What is the Great Depression? Major depression, also known as unipolar or major depressive disorder (MDD), is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness or lack of interest in external stimuli. Unipolar describes the difference between major depression and bipolar depression, which refers to an oscillating state between depression and mania. Instead, unipolar depression focuses solely on the “lows,” or negative emotions and symptoms you may have experienced.
Fortunately, major depression is well known in the medical community and is often easily treatable with a combination of medication and gazebo therapy. Below is a guide to the symptoms and causes of major depression, as well as statistics and treatments that you can consult with a medical professional if you need help.
Causes and symptoms
Usually a person realizes that he is depressed. It is characterized by three main features:
- depressed mood and inability to experience joyful emotions;
- negative thoughts;
- decreased activity.
There are many reasons why it occurs. This could be a divorce, a breakup, the death of a friend or relative, a serious illness, or loss of a job. It is important to recognize this condition in time and consult a specialist.
The period of depression is individual for each person. Some are freed from it after just a few months, while others suffer for years. In rare cases, it is practically untreatable.
Causes
Although the prevalence of major depression is widespread, the causes of major depression are just as numerous and come from many different places. The medical journal Neuron cites genetics as a major cause of depressive disorder: “approximately three times the risk of developing MDD [major depressive disorder] in first-degree relatives (parents, siblings, offspring) of individuals with MDD compared with the general population.” This means that the biggest determinant of depression can be found in ancestry, but there is also a significant physiological and anatomical basis.
Concurrent illnesses and health conditions can be a significant risk factor for a depressive episode.
In addition, symptoms of the disorder itself can cause depression. For example:
- Change in appetite, overeating, or shortness of breath;
- Deregulation of sleep schedule or shift in circadian rhythm.
Changing these patterns and habits often won't help you get rid of depression, but they can be an excellent step in relieving other symptoms when combined with professional treatment.
The extent to which anatomical and physiological factors influence major depression is unknown, but it is believed to be significant. Along with socioeconomic factors (such as job loss and feelings of economic limitation), the above factors are considered to be the main reasons why you may be suffering from major depressive disorder.
Major depressive disorder is often treated to improve quality of life.
Factors influencing duration
Sometimes a person may have the impression that such a depressed state will last forever. Of course, no one can say exactly how long depression lasts. This is influenced by several factors:
- Heaviness. Its mild and medium forms last up to 9 months. Most people cope with depression on their own. If the form is severe, then you cannot do without the help of specialists.
- Cause of occurrence. Usually depression recedes if the cause that caused it is removed. For example, depression is caused by job loss. It is logical to expect that it will pass when a person finds a new one. If depression arose due to the death of a loved one, then relief will come only after a year. In cases where the cause disappears, but the depressed state remains, it means the depression is physiological in nature. To get rid of it, you will need to take medications. When the problem lies in childhood psychological trauma, a deep and thorough study with a psychotherapist is necessary.
- Treatment. It includes medication and psychotherapy. If depression appears due to psychological reasons, it will not be possible to cure it only by taking pills. With regular therapy, you can fully recover after six months, but this is an approximate time frame.
- Timely contact with a specialist. The sooner a person consults a doctor, the more effective the treatment will be. If you postpone a visit to a psychologist, the condition will gradually worsen. Then you will have to look for reasons for a long time and deal with the accumulated load.
It is also necessary to take into account your personality type. If a person has a sensitive psyche, he quickly gets involved in the problem, worries actively and for quite a long time.
Types (types) of major depression
You may be surprised to learn that there are many different types of major depressive disorders that can affect your daily life. Each type often has its own causes, but usually involves the same feeling of disinterest in activities you once loved and a general feeling of melancholy. They are divided into subtypes called specifiers, which determine how long a depression diagnosis will last and define the characteristics of each type.
- Seasonal affective disorder or SAD is classified as a condition directly caused by the seasons. This most often occurs during the winter months when sunlight is not as easily available. The National Institute of Mental Health states that SAD can be "effectively treated with light therapy, but nearly half of patients with SAD do not do better with light therapy alone."
Counseling and medication are also recommended.
- Psychotic depression often develops if you have hallucinated or believe in illusions that are not connected to reality. This may be caused by a traumatic event or a past form of depression.
- Postpartum depression is common among new mothers experiencing hormonal changes after childbirth. The stress of raising a new baby and the changes in your body can greatly affect your mood. Additionally, the Canadian Mental Health Association states that adoptive parents may also suffer from some symptoms of postpartum depression.
- People with melancholic depression often exhibit the most characteristic signs of depression, including weight loss and decreased interest in activities they once enjoyed. You may experience depressed mood, similar to the loss of a loved one or intense grief.
- Atypical depression is often directly related to your mood and your interactions with other people. Symptoms include hypersomnia, heaviness in the limbs, and social anxiety.
- If you suffer from catatonic depression, you are likely to have problems with your motor system and behavior. You may be immobilized or have involuntary movements.
We invite you to read: What is hypersexuality?
Features of female and male depression
Representatives of the fairer sex are more emotional. It is easier to unsettle them and make them feel worthless, so they are at risk. Women often suffer from prolonged depression. They occur during menopause, pregnancy or childbirth. Various psychological traumas bring them more suffering than men. Let's consider how long depression can last in women during the period:
- Divorce. A woman can worry about separation for about two years. Creating a new family can shorten this period.
- Postpartum depression. It can go on for years. It is aggravated by the development of psychological disorders. With timely treatment, you can get rid of it in six months.
- Refusal of alcoholic beverages. This decision may also cause depressed feelings. It is impossible to say exactly how many days depression associated with alcohol withdrawal lasts. But usually this is no more than a month. If there is a mental illness associated with alcoholism, then a state of depression can be observed for several years in a row.
- Parting with a loved one. Here everything will depend on the age and individual characteristics of the woman. In severe cases, the condition persists for years.
- Menopause. A depressive state can last from a year to 5 years.
It is worth noting that depression in men is 10 times less common. They are taught from childhood to control their emotions, but no matter how hard they try, a depressed state still arises.
Depression most often affects men:
- previously suffered from this disease;
- having relatives susceptible to depression;
- having low levels of income.
Men with severe illness are also susceptible to depression. For example, if there is cancer, diabetes, AIDS and the like. Symptoms of depression due to illness can last for several months.
Features of male depression are aggression, craving for alcoholic beverages and inappropriate behavior. They rarely admit to their condition, so the disease may go untreated for a long time. Mostly men are affected by:
- Major depression. It interferes with work, sleep, and leading a normal lifestyle. Her symptoms are vivid and last for several months.
- Dysthymia. Its symptoms are milder than those of major depression, but the duration is much longer.
- Bipolar disorder. The person is either depressed or euphoric.
Taking antidepressants and psychotherapy helps get rid of depression in men.
Teenage depression
Adolescence is the most difficult period in a person’s life. Boys and girls are trying to find themselves, so they are often in a stressful state. They may worry about their first love, worry about quarrels in the family, but this period must be passed. This condition lasts from a couple of weeks to several months.
Often teenage depression is not treated in a timely manner. Sometimes the parents themselves are to blame for this. They simply attribute symptoms of depression to a difficult age. In some cases, teenagers try to drown out their depressed state by using drugs and alcohol.
Depression in older people
It is generally accepted that depression in old age is quite common. This statement is not true. Typically, older people are satisfied with their lives. Depression occurs in older people due to illness or loss of loved ones. It is rarely diagnosed, since older people often complain about their physical health and do not pay much attention to their emotional state.
Typically, symptoms of depression in older people are subtle. When the disease is diagnosed, medications and psychotherapy are prescribed. Often the latter is sufficient, since older people do not want to take medications. Depression at this age can be treated quite quickly.
Resistant type
This is the most difficult form of depression. It is long-lasting and has pronounced relapses. With each appearance their intensity increases. The resistant type is difficult to treat. There is no particular relief observed after the procedures. It usually occurs against the background of dysthymia. Its temporary reduction in symptoms is followed by a pronounced relapse.
Patient statistics
There are several reasons why women are more likely to suffer from major depressive disorder, but it is mainly due to the tendency for depression to co-occur with other illnesses and mental disorders.
It is important to note that women are disproportionately affected by major depression compared to men, as evidenced by the significant difference in percentages discussed above.
This can lead to everything from pregnancy to more chronic or recurring problems being compared to anything. The National Institute of Mental Health noted that 25% of cancer patients, a third of people living with HIV, and a third of heart attack survivors suffer from major depression.
Although these specific conditions are more common among men, Psychology Today said the physiological reason for women experiencing more depression than men is due to fluctuating hormone levels and genetic predisposition, particularly during puberty, childbirth and menopause.
Major depression is a serious problem for both sexes, which can lead to serious consequences if left untreated. Fortunately, there is good news. The National Institutes of Health noted that approximately 80% of patients seeking treatment for major depression show improvement within four to six weeks after “starting medication, psychotherapy, attending support groups, or a combination of these treatments.”
We suggest you read: Borderline schizophrenia
Treatment
This mainly involves taking antidepressants and psychotherapy. With a mild form, you can do without taking medications. Combined treatment alleviates symptoms and helps cope with life's problems. Severe forms are additionally treated with electroconvulsive therapy. The session is performed under short anesthesia.
When taking antidepressants, improvement occurs within the first week. To achieve a lasting effect, they should be taken for about a month. You should not stop taking medications on your own. Refusal of them may lead to relapse. Usually medications are withdrawn gradually. This gives the body the opportunity to readjust.
Coding is not used in the treatment of depression.
Can it drag on for years?
How long can you live with depression? Depression is one of the mental disorders in which the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and psyche play a key role.
In some cases, it is possible to get rid of this condition within a few months, but in the presence of certain factors, symptoms can persist for years and are practically resistant to treatment.
One of the most difficult forms of depression is the resistant type. After a clear remission, pronounced relapses occur, the intensity of which increases with each manifestation.
Features of resistant depression:
- There is no improvement in the patient’s condition after the procedures;
- there is no tendency to recovery when using various therapy methods;
- after a temporary decrease in depression symptoms, a pronounced relapse occurs;
- depression arose against the background of dysthymia (this condition is sometimes considered a distinctive character trait).
Symptoms of the end of the disease
We've looked at how long depression lasts, now let's look at how it ends. You can understand that the disease is receding by the following signs:
- the person has become more cheerful and sociable;
- he had new plans, an interest in life;
- he better concentrates his attention on what is happening, his performance has increased;
- symptoms of insomnia disappeared.
It is important to remember that depression needs to be treated. The illness must not be allowed to drag on. This can lead to unpleasant consequences.
How long does depression last and when does it end?
How long does depression last? There are no specific indicators for the duration of depression. The period of manifestation of symptoms of mental disorders of this category is influenced by many factors.
These include the form of existing depression, the individual characteristics of the patient’s mental state and the presence of concomitant diseases of the nervous system.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
In some cases, psycho-emotional disorders are limited to certain periods, but they cannot fully comply with them.
Positive attitude
A psychotherapist is not a magician, he only helps a person cope with suppressed feelings. The positive attitude of the patient himself gives great benefit during treatment. To speed up the process, you need to:
- Always remember that depression does not last forever. Over time, everything will fall into place. Life goes on, a person forges his own happiness.
- Avoid unnecessary stress and making important decisions when depressed. Let everything take its course.
- If possible, go for walks and play active games with friends. Go outdoors with a noisy group.
- Surround yourself with things that bring joy. It could be a favorite book, a sweet, a relaxing bath.
- Ask your friends for help. Loving people will always listen and help with advice.
In order not to aggravate the situation, you need to give up alcohol and negative thoughts. Make it a goal to take care of your body. Eat right, have pleasant cosmetic procedures.
How does depression begin?
Unmasked depression begins with a deterioration in well-being: weakness, fatigue, increased sensitivity to previously undisturbed stimuli, headaches, and attacks of tachycardia.
There are early awakenings, vulnerability, and tearfulness. Another striking sign is the loss of a sense of satisfaction and joy. Often there is a rejection of habits that previously brought pleasure - treats, meeting with friends, playing sports, etc. Everything that used to be interesting now causes boredom, and there is no desire to do what you love.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
A pessimistic view of things appears, self-confidence is lost, and periodic attacks of vague discomfort appear. A desire for privacy arises, and distance from loved ones occurs.
Preventive actions
To avoid prolonged depression, you need to consult a psychologist, psychiatrist or psychotherapist at the first sign of depression. You can also reduce its symptoms at home by:
- attend trainings to improve self-esteem;
- tune in to positive thoughts;
- exercise regularly;
- stop watching dramas;
- change communication if it leads to negative thoughts;
- get rid of bad habits.
When asked how long to treat depression, doctors answer: about 4-9 months. With bipolar affective disorder and a chronic illness, a person is forced to take medications throughout his life.
Psychological disorders after childbirth - how long does postpartum depression last?
After childbirth, a woman’s psyche is very unstable. Mom becomes sensitive and very vulnerable.
According to statistics, half of women in labor experience an illness such as postpartum depression.
This disturbance in a woman’s emotional background must be combated, otherwise it may subsequently lead to aggravation of the situation and serious consequences.
Often, after childbirth, it is not possible to recover from it on your own, because in addition to caring for the child, the young mother tries to make life comfortable for other household members.
Postpartum depression is a pathology caused by hormonal changes in the body, monotony of life, and the busy schedule of the mother’s life.
The reasons for the appearance of this condition are always psychological and emotional in nature, namely:
- The degree of responsibility increases, the woman begins to react very sharply to everything.
- Adaptation to a new social role. A woman tries to try on the role of a mother, comparing her condition and behavior with the memories of her parents.
- Fear of changes in the body. Excess weight, problems with hair and nails, etc.
- Discrepancy between expectations and reality.
The sooner treatment begins, the faster you will be able to break out of this state. Postpartum depression will not go away on its own - it will get worse from month to month, manifesting itself in all areas of life.
When does it start?
Postpartum depression does not necessarily begin after childbirth.
It often happens that it begins to develop even during the period of pregnancy, and after childbirth the mother’s condition worsens.
It can also begin some time after the birth of the child.
This period can range from several weeks to several months. At first, the woman rejoices in her role as a mother and cares for the child, but at some point the joy is replaced by depression and despondency.
Postpartum depression is very similar in its manifestations to psychosis or melancholia, which is why many doctors do not classify it as a separate group. Its symptoms are indeed similar to other psychological disorders and are as follows:
- Hysterics and frequent tearful states for no apparent reason;
- Frequent mood swings;
- Outbursts of anger that are almost impossible to control;
- Feeling guilty for everything that is happening;
- Increased anxiety;
- Depressed state;
- Shortness of breath, frequent colds, rapid heartbeat;
- Reduced immunity;
- Poor appetite;
- Lack of desire for intimate life;
- Changes in attitude towards the child (either overprotection or indifference);
- Apathy (hobbies and other positive things no longer please and captivate);
- Sleep problems.
For each woman, the presence and degree of manifestation of these signs is strictly individual. One has a mild form of postpartum depression, the number of symptoms is minimal, and the condition itself is not acute.
The impetus for the appearance of such a condition can be various factors, but in most cases there are several most common ones:
- Low standard of living.
- Recently experienced depression (both before pregnancy and during pregnancy).
- Presence of bad habits (mostly alcohol abuse).
- Lack of help and moral support in household chores and child care.
- The presence of conflict with the mother in adolescence or adulthood.
- Poor knowledge of childbirth and baby care.
There is no definite answer to this question, because its course and manifestation are individual.
Some women recover from depression within a few weeks, while others continue to be depressed until they return to work.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
It all depends on the severity of the disease.
Postpartum depression may be accompanied by episodes of psychosis. In this case, it can last more than one year.
Its presence and severity are greatly influenced by the atmosphere in the family. In the absence of support from a partner, parents or other significant persons for a woman, this pathology in most cases will certainly manifest itself. The greater the totality of negative factors, the more severe the condition will be and the longer the process of getting out of it.
In most cases, this condition does not require any special treatment, because it is a natural reaction of the body to the period of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as to the process of adaptation to a new role.
In the period between the first three and nine months, the risk of postpartum depression is considered to be the highest, but by 10-11 months this condition passes - the woman adapts and accepts her new self.
In some cases, you cannot do without consulting a doctor. He conducts an examination, makes a diagnosis and, based on the findings, prescribes medications appropriate to the case.
Often, medication is not required, just lifestyle changes are enough. But before you start fighting depression, you should find out what reasons gave rise to its appearance. It is necessary to highlight the main points - those that manifest themselves most clearly and cause the most inconvenience.
Postpartum depression cannot be treated alone. You need to talk about your problem and turn to your loved ones to solve it together.
But, even if a woman sent her father for a walk with the child, and at that time she began to pay attention to herself (read her favorite books, chat with friends, go shopping, etc.), this does not mean that the problem will be solved on its own. yourself. There are some conditions that a woman must comply with herself. They all relate to her lifestyle, namely:
- Maintain a healthy, balanced diet. You should eat small portions 5-6 times a day.
- Physical exercise. You should exercise regularly, walk more, and get out into nature.
- It is very important to take care of yourself. A well-groomed appearance of a woman can restore her self-confidence, while an unkempt appearance, on the contrary, can drive her into even deeper depression.
- Get enough sleep. If a woman cannot afford uninterrupted sleep at night, then it is necessary to compensate for this time during the day. You can sleep an extra 2-3 hours with your child, and then the body will be able to get the required amount of strength.
Of course, these instructions do not always give the desired result, sometimes there is none at all. In this case, you should seek the help of a specialist who will prescribe a course of antidepressants.
If there are no clear manifestations of this disease, but the woman still experiences anxiety and suspicions about her condition, then the best option would be to consult a doctor. He will be able to either refute fears and thereby reassure the new mother, or tell him how best to cope with postpartum depression.
Allergies in infants are due to the fact that the child’s gastrointestinal tract is not yet fully formed. A hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers will help prevent the development of hypersensitivity in the baby.
Gradation and forms of depression
Depression is divided into three levels of severity:
Mild depression
There are at least three of the symptoms listed above, two of which are in the first category (depressed mood, loss of interest or pleasure, decreased desire). The patient feels unwell and seeks medical attention, but despite the loss of work capacity, he or she can perform all professional and personal responsibilities as long as it is routine.
Moderate depression
A total of at least six symptoms listed above, two of them from the first category. Professional or personal responsibilities can no longer be performed or are performed only on a temporary basis.
Severe depression
There are at least eight symptoms listed above, including all three from the first category. In severe depressive episodes without psychotic symptoms, the patient requires ongoing care. In a depressive episode with psychotic symptoms, e.g. delusional thoughts, absurd feelings of guilt and/or fears of illness.
In addition, a distinction is made between different forms of depression. Depending on the severity, causes and symptoms, the cause that caused it is, among others, divided into:
Unipolar depression
Unipolar depression is the most common form of depression. The onset is very slow, with patients showing symptoms only after several days, weeks or months. In many cases, they will disappear again on their own.
Atypical depression
In atypical depression, mood may appear normal for up to two months, with periods of agitated mood alternating with periods of depressed mood. This type of depression is also called cyclothymia.
Situational depression
In situational depression, feelings of depression occur in response to certain events. This type of depression is also called adjustment disorder and usually goes away on its own without the need for treatment.
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder describes a form of depression that alternates between periods of severe depressive mood and manic, euphoric episodes. Therefore, this type of depression is also called manic depression. Treatment is carried out using special drugs to stabilize mood.
Persistent depressive disorder
In this type of depression, also called dysthymia, the symptoms are milder but persist for at least two years. This type of depression is especially characterized by a feeling of hopelessness.
Psychosis
Psychosis is a serious form of depression in which underlying feelings and sensations are expressed through delusions and hallucinations. This type of depression requires treatment with psychotropic medications or, in rare cases, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).
Depression during pregnancy
By definition, pregnancy depression can occur between conception and the baby's first birthday. Women who have previously had some form of depression have an increased risk of being affected by pregnancy depression. This type of depression results from a combination of anxiety associated with both the birth of a child and the drastic life changes that birth brings about. This type of depression is treated in the same way as other types of depression.
Women who have previously had some form of depression have an increased risk of being affected by pregnancy depression
Seasonal Depression
Seasonal depression is less common than other forms of depression. They, as the name suggests, depend on a specific time of year (for example, winter depression).
Depending on the course of the disease and the success of treatment, each depression is divided into a depressive episode (may occur one or more times) or chronic depression (if symptoms persist for more than two years). If complete restoration of health occurs, they speak of remission. A condition in which symptoms improve significantly but do not disappear completely is called incomplete remission.
Seasonal affective disorder (winter depression). Winter depression occurs during the cold and dark seasons. It affects women four times more often than men and is observed mainly in Scandinavian and Central European countries. In southern countries, winter depression is practically not common. The trigger for winter depression is the lack of natural daylight, as well as decreased light intensity in winter and lower temperatures. The body responds to a lack of light by increasing the release of melatonin, a hormone that, for example, is responsible for sleep rhythm. As a result, we are more likely to be tired and our mood worsens.
Typical symptoms of winter depression include increased need for sleep, morning fatigue, lethargy, lack of energy, imbalance and depressed mood.
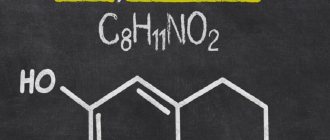
Because the brain also lacks serotonin in winter depression (a hormone that is involved in regulating sleep, body temperature, sex drive and state of mind), people suffering from winter depression also experience increased cravings for sweets, as sugar helps the brain compensate for the lack serotonin.
SEROTONIN | Seasonal depression
Definition of Depression
According to ICD-10 (10th edition of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems), the inclusion criteria for a depressive episode are met if at least two of the following three symptoms persist for at least two weeks:
- Depressed mood, at a level that is noticeably unusual for those affected, for a significant portion of the day, almost daily, and largely independent of external factors
- Loss of enjoyment from hobbies or other favorite activities
- A person gets tired quickly and is inactive
In addition, at least one of the following symptoms must be present:
- Loss of self-confidence and self-esteem
- Self-reproaches for no reason, feelings of guilt
- Regular thoughts of suicide.
Most sufferers experience suicidal thoughts at some point, and 10 to 15% of all patients with recurrent major depressive episodes die by suicide.
- Decreased ability to think or concentrate, lack of determination
- Psychomotor pathological restlessness or retardation
- Insomnia and other sleep disorders
- Poor appetite, or, conversely, increased appetite with a corresponding change in weight
The transition from a low mood to a pathological depressive episode is perceived by most people as something with a very fine line. However, an experienced physician can make the distinction.
Treatment of depression
Once the correct diagnosis is made, the situation is not at all hopeless. Over the past decades, much has been done regarding therapy, and more than 80% of patients can receive treatment on a permanent and successful basis. It is therefore all the more important that the general population is informed and educated about this issue: depression can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender and social status.
Based on the interview between the doctor and the patient and the results of the examination, a suitable treatment plan will be drawn up. Depression can be treated with medications and psychotherapy. In many cases, a combination of both treatments is particularly effective. It is important to understand that therapy requires patience—depression does not disappear overnight, even with optimal care.
Antidepressants
Medicines prescribed to treat depression are called antidepressants. Antidepressants work by affecting various neurotransmitter systems in the brain and compensating for neurotransmitter deficiencies. There are many different antidepressants - modern medications are much more targeted than older antidepressants (such as tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants) and have fewer side effects.
The drugs used today to treat depression use so-called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (block molecules that return serotonin back to its reservoirs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (prevent the return of norepinephrine and serotonin to the brain), and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (inhibit the reverse transport of norepinephrine and dopamine in nerve cells of the brain). The active ingredients of modern antidepressants include: Citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, duloxetine, milnacipran, venlafaxine, bupropion and reboxetine.
Depending on the antidepressant, it may take an average of eight days to three weeks for your mood to improve. If drug therapy does not produce the desired effect, your doctor will adjust the dose or use a different antidepressant to treat your depression.
The drugs used today to treat depression use so-called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Psychotherapy
While medications can help balance neurotransmitter deficiencies in the brain, they cannot change the lives of those affected from scratch. In the context of psychotherapy, people with depression can learn to better cope with (internal) conflicts and emotions, cope more consciously with separation, and resolve social conflicts. If the reasons for your low mood are unknown, talking to a therapist can help identify them. There are many different types of psychotherapy. For example, in psychodynamic therapy, deep-rooted problems that originate in childhood recede step by step while working with a therapist. In behavioral therapy, the therapist assists his patient in developing new behavioral strategies and helps him give up negative behaviors and thought patterns.
A good relationship between therapist and patient is especially important for successful psychotherapy. An honest, trusting relationship is absolutely necessary to fully resolve any issues in therapy.
In addition to drug therapy and psychotherapy, other treatment options include magnetic stimulation, exercise therapy, electroconvulsive therapy, and light therapy. The latter is often used to treat winter depression. The patient sits in front of a light fixture with six or eight fluorescent tubes that emits fluorescent light (without ultraviolet content). The intensity of the emitted light approximately corresponds to the light of a bright spring day and has a positive effect on certain brain structures. The daily recommended duration of light therapy is between half an hour and four hours. The use of these and other measures should always precede medical advice.
With psychotherapy, people with depression can learn to better cope with (internal) conflicts and emotions, cope more consciously with separation and resolve social conflicts
How it manifests itself - symptoms and signs
Male depression is more difficult to recognize than female depression. This is explained by the denial of feelings: men hide them from others and even from themselves, disguising them as unusual behavior.
Signs of male depression that serve as a defense to help you forget about disturbing thoughts:
- aggressive behavior - a man can verbally or physically insult loved ones;
- isolation, no communicative interaction with people;
- addiction to alcohol and drugs, which had not previously been noticed in a man;
- addiction to gambling;
- a desire for risk, manifested in extreme sports or driving at high speed.
The symptoms of male and female depression are very different, but they have one thing in common - self-medication. The stronger sex tends to blame others for their own problems.
Men tend to get angry, become irritable, hot-tempered, suspicious and conflictual.
There is anxiety and excitement, a desire to control everything, a fear of admitting one’s own weakness, uncertainty, and despair.
The manifestation of depression is not only the emotional state of a man, but also indigestion, back and head pain, and insomnia.
Such symptoms do not respond to conventional treatment, since the somatic diseases that appear are the result of mental disorders.
Initially, it is necessary to normalize the psycho-emotional state.
How depression manifests itself, symptoms:
| Apathy | A man ceases to be interested in anything, he gives up activities that previously brought pleasure. Communication with friends and loved ones is reduced to a minimum. In severe cases, a person does not leave the house and refuses to do anything |
| Bad mood | Such a symptom is often not noticed, since pessimism, a gloomy disposition or irritability do not seem strange. A feeling of hopelessness, melancholy and lack of joy for several months requires the help of a psychotherapist. Otherwise, not knowing how to get out of a depressed state, a man can immerse himself in computer games. Become addicted to drugs and alcohol, get involved in dangerous sports, or risk your health by getting involved in adventures |
| Retardation (thinking and motor) | As the condition becomes more severe, it is difficult for a man to force himself to concentrate on any task. He prefers to do work that does not require much mental effort. Later, the slowdown in thinking is noticed by others - they conclude that he is not suitable for the position he holds or even that he is mentally incompetent. Patients may refuse to get out of bed due to decreased physical activity |
| Somatic manifestations | Weakness, migraine, palpitations appear, appetite, sleep and sex life are disrupted. Sweating increases, stomach, heart and other organs hurt |
The earlier depression is detected, the more successful and shorter its treatment will be. In advanced cases, it is impossible to do without the help of a psychotherapist.
Diagnosis of depression
Many people do not go to the doctor and suppress their symptoms due to the wrong feeling of shame. A medical consultation can help identify possible causes of mood changes and begin with appropriate treatment. The diagnosis is made by a qualified family doctor or psychiatrist and is based mainly on a detailed interview with the patient.
In some cases, a blood sample is also tested in a laboratory and a computed tomography (CT) scan is performed to detect or rule out physical changes such as vitamin B12 deficiency, hormonal changes, or low blood sugar as a cause of depression.
Consequences of prolonged depression
If depression lasts too long, quality of life deteriorates. Since this condition deteriorates performance, a person may lose his job or lose his place of study. It is possible to stop communicating with close friends, or to part with a lover due to illness.
Often the causes of mental illness are related to the functioning of the brain. If left untreated, various mental disorders may appear. Suicidal tendencies appear. Destructive behavior and the emergence of bad habits are possible: after intoxication, symptoms often temporarily weaken, which attracts the patient.
Development of depression
Further, all manifestations worsen: attacks of melancholy become more frequent and lengthened, physical retardation becomes more pronounced, desire decreases until libido fades. Speech becomes impoverished, becomes monosyllabic, “dull,” and slow. Professional skills are partially lost.
Women have a tendency to self-blame. They consider themselves incapable of professional activity, unsuitable for family relationships, and incompetent in terms of raising a child. During this period, daily mood swings are common, with patients feeling worse in the morning than in the evening.
Difference between depression and bad mood
Conflicts at work, tension in relationships, separation, arguments, financial problems, an accident or the loss of a loved one can make anyone feel depressed. Exhaustion, inner restlessness, grief, gloom and joylessness are completely normal feelings. Everyone experiences these reactions, some more often than others. Discomfort, however, should be distinguished from depression in the medical sense and is often closely associated with a stressful event and/or a stressful phase - the release of stress and pain is usually mood-elevating.