air, communicating with pets, music therapy, physical exercise, and traveling will help you get rid of severe “blues.”
Sometimes you can even get out of long-term depression on your own by radically changing your usual lifestyle, neutralizing traumatic situations, devoting time to proper rest, sleep, exercise and good nutrition.
Psychotherapy helps to get rid of most problems, but in cases of prolonged mental disorder, such methods are most often not enough and therapy begins with restoring the emotional state with the help of potent drugs.
Psychotherapy can help you get rid of most problems.
Causes of deep depression
Psychotherapists identify several groups of factors that cause severe depression.
Psychological factors
This category includes:
- suffered stress;
- problems in the family, at work or at school;
- disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- severe mental trauma (death of loved ones, disability, physical or sexual violence);
- violation of internal harmony;
- lack of life goals and aspirations;
- frustration - the discrepancy between life realities and a person’s hopes and ideas;
- personal conflicts;
- loss of meaning in life.
Biological factors
Severe depression can develop due to health problems and the following biological factors:
- hormonal imbalances;
- lack of regular, fulfilling sex life;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- drug overdose or prolonged use;
- severe physical, mental, psycho-emotional fatigue;
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of hormonal and psychotropic drugs;
- severe form of intoxication of the body;
- insufficient physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- disruption of cerebral circulation processes;
- Parkinson's disease;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
Social factors
Depression can be triggered by:
- destruction of family relationships (divorce, loss of parents);
- change in social status;
- protracted conflicts in the family or team;
- destruction and failure of previous life strategies;
- social isolation.
Causes
Any form of depression can become prolonged. Most often, it develops into a seasonal form, which initially appears in the spring or autumn, or a postpartum type, which occurs in a woman in the first days after childbirth. Diseases of major, atypical, psychotic, bipolar and physical forms can also become chronic.
The main characteristic of protracted depression is the long period of its manifestation. For children they are one year, for adults – at least two. Usually it is combined with relatively mild symptoms, but even this becomes a big problem for patients. Women experience the disease more often, which is partly due to the fact that men can carry the disease in a latent form for several years.
The chronic type of illness usually becomes the result of depression initially belonging to this type, its natural development or incorrect treatment. Regular stress or a serious mental blow can also lead to it.
Most often, symptoms of prolonged depression appear due to the following factors:
- chronic fatigue, overwork;
- increased responsibility, excessive sense of duty;
- anxiety, shyness, vulnerability, serious fears;
- mental disorders or injuries;
- loss of a loved one or illness;
- making a serious diagnosis;
- the development of certain diseases, especially endocrine ones;
- financial problems, large debts or loss of money;
- difficulties at work, poor relationships with the team;
- conflict situation within the family;
- separation from a loved one or divorce;
- reaching old age and retirement;
- alcohol abuse or drug use.
Most of these factors are faced by young girls, which also causes the widespread spread of the disease among women. In some cases, it is enough to endure any of the listed events once, while in others the psyche can cope with problems tens or hundreds of times.
Most often, a protracted type of depression manifests itself in the spring or autumn months, and the presence of obvious causes does not always occur.
Stages of pathological syndrome formation
Severe depression does not occur suddenly, but develops gradually. Stages of pathological syndrome formation:
- Negation. Outwardly, a person’s lifestyle does not change, but he experiences a severe internal conflict. The patient turns on psychological defense mechanisms based on denial of reality. It manifests itself as changes in eating behavior, psycho-emotional instability, and sudden mood swings.
- Resentment and anger. At this stage, a person begins to look for those to blame for his serious condition. Signs such as attacks of uncontrolled aggression, tearfulness, increased anxiety, and irritability appear.
- Stage 3. The patient experiences hormonal disruptions, and the production of serotonin, the pleasure hormone, decreases. A person begins to lose or rapidly gain weight, suffer from insomnia, headaches, and suffer from exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
- Last stage. It is characterized by pathological processes that destroy the physical health and psyche of a person. The patient loses control over his own behavior, the ability for adequate, rational thinking, and becomes potentially dangerous both for himself and the people around him.
Psychotic signs of major depression
Major depression can be expressed psychotically:
- hallucinations;
- obsessive states;
- denial of life's realities;
- intolerance to other people's opinions;
- hypertrophied feeling of guilt;
- panic fear;
- expectation of something terrible (fatal illness, disaster, death of loved ones).
Somatic signs of prolonged depression
Prolonged depression has somatic signs:
- heart pain;
- disturbances of heart rhythm and palpitations;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the hypochondrium;
- prostration;
- problems with the functioning of the digestive system.
Patients complain of various painful sensations and often convince themselves of the presence of severe pathologies, but medical studies and analyzes do not reveal any physiological abnormalities in a person.
Other treatments
In severe situations, additional treatment methods are used in complex therapy of a protracted pathological condition. How to get out of deep depression with their help:
- Magnetotherapy – magnetic waves act on the cerebral cortex; by stimulating individual areas of the “gray matter,” a person’s mood and general condition are restored.
- Electroconvulsive physiotherapy is a traumatic, dangerous method of treatment, prescribed in the absence of effectiveness from other methods; the patient is put into a narcotic trance, an electric current is applied to the brain, due to which the “joy” hormones necessary for a person are synthesized.
Long-term depressive disorder is a dangerous mental condition, which is very difficult to overcome on your own; to do this, you should resort to drug therapy and use the help of qualified doctors.
Without a psychotherapist, it is impossible to get rid of protracted pathology forever. Integrated therapy uses cognitive behavioral, cognitive, rational, and family therapy. This technique allows the patient to cope with their problems that provoked the development of the disease.
Complex therapy will help get rid of protracted pathology
Peculiarities of thinking of depressed individuals
The depressive personality type occurs in people who are especially prone to developing depression. In most cases, they are pessimists and see the world in “black terms”.
Personalities of this type are not satisfied with themselves and those around them, no matter how much success they achieve in the social sphere. Most often, such people are introverts, reserved, difficult to make contact, and prefer solitude.
They are characterized by excessive feelings of guilt, self-doubt, fear of failure, panic states that arise during any changes, changes, or life difficulties.
Types of depressive disorder
After giving birth, a new mother may experience postpartum depression
Having understood what is called a state of major depression, it becomes clear that this term hides a description of the severity of the clinical symptoms of a depressive disorder of any type. Depending on the predominance of certain symptoms, as well as the causes of the development of the disorder, the following types of major depression are distinguished:
- anxious;
- apathetic;
- asthenic;
- postpartum;
- endogenous;
- bipolar.
Anxious depression manifests itself with symptoms of an anxiety disorder. Deep anxious depression is a dangerous condition in which a person constantly feels fear and a sense of impending danger. A sign of deep depression in this case is also the presence of a specific depressive triad - depressed mood, deterioration of thinking and motor retardation. Moreover, the last symptom can be replaced by volitional inhibition - a condition in which a person loses the ability to quickly make decisions.
Apathetic major depression is the most common type of disorder. This type of major depression can occur in adolescents or adults, but women are three times more likely to experience the disorder than men. The main manifestation of this disorder is a severe form of anhedonia (inability to enjoy life), indifference to the surrounding world, and paucity of emotions.
With the asthenic form of deep depression, loss of strength and constant fatigue, also called asthenia, come to the fore. Patients with this form of disorder prefer to spend most of the day in bed; their sleep can increase to 10-14 hours a day.
Postpartum major depression is a severe form of clinical depression that occurs in the first weeks after childbirth. Women of all ages face this pathology.
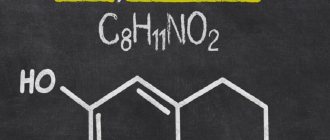
Endogenous major depression is a psychopathology caused by impaired production of serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine.
Bipolar depression is the depressive phase of bipolar affective disorder. In some people with this diagnosis, the manic phase may be absent and completely replaced by a depressive period, which is called major depression.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of depressive syndrome begins with a consultation with a psychotherapist. While talking with the patient, the doctor evaluates his speech, speed of reactions, and cognitive functions. Conducts an analysis of concomitant symptoms and the results of the collected anamnesis.
To make an accurate diagnosis and determine the stage of depression, a pathopsychological examination, differential diagnosis, and psychological tests are performed.
Patients are prescribed laboratory tests, an ECG, a consultation with a narcologist and a therapist in order to exclude Parkinson's disease, hypothyroidism, drug or alcohol addiction, and oncology.
Characteristic manifestations
Scientifically, the signs of severe depression are divided into three depressive episodes. The first degree is mild, then moderate and severe depressive episode with or without psychotic symptoms. Serious signs of the disease are impaired clarity of thinking and limited functionality of the motor system.
The patient's mood level has been depressed for at least two weeks. This manifests itself in the form of regular melancholy, sadness, and apathy. Tears “run” for a week, and then the person wants, but is physically unable to cry. In the early stages of this condition, it is recommended to contact a professional psychologist, for example Nikita Valerievich Baturin.
It is still possible for a person to regain lost interest in activities that are simpler than creative, more difficult than routine and monotonous. Severe fatigue and lack of strength are returned by studying the causes of severe depression at the first stage and formulating a vitamin complex.
Characteristic manifestations of symptoms that require the attention of specialists:
- lack of appetite, weight loss;
- insomnia or frequent nightmares;
- a feeling of self-doubt, reluctance to make decisions;
- lethargy or increased excitability;
- regular problems with memory, attention, concentration;
- gloomy pictures of the imagination;
- pessimistic vision of the future and present;
- feelings of guilt and thoughts of suicide;
- condemnation of oneself and one's immediate environment in all troubles.
Signs of severe depression are divided into two powerful groups. The first group is somatic signs. These include lack of sexual desire, decreased reaction time, problems with reflexes, difficulty waking up, loss of weight and appetite. The second group is psychotic symptoms. They are more serious for the patient - immobility, hallucinations, delusions.
Treatment of severe depression
The treatment of severe depressive syndrome should be approached comprehensively and very seriously. The following methods of therapy are most effective:
- use of antidepressants;
- diet therapy;
- psychotherapy;
- insulin;
- electroconvulsive.
Medications allow you to relieve the physiological and somatic manifestations of depression, and sessions with a psychologist help you find a purpose in life and find a way out of the current difficult situation.
To achieve a positive result, it is important to provide the patient with a balanced and fortified diet, good rest, walks in the fresh air, physical activity, and protect him as much as possible from stress factors.
The task of a person in this state is to make his life as harmonious and easy as possible: positive emotions, joyful meetings with pleasant people, improving skills in his favorite hobby.
Which specialist should I contact?
Diagnosis and treatment of severe depressive conditions are carried out by specialists such as neurologists, psychologists, and psychotherapists. In especially advanced cases, you will need the help of a psychiatrist who will help you choose the right medications and methods of psychotherapeutic correction.
Drug treatment
The following medications are used to relieve the syndrome:
- atypical antidepressants;
- drugs that promote serotonin reuptake;
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors;
- tricyclic antidepressants.
Drug therapy also involves the use of tranquilizers, which eliminate the feeling of anxiety and have pronounced sedative properties.
Nootropic drugs help improve blood circulation and normalize brain functions.
Immunomodulating agents, vitamin-mineral complexes, and sleeping pills are also prescribed.
Psychologist's advice
The patient needs individual psychological consultations using methods of occupational, Gestalt and art therapy. Classes in self-help groups give good results.
To eliminate a depressive state, you should pay attention to the advice of a psychologist:
- do not engage in self-flagellation;
- reduce the load and give the body proper rest;
- spend more time in nature, take walks in the fresh air;
- get a good night's sleep;
- lead a regular intimate life.
It is important not to be ashamed of your emotions and not to hide them, to find the meaning of life and a sense of significance by caring for children, animals, and performing social tasks. A person needs to reconsider his life, evaluate his own successes and make plans for the future, without setting unattainable goals.
You should not withdraw into yourself, you need to go out to people, communicate even in the absence of such a desire.
How to get out of deep depression on your own?
Getting out of deep depression on your own is an extremely difficult task. First of all, a person needs to realize that there is a problem and get support from family and friends.
The following recommendations will help you overcome depressive syndrome:
- Positive thinking. It is difficult to think optimistically while in such a state, but you should control your thoughts and promptly replace negative language with positive one.
- Keeping a diary and doing creative work are methods that allow you to throw out your negative experiences and analyze your own thinking.
- Physical activity. In case of depression, you should play sports and give your body regular, feasible physical activity.
- Improving quality of life. A person needs to try to bring as many positive emotions into his life as possible. To do this, you should try to make your old dream come true, to do those things that previously brought pleasure and joy.
Treatment
Some types of depression are classified as incurable. Often this also applies to protracted ones. But even if it is impossible to completely cure the disease, it is possible to achieve suppression of all symptoms and normalization of life. Therefore, it is very important to engage in therapy. Before this, you just need to undergo a diagnosis, including performing mental tests and talking with a psychotherapist. Based on this, the doctor will make a diagnosis and also prescribe therapy appropriate to the case.
Psychotherapy is recognized as the main way to treat depressive disorders. It includes regular cognitive-behavioural, interpersonal and family sessions with a specialist. Their goal is to put the patient’s psyche in order, return him to a positive outlook on the world, establish social activity and achieve relief from all symptoms. Such psychotherapeutic courses can be supplemented by other subtypes of treatment. Usually they are carried out almost daily - at least 3-4 times a week.
The second option for treating prolonged depression is medication. It is aimed at suppressing symptoms, restoring the nervous system and reducing susceptibility to any irritants. It is important to consider that some tablets may not provide a positive effect even after the full course of use. In such cases, the doctor prescribes other drugs until an effective option can be found.
Groups of drugs used:
- stimulating antidepressants (Fluoxetine, Imipramine) – relieve melancholy, apathy and lethargy;
- sedative antidepressants (“Mirtazapine”, “Paroxetine”) - help fight irritability, anxiety, and sleep disorders;
- herbal sedatives (“Hypericin”) are easily tolerated medications that suppress symptoms of depression when they are mild.
Some drugs increase anxiety. This is especially true when treated with stimulant antidepressants. In such situations, tranquilizers may be prescribed to normalize the condition.
Electroconvulsive therapy provides good assistance in the fight against depression. It involves deliberately stimulating seizures through electrical stimulation. The result is the production of mood-enhancing substances.
Disease prevention
The following preventive measures will help prevent the development of this disease:
- adherence to daily routine;
- adequate sleep (at least 8 hours throughout the day);
- spending time together with family members and friends;
- healthy lifestyle, giving up cigarettes and alcohol abuse;
- regular physical activity;
- proper, balanced nutrition;
- reducing stress levels in life to a minimum.
Even with a busy schedule, it is important to find time for self-development, entertainment, doing what you love, and communicating with interesting, pleasant people. Making plans for the future and defining clear life goals will also reduce the risk of developing depression.
Prevention
After exiting the pathological state, it is necessary to take all measures to ensure that emotional stability is maintained. To do this you need:
- exclude unpleasant people who cause negativity from your social circle;
- develop supportive relationships;
- lead a socially active lifestyle;
- maintain a sleep schedule;
- master relaxation techniques;
- improve relationships with loved ones;
- fight bouts of negative thinking;
- avoid stress, breakdowns, hysterical attacks;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- take care of yourself;
- get an animal;
- hike;
- find a hobby.
If, despite following all the recommendations, the pathological condition returns, do not hesitate to contact a specialist. Needing help does not indicate weakness or worthlessness. Various situations in life cause severe damage to the psyche, and the body cannot always cope with severe depression the first time. Providing timely medical care will help get rid of the abnormal condition and return to a normal, fulfilling life.
Main symptoms of prolonged depression
A person experiencing depression most often experiences an emotion such as sadness. She is considered key. And also a number of others, including anger, contempt, disgust, and guilt. He is often depressed, often focused on negative experiences related to the past. He constantly returns in his thoughts to those events that he believes could have happened through his fault. Throughout the entire period of depression, the patient experiences rapid fatigue, leading to a significant decrease in productivity in any type of work activity.
The danger of prolonged depression lies in possible suicide attempts and suicides.
In difficult life situations - with the loss of loved ones, betrayal of a loved one, divorce, even mentally healthy and balanced people can become depressed.
All depression is divided into two main types - endogenous, caused by biological factors, and psychogenic, with a predominance of psychosocial components.
However, all recorded the following symptoms:
- feeling of hopelessness;
- motor retardation;
- persistent reluctance to even make an effort to do anything;
- constant melancholy;
- lack of reactions to both joyful and negative events;
- distrust of family and friends, wary attitude towards work colleagues;
- in most cases, refusal of the offered help;
- self-flagellation, sleep disturbances, appetite disorders;
- apathy and longing.
For some people, individual symptoms may coincide. But this does not mean that they have prolonged depression. These are probably personality traits or character traits.
But if almost all of them coincide, you should urgently go to see a psychotherapist.
Physiological reasons
But in addition to psychological reasons, there may also be physiological ones that can lead a person to a depressive state. These include:
- Poisoning with various drugs, drugs or alcohol. Such severe intoxication of the body leads to a malfunction of the brain and nervous system, which is fraught with various psycho-emotional disorders.
- An unhealthy lifestyle, namely poor nutrition and lack of exercise, leads to problems with excess weight, which often become the cause of severe depression.
- Traumatic brain injuries also affect the functioning of the brain and central nervous system, which can lead to apathy.
- Diseases of the heart and the entire cardiovascular system are an important factor for the appearance of deviations in the psycho-emotional state. It has been observed that approximately 30% of people suffering from apathy have heart problems.
- Hormones also play a big role in our lives. Disorders of the internal secretion organs lead to many mental problems.
- A personality crisis, for example, an existential crisis, manifests itself in an anxious feeling when a person feels acute discomfort and loses the meaning of life.
- Severe harm from natural and man-made factors, for example, disasters, terrorist attacks, wars, etc.
- Frustration is a mixed cause that contains the basis of physical and mental problems. It is a state into which a person falls when it is impossible to satisfy his needs.
Now you understand that treatment for severe depression must begin as soon as you notice the first symptoms that arise due to any of the above reasons.
Causes of the disease
Depression never develops out of the blue. Most often, a combination of several reasons leads a person to such a sad state.
Here are some of them:
- Dissatisfaction with life, personality crisis, unfulfilled deep desires or a prolonged stressful situation are considered psychogenic factors. It’s difficult to notice them from the outside, which is why seemingly prosperous people who have a family and income admit that they are unhappy. The human psyche is a rather delicate thing. Negative events can accumulate and develop into depression over the years. In the end, each person has his own “margin of safety”.
- Alcohol abuse, hormonal imbalance, vitamin deficiency can become biological factors in the development of depression. A lack of melatonin or serotonin makes a person apathetic, reduces the emotional background and quality of life. In such cases, it is important to correctly diagnose the problem and eliminate negative factors.
Psychological reasons
If in a child the biological causes of depression come to the fore, in an adult they are usually hidden in problems of a psychological nature. They can also be of different types. For example, the first are sudden and difficult situations that knock a person out of the usual rhythm of life. These include:
- Death of a close relative.
- Losing my job.
- Experience of physical violence, etc.
In this case, depression may arise suddenly and immediately become serious. Its main difference is that it can gradually go away on its own. 2-3 months are enough for complete recovery.
But there are cases when, without proper psychological help, this disease turns into very severe depression, so you cannot delay treatment.
The second includes reasons that seem to sharpen a stone. These are problems that do not have much pressure on a person, but have the ability to accumulate and drive their owner more and more into depression. These include:
- Living with a person who is unpleasant or annoying to you.
- Neighborhood with noisy people.
- Sleep problems.
- Dissatisfaction with your own place of work.
- Family quarrels.
- Failures in your personal life, etc.
Despite the fact that these reasons are not critical and, it would seem, can be dealt with, they are the most terrible. These problems can slowly and imperceptibly drive a person into a severe degree of depression, which in most cases he can no longer cope with on his own.
Visiting a therapist and other doctors
But, as mentioned above, sometimes it happens that the true cause of depression lies not in our psychological problems, but in health problems. If the psychologist has not given you the results you need, it's time to visit a therapist.
This specialist will carry out a basic examination, issue the necessary referrals to specialists and tests in order to identify the presence of any diseases. You may be referred to:
- cardiologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- neurologist, etc.
You may have to visit a lot of doctors before they can give a clear verdict on whether you are sick or not. In addition, going to the hospital will help you find out for sure whether any ailments are a real illness or a psychosomatic symptom. If the latter is confirmed, then more serious help will be needed.
Signs
If a person for a long time does not have enough strength or desire for anything and cannot force himself to start doing at least something, while a bad, indifferent mood is constantly present, then these are signs of a depressive state. Laziness, under the guise of which hides apathy and lack of desire for any activity, is also a sign of illness.
In a person with severe depression, the biochemical processes in the brain change, and these changes provoke laziness. In the brain, the transmission of three neurotransmitters is disrupted: serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine. If they are not sufficiently transmitted from one neuron to another, then the patient experiences a deficiency of energy, a decrease in mood, and apathy appears. It becomes impossible to “pump yourself up”. If you do not include drug treatment, then over time the person will be too lazy to get out of bed, he will lose all interest in life, in people. Severe depression can trigger various negative consequences. The person will become anxious and experience manic fear.
Severe depression in pregnant women can lead to miscarriage, so expectant mothers should be careful about their health, and if they notice the first signs of depression, consult a doctor.