Asthenia - what is it?
The term came to us from the Greek language, the prefix “a” means negation, absence, “sten” - strength. As a result, we get that asthenia is translated as “lack of strength”, “powerlessness”. A synonym for asthenia is fatigue.
There are two types of fatigue:
- normal (physiological);
- pathological
The first occurs after an objective event (hard physical and mental work, illness, starvation). After eliminating these causes and resting, fatigue goes away. And the person feels rested and healthy.
Pathological fatigue is a more insidious condition. No provocateurs are needed for its occurrence; a person wakes up with it in the morning. It can last days, weeks. And it is very difficult to cope with it on your own. They even came up with a special name for people suffering from pathological fatigue - asthenic. An asthenic person is unpleasant in communication, constantly complains about his poor health, lacks initiative, and everything is always bad for him.
Symptoms
The main problem of this pathology is that it is difficult to identify astheno-anxiety syndrome. Signs of this condition are characteristic of a large number of different diseases of the nervous system. In fact, the symptoms of asthenia are subjective for each specific case. The syndrome can be suspected if the following signs are detected in a person:
- Apathy that progresses over time. The symptom appears almost immediately. The patient loses interest in his own work and favorite activities.
- Severe weakness. The patient himself and those around him cannot explain the appearance of this condition.
- Sleep disturbance. A person may wake up constantly, have nightmares, or not sleep at all at night.
- A sharp decrease in performance. The patient does not have time to do anything, becomes nervous and irritable.
- Daytime sleepiness. The sign can be noticed at a time when a person should still be cheerful and full of energy.
- Periodic surges in blood pressure (blood pressure).
- Malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system. The patient may notice problems in the functioning of the liver, kidneys, lower back pain, and disturbances in the urination process.
- Periodic shortness of breath.
- Memory impairment.
- Change in character for the worse.
- Phobias.
- Tearfulness.
The signs of asthenic neurosis can be considered in the context of two types of disease: hypersthenic and hyposthenic. In the first case, the patient experiences increased excitability. Against this background, various types of irritants become unbearable for him: bright lights, loud music, screams or laughter of children, noises. As a result, a person tries to avoid these factors and often suffers from headaches and vegetative-vascular disorders.
The hyposthenic form of asthenic neuroses is characterized by the patient’s low sensitivity to any external stimuli. It is characterized by a person’s depressed state, lethargy, passivity, and drowsiness. Often patients with this type of asthenic disorder experience apathy, unmotivated sadness, anxiety, and tearfulness.
In children
Children of all ages, including infants, are susceptible to asthenic syndromes. The baby becomes excitable, constantly mischievous, and eats poorly. A manifestation of asthenia in infants is causeless tearfulness, fear of any sounds, even subtle ones. A child may get tired from being rocked in their arms for a long time and communicating with adults. It is difficult to lull a baby with asthenia to sleep; he takes a long time to fall asleep, is capricious, and constantly wakes up at night. It is important to consider that children with this syndrome are able to fall asleep faster in the absence of their parents. You should leave the baby in the crib and leave his room.
Psychological exhaustion of a child can provoke registration in kindergarten. Separation from mother is very stressful for many. In addition, asthenic neurosis can develop against the background of early entry into school (from 6 years of age). The child is faced with a large number of new requirements and rules. He needs to sit quietly in class and remember new information. As a result, asthenia develops. Symptoms of this syndrome in children of preschool and primary school age are the following:
- nervousness;
- isolation;
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue, the child may be indifferent to favorite activities and toys;
- poor memory;
- difficulty concentrating;
- headache from loud noises;
- photophobia;
- fear of strangers;
- poor appetite.
Adolescents can also develop encephalasthenic syndrome and other forms of this disorder. Symptoms of pathology characteristic of children of senior school age:
- Violation of rules of behavior in lessons, generally accepted norms of communication with others:
- rudeness towards peers and adults;
- poor appetite;
- recurrent headaches;
- weakness;
- apathy;
- poor performance at school;
- problems with concentration;
- absent-mindedness;
- conflict, desire to argue on any issues;
- increased fatigue;
- instant changes in mood;
- sleep problems.
All these manifestations of asthenic syndrome in children can be combined with signs of concomitant diseases that caused the disorder. It is important to consider that asthenia is a whole complex of symptoms that progress over time. If a child has 3 or more signs of the syndrome, you should seek help from a neurologist, pediatrician or child psychiatrist. It is difficult to diagnose asthenic disorders in children, because some of their symptoms do not differ from the personal characteristics of young patients.
Asthenic syndrome - what is it?
Why do you need to feel tired?
Yes, yes, you don’t need to think that fatigue only brings negativity. After all, what does it exist for? Our body is very smart, it itself can regulate all the processes occurring inside it (from wakefulness and digestion of food, to the production of hormones, muscle function, etc.). To do this, he needs only one thing - energy. He accumulates it, synthesizes it from everything he can - from food, inhaled air. When energy becomes low, the body understands the threat looming over it and defends itself. Namely, it sends signals to a person’s brain with instructions to stop what he is doing. Stop, rest, doze off, feel hungry and thirsty, etc., all this is needed to replenish energy reserves.
Asthenia as a manifestation of the disease
Unfortunately, fatigue is not always a normal reaction of the body. An asthenic condition may be the first manifestation of the disease. Here are just some of the conditions accompanied by biased fatigue:
- endocrine diseases (disturbance of the pancreas, thyroid, adrenal glands, obesity);
- lung diseases (bronchial asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis);
- heart (cardiovascular failure, previous heart attack);
- oncological diseases;
- chronic kidney disease;
- neurological diseases (Parkinson's disease, sclerosis, stroke);
- infections (colds, flu, tuberculosis, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome);
- mental (alcoholism, depression, schizophrenia).
Other causes of asthenia
These include:
- taking certain medications (sleeping pills);
- starvation;
- climate change;
- severe emotional stress;
- working at night;
- pregnancy;
- caring for an infant;
- vitamin deficiency;
- work in several places at the same time;
- heavy workload;
- exams;
- recovery after operations, injuries;
- personal characteristics.
Asthenic condition
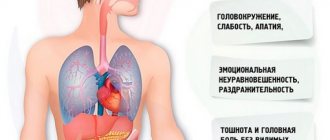
Asthenic conditions are united by the concept of syndrome, that is, a set of symptoms and complaints of the patient. Most often they complain of weakness, even with the slightest physical effort, in combination with certain symptoms. Asthenic syndrome symptoms include the following:
- emotional disorders (lack of mood, anxiety, irritability, panic, melancholy, etc.);
- mental (inability to concentrate, absent-mindedness, memory impairment);
- dizziness, nausea, rapid heartbeat, increased sweating, increased or decreased body temperature;
- unexplained pain in muscles, back, stomach, headache;
- sleep disturbance (difficulty falling asleep/waking up), decreased or increased appetite, weight loss, sexual desire disorder;
- Women may experience a delay in menstruation;
- intolerance to loud sounds, bright light.
Let us remind you that the above symptoms do not go away after rest.
Signs of asthenia in women and its forms:
Medicine distinguishes three forms of asthenia:
Hypersthenic:
- With this form of asthenia, women experience increased anxiety.
- Constant anxiety.
- Marked impatience, nervousness.
- These symptoms are expressed even in neutral life situations.
Hyposthenic:
- Here it's the other way around:
- I don’t care about everything, everything is indifferent.
- Symptoms of depression appear.
- Tearfulness, absent-mindedness.
- Performance is clearly reduced.
- Muscle weakness is pronounced.
- Sleep is disturbed.
- Memory suffers, attention weakens.
- No self-confidence.
- Focusing on solving any problem is an impossible task.
- Appetite is reduced.
- Sexual disorders are pronounced.
- There is shortness of breath.
Irritability and weakness:
- It’s like a middle ground between the two forms of asthenia described above in women.
- The woman is excited, but at the same time weak and exhausted.
- There are sharp transitions from obvious activity to complete apathy.
Chronic fatigue syndrome
It is a variant of asthenia. In the literature there is also a synonym for chronic fatigue syndrome - neurasthenia. The study of this disease began in the eighties in America. Criteria for the disease have been developed and are now used throughout the world:
- constant weakness lasting at least six months;
- absence of a causative disease;
- 4 or more symptoms must be present:
- Problems with memory and attention.
- A sore throat
- Painful and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and armpits.
- Muscle stiffness, soreness.
- Joint pain.
- Headache.
- Sleep disorders.
- Fatigue after exercise lasts more than 24 hours.
Thus, chronic fatigue syndrome from asthenia is distinguished by its duration (more than 6 months) and the absence of concomitant diseases.
"Pentovit"
A complex medicine for chronic fatigue (vitamin complex) is prescribed to patients with a lack of vitamin B in the body and signs of asthenia. Asthenic syndrome is a condition characterized by increased fatigue, neuropsychic and physical weakness, sleep disturbances, and extreme mood instability. Pentovit contains B vitamins, nicotinamide and other beneficial microelements. After a full course of therapy, patients experience a general improvement in their condition, activation of metabolic processes, and normalization of the central nervous system. Reviews about the vitamin complex are positive. The effect of use is noticeable even before the end of the course of therapy.
Astheno-vegetative syndrome
Another variant of asthenia. With it, the disorder affects the autonomic nervous system. That is, as with any asthenia, the body, in the event of a threat, will send signals so that the person stops expending energy. But these signals in this case will manifest themselves as a malfunction in the autonomic system.
The autonomic part of the nervous system regulates the functioning of internal organs (lungs, heart, kidneys, liver, etc.), glands (thyroid, pancreas, etc.), blood vessels (arteries and veins) and lymphatic vessels.
Signs of astheno-vegetative syndrome:
- increased sweating;
- headache;
- pain in the heart area;
- blood pressure surges;
- trembling of fingers;
- cardiopalmus;
- labored breathing;
- increase in the number of breathing movements;
- nausea and even vomiting.
Reasons for the development of the pathological condition
The reasons for the development of asthenia of the central nervous system are varied.
They can affect the human body in combination, often for a long time. But sometimes the syndrome can be triggered by previous diseases or pathological processes.
Factors provoking asthenia include:
- one of the symptoms of brain stem disorders;
- constant stress;
- head injuries;
- undergone surgery;
- infections of both viral and bacterial etiology, especially if they affected the central nervous system;
- birth injury;
- fetal hypoxia;
- unbalanced diet;
- nicotine and alcohol addiction;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- sleep deficiency;
- lack of vitamins;
- abuse of specific medications;
- certain environmental conditions, for example, living in the Arctic Circle, deficiency of UV rays from the sun.
Senile asthenia
In old and senile age (60 years and older), asthenia is called “fragility”, its manifestations:
- slowness of movements;
- decreased walking speed;
- impotence;
- vulnerability;
- unreasonable fatigue;
- weight loss;
- inability to control physiological functions (urination, defecation);
- falls;
- impaired memory, hearing, vision, etc.
At the same time, the pensioner loses the ability to adequately assess his condition. Outside help in everyday life becomes necessary.
Diagnosis of asthenia
Unfortunately, there are no clear criteria (symptoms) of asthenia to make such a diagnosis. It would be more accurate to call it a diagnosis of exclusion. After conducting an expanded set of studies, the doctor will rule out other diseases (the symptom of which is fatigue). And only in this situation will he be able to write the diagnosis “asthenia” on the card.
When visiting a medical institution, the doctor will adhere to the following plan:
- collection of patient complaints;
- inspection;
- palpation (palpation);
- tapping (percussion);
- auscultation (auscultation);
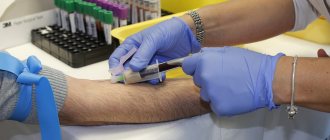
- laboratory tests of blood, urine, feces;
- instrumental studies (x-ray, ultrasound, etc.).
The patient voices his complaints, and it is possible to take into account the opinions and notes of relatives. Attention is paid to living conditions, sleep, and whether the person has proper nutrition. Family relationships, presence of relatives, work, psychological comfort at home, life priorities.
In addition, active problem identification is carried out. Special questionnaires, memory tests, and mood tests can be used.
Special questionnaires include:
- “well-being, activity, mood” or SAM;
- a scale for assessing asthenia according to the patient’s own sensations;
- Excessive Fatigue Questionnaire;
- assessment of fatigue severity.
In addition, there are special tables with all the symptoms of asthenia. The patient is asked to choose those present at his place.
Questionnaires:
- pain;
- disorders of the autonomic system;
- depression;
- sleep disorders;
- for memory testing, etc.
The examination is carried out according to the systems, the doctor tries to suspect diseases of the heart, blood vessels, lungs, liver, kidneys, nervous system, psychological and psychiatric disorders.
The safety of the elderly is determined - muscle strength, gait, ability to self-care, functions of hearing, vision, smell.
Research:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- determination of thyroid hormone levels;
- general urine test and others if necessary;
- X-ray examination of the chest organs;
- electrocardiographic study of heart activity;
- and many others if necessary.
Only an experienced and attentive doctor can suspect and make a diagnosis. An independent adequate assessment of one's own condition is impossible.
Development mechanism
Normally, the body of a healthy person responds to any stimulus in the form of a peak reaction, which has a certain period of decay. The more powerful the stimulus, the larger the peak and the longer the decay period. From such peaks and periods, the “working background” and normal performance are formed.
What happens when the body experiences an asthenic state?
Even the smallest stimulus produces a maximum peak, after which the recovery period is disrupted. This occurs due to the fact that the patient’s nervous system is exhausted and weakened under the influence of certain causative factors.
Such an excessive response to any trigger leads to the fact that the nervous system is in constant, chronic tension, the body does not relax, and there is no adequate recovery period.
The asthenic state includes increased excitability, and at the same time, excessive exhaustion of nervous processes with a corresponding clinical picture.
Asthenic syndrome. Treatment
Lifestyle
Since there are real diseases, one of the manifestations of which is asthenia, the disease itself must be treated. In this case, acting only on fatigue will lead to nothing. After all, the reason will remain, and asthenia will appear again and again. So, the most important thing in treating asthenia is to eliminate its cause.
If asthenia is an independent disease, then its treatment should use the following principles:
- reduction in the severity of symptoms;
- improving the quality of life of the patient;
- increasing the level of daily physical activity.
In order to deal with other causes of asthenia (not the presence of an underlying disease), it is worth contacting a psychologist or psychotherapist. It will help to identify the causes of fatigue, the mechanism of its occurrence, and find the “key” to eliminating these disorders.
The primary goal in the treatment of asthenia is to change a person’s lifestyle if it has become the cause of the pathological condition:
- change of job, profession;
- normalization of sleep and wakefulness patterns;
- nutrition correction;
- change of place of residence, environment;
- working with a psychotherapist;
- changing your attitude towards yourself and others;
- training in methods of relaxation and distraction;
- support of relatives and friends, people with similar problems;
- eliminating bad habits, etc.
Physical training
In the treatment of neurasthenia (chronic fatigue syndrome), it is necessary to engage in physical exercise, work with a psychotherapist, and take medications (they will be discussed below).
Most experts believe that physical education is an essential element in the treatment of any asthenia. There is a popular concept: “a healthy mind in a healthy body.” You should only engage in activities that bring positive emotions. For example, if playing volleyball provokes a panic attack, then preference should be given to calmer games.
Physical exercise should be gradual, taking into account the general fitness and desire of the patient himself. Perfect for:
- yoga;
- massage;
- swimming;
- walking;
- run;
- a ride on the bicycle;
- skis;
- cold and hot shower;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture.
For psychopathological reasons, treatment with music, light, heat, play, etc. will have a beneficial effect. There are a lot of techniques, they are selected individually.
Psychotherapeutic approaches in the treatment of asthenia:
- correction of symptoms;
- interruption of pathological perception of irritating factors;
- correction of psychological problems of the individual.
Trainings, family, individual and group sessions, suggestion, hypnosis, and self-hypnosis are used. Thanks to this treatment, anxiety is relieved, a person becomes more confident, complexes and fears are corrected, and the desire to lead a healthy lifestyle increases.
Diet
The second stage after physical activity in treatment should be diet. The food eaten must comply with the principle of rationality. That is, do not overeat, do not overeat! And eat often, in small portions, at a calm stop. The patient’s menu should include fish, different types of meat, fruits, vegetables, seafood, dairy products, and bread. Food should be varied and tasty.
Some experts recommend taking vitamins in winter and spring. Whether or not to listen to this advice is up to the person himself. It would still be more physiological to increase the amount of fruits, vegetables, and berry fruit drinks in the menu.
Diet restrictions should include fatty foods (fried foods, cheese), salty foods and canned foods. It is also necessary to control the amount of sweets you eat.
In the treatment of senile asthenia, attention should be paid to the patient’s teeth. Can he chew and swallow food normally? If food is supplied in insufficient quantities, then there will be no energy or vitality. In this case, it is necessary to choose dentures.
Drug treatment
It is carried out according to strict indications and when non-drug methods are ineffective. The drugs used in the treatment of asthenia vary, from herbal and safe ones to serious ones prescribed on prescription forms.
Pharmacological groups:
- vitamins (C, group B, E);
- minerals (calcium, magnesium);
- restoratives (decoctions of herbs, rose hips);
- immunomodulators (interferon);
- biologically active additives;
- adaptogens (eleutherococcus, ginseng);
- nootropics (piracetam, cerebrolysin, lipoic acid preparations, glycine, Ginko Biloba);
- sleeping pills (novopassit, persen, valerian);
- psychostimulants (coffee);
- antidepressants (gelarium);
- tranquilizers (diazepam, clonazepam) and others.
Drugs affecting the central nervous system
Sodium polydihydroxyphenylene thiosulfonate (sold in pharmacies under the trade names “Hypoxen” and “Olifen”) significantly increases the body’s performance under adverse conditions. The medicine for fatigue and drowsiness belongs to the group of antioxidants. “Hypoxen” and “Olifen” improve tissue respiration (especially in organs with active metabolism: liver, brain, heart), increase resistance to significant mental and physical stress, and are used in the complex treatment of heavy blood loss, significant surgical interventions, and respiratory pathologies , severe injuries, angina pectoris and chronic heart failure (including for the purpose of prevention). These are good medicines for eye fatigue and increased fatigue of the whole body. "Hypoxen", for example, is recommended for people who work in extreme and unfavorable conditions (operators, submariners, polar explorers).
Another medicine for fatigue and stress that affects the functioning of the central nervous system is aminoacetic acid (“Glycine”). “Glycine” normalizes metabolic processes, reduces psycho-emotional stress, increases mental performance, and regulates metabolism. The use of aminoacetic acid is accompanied by a decrease in conflict, normalization of sleep, increased social adaptation, improved mood, and a decrease in the severity of symptoms of vegetative-vascular disorders. Available without a prescription. There are no contraindications (except intolerance to the components) or side effects recorded.
The nootropic drug "Semax" (methionyl-glutamyl-histidyl-phenylalanyl-prolyl-glycyl-proline) in small doses has a pronounced neurometabolic effect. Higher doses have antioxidant, neutrotrophic, angioprotective effects while maintaining the neurometabolic effect. Thus, a medicine for fatigue and drowsiness improves memory, enhances concentration, the speed of mental processes, stimulates brain function, and normalizes psycho-emotional reactions. Semax is contraindicated in childhood (under 5 years), during pregnancy and lactation, with anxiety and severe psychosis, with hypersensitivity to components, or a history of seizures. Intended for intranasal use.