Hallucinosis (hallucinatory syndrome) is a mental disorder manifested by an abundant influx of hallucinations (imaginary perception of various phenomena that do not exist in reality) without any disorder of consciousness. The term “hallucinosis” was first used in 1900 by the German psychoneurologist K. Wernicke when describing a condition that occurs in alcoholics, accompanied by multiple auditory hallucinations against the background of absolutely intact consciousness.
Hallucinosis is a mental disorder accompanied by multiple hallucinations against the background of preserved consciousness.
Causes and risk factors
Most often, hallucinosis develops under the influence of the following conditions:
- epilepsy;
- organic brain lesions (tumors, hemorrhages, injuries);
- encephalitis;
- schizophrenia;
- severe infectious and somatic diseases;
- chronic alcoholism.
Hallucinosis requires differential diagnosis with schizophrenia, oneiric syndrome and a number of other mental illnesses, the clinical picture of which also includes hallucinations.
Hallucinosis: is it only organic?
In addition to the option discussed above, atherosclerotic and alcoholic hallucinosis occurs. The first is diagnosed if its development is explained by atherosclerosis. This is always a chronic pathology, the symptoms of which gradually increase in accordance with the progress of the underlying disease.
Alcoholic hallucinosis is more characteristic of the period of abstinence from alcohol and is accompanied by somatic disorders. Occurs somewhat less frequently during heavy drinking. The patient is oriented in space, in his own personality, and the hallucinations are predominantly verbal. Sounds and words are heard, neutral at first. Due to the lack of critical perception, the patient tries to find the source of the sounds, which is accompanied by increased anxiety and horror. Hallucinations become stronger, several voices are heard communicating with each other regarding the patient’s personality. Multi-voice scenes are possible (for example, court). Since there is no critical attitude towards the condition, the patient is haunted by delusional ideas associated with the plot of a particular vision.
Forms
Depending on the duration of the course, acute and chronic hallucinosis are distinguished. The acute form usually lasts no more than two weeks and is manifested by motor agitation and pronounced affect. Chronic hallucinosis can last for several years; it is characterized by the presence of “voices in the head” or other monotonous hallucinations.
Based on the type of sensory deception, the following forms of hallucinatory syndromes are distinguished:
- verbal hallucinosis;
- peduncular visual hallucinosis (Lhermitte syndrome);
- Van Bogaert visual hallucinosis;
- Bonnet visual hallucinosis;
- Gobek's olfactory hallucinosis;
- tactile hallucinosis.
Treatment
Before starting therapy, the cause of hallucinosis must be clearly established. This requires face-to-face consultation with an experienced specialist, sometimes more than once. The underlying disease needs to be treated. Basically, the presence of hallucinations indicates mental disorders. If a patient with acute hallucinosis poses a threat to society, treatment in a specialized clinic is needed.
Therapy should include means to relieve symptoms. The doctor prescribes psychotropic medications. Also, with the alcoholic nature of hallucinosis, detoxification is necessary. Part of complex therapy is, of course, psychotherapy.
Drugs for the symptomatic treatment of hallucinosis:
- diazepam (iv)
- relanium
- seduxen
- aminazine (i.m.)
Signs
The clinical picture of different forms of hallucinosis varies.
Lhermitte syndrome, or peduncular visual hallucinosis, is manifested by visual hallucinations that occur at night in the form of blurry figures of animals or people, small objects. Patients remain critical of their condition.
Hallucinations in the form of cartoons, people with distorted facial features, or geometric shapes are characteristic of Bonnet visual hallucinosis. Visions occur spontaneously in people with organic visual impairments and quickly disappear. Criticism of one’s condition has been preserved in full.
Van Bogart visual hallucinosis is accompanied by an abundance of bright images of small size (birds, flowers, butterflies). Often, with this form of mental disorder, visual hallucinations are combined with auditory ones.
With verbal hallucinosis, auditory hallucinations occur. Patients can hear either one voice or several, which enter into active dialogues with each other. These “voices” discuss the reality surrounding the patient or give him instructions to perform certain actions. Over time, auditory hallucinations lead to the formation of hallucinatory-delusional syndromes, in which criticism of one’s condition is lost.
With verbal hallucinosis, a person hears one or more voices at once
Olfactory hallucinosis is rare and is usually a symptom of schizophrenia. Patients perceive unpleasant odors emanating from their body or surrounding objects.
Hallucinosis of the general sense has many manifestations. Most often, patients complain of the sensation of insects crawling over their body (tactile hallucinosis, dermatozoan delirium). Much less often, patients complain of insects inside their body (visceral hallucinosis).
Treatment
Treatment of the disease is carried out in a drug treatment hospital, which means hospitalization of the alcoholic. The treatment regimen includes:
- intoxication;
- elimination of psychotic phenomena;
- restoration of the functioning of various organs and systems;
- normalization of metabolic processes;
- prevention of the development of persistent cognitive-behavioral disorders.
During detoxification, Hemodez, Reopoliglucin, and saline solutions are used. The doctor prescribes the patient to take B vitamins, Inosine, Cocarboxylase, and ascorbic acid. For the preventive purpose of developing brain disorders, meldonium, ethylmethylhydroxypyridine, and Piracetam are used. To relieve psychotic phenomena in acute forms of hallucinosis, the following are used:
- Risperidone;
- Olanzapine;
- Haloperidol;
- Azacyclonol.
As a rule, drugs are administered through a dropper, less often - orally. The speed at which the hallucinogenic syndrome passes depends on the severity of the psychosis and its duration. The sooner therapy is started, the faster psychosis can be stopped. In the presence of chronic hallucinosis, more aggressive methods can be used - taking antipsychotics, insulin (hypoglycemic) coma, electric shock. With any treatment regimen, a mandatory condition is complete abstinence from alcohol.
Detoxification
An important stage during the treatment of a mental disorder caused by alcohol abuse is the period of cleansing the body of its breakdown products. Even with their partial removal, the patient feels much better. With the help of special solutions for detoxification, it is possible to achieve normalization of metabolism, which has a positive effect on a person’s well-being. As a rule, the following are used for this purpose:
- Hemodez;
- Reopoliglyukin;
- Rheosorbilact;
- saline infusions with vitamins and nutrients.
In addition to the listed solutions, the doctor can administer glucose, Riboxin, B vitamins and ascorbic acid to the patient. To prevent the negative effect of alcohol metabolites on the brain and maintain its health, the use of nootropic medications is recommended. So, in parallel with parenteral solutions, the following are used:
- Mexidol;
- Piracetam, etc.
Antipsychotic
Any hallucinations indicate the onset of acute psychosis and require immediate initiation of treatment with antipsychotic drugs. Indications for their use are also delusional ideas that arise during alcoholic hallucinosis. When treating such a disorder, timeliness is very important. The earlier antipsychotic therapy is started, the more favorable the prognosis.
In cases where the symptoms of psychosis have been observed for a long time (for several weeks, months), a rapid improvement in the patient’s condition should not be expected. The choice of treatment method lies with the doctor, who is based on the severity of the pathology, its neglect, and other individual factors. The following drugs and techniques may be prescribed:
- Neuroleptics. The group of drugs differs in their effectiveness, selectivity, and duration of action, so the doctor can choose the most suitable drug for each specific case. As a rule, Olapanzapine, Haloperidol, Respiridone or their analogues are used.
- Electric shock. It is used in the most hopeless cases when antipsychotic medications do not produce results. Dosed exposure to current on the brain can cause various negative consequences, but this technique has many more positive qualities.
- Insulin comatose therapy. The effect of such treatment is achieved by depleting glucose reserves in the human body, as a result of which the patient falls into a coma. This mobilizes the body's reserve forces and stimulates a “reboot” of the central nervous system. Today, such therapy is practically not used, since its role is played by antipsychotic drugs.
Psychotherapeutic
This element of complex therapy for alcoholic hallucinosis is used after the symptoms disappear. Psychotherapeutic treatment serves as part of the rehabilitation period, which includes actions that are necessary to restore a person’s psycho-emotional health for his subsequent return to normal life. Most methods in this area are aimed at preventing the development of alcoholic psychoses in the future and gradual cessation of alcohol consumption.
The patient visits a psychologist who conducts cognitive behavioral therapy sessions with him. During the classes, the necessary guidelines for a healthy lifestyle are determined, and values are reviewed. An experienced psychotherapist helps an alcoholic overcome addiction and gradually return to normal life. The effectiveness of such treatment depends entirely on the patient and his desire to overcome the disease.
Diagnostics
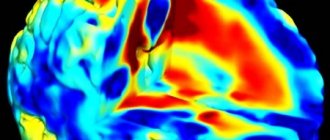
In case of hallucinosis, a medical examination is necessary to determine the cause of the hallucinations. In order to detect (or exclude) organic brain lesions, computer and (or) magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is performed.
MRI can detect organic brain lesions leading to hallucinosis
Hallucinosis requires differential diagnosis with schizophrenia, oneiric syndrome and a number of other mental illnesses, the clinical picture of which also includes hallucinations.
The term “hallucinosis” was first used in 1900 by the German psychoneurologist K. Wernicke when describing a condition that occurs in alcoholics, accompanied by multiple auditory hallucinations against the background of absolutely intact consciousness.
Hallucinosis: what is it?
This term usually refers to a condition when a person suffers from hallucinations, while consciousness is retained. In the predominant percentage of cases, hallucinations always belong to the same type. The pathological condition accompanies a person for many years and can cause delirium.
At the moment, it is difficult to say for sure whether all the causes of hallucinosis are known. They can appear in schizophrenia, epilepsy, and can be of a somatic nature. Hallucinosis is possible in bipolar disorders, malignant diseases, and impaired functioning of the sensory organs. There are known cases of hallucinosis during migraine, due to the abuse of alcohol, narcotic compounds, and surrogates.
Certain forms of hallucinosis are possible when the functionality of the heart, blood vessels, and thyroid gland is impaired.