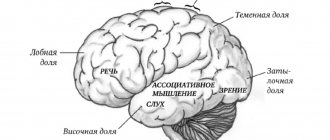
Every person is endowed with five basic senses: vision, hearing, touch, smell, taste. But, depending on the characteristics of perception and processing of information, people can be divided into three main categories: visual, auditory and kinesthetic. And each person will definitely have one dominant sense organ. A lot depends on how we perceive reality.
If you ask several people to remember, for example, a forest, then one will immediately imagine a green crown of trees; another will associate the forest with birdsong; and the third will remember the fresh air and the touch of grass, leaves, cobwebs on the skin.
Also children. One child must write everything down in order to understand, another just needs to hear the information, and the third, if he doesn’t touch it, won’t remember anything.
School learning for a child is mainly a process of perception and assimilation of the information offered. The development of many important skills depends on which channel the child has.
Let's consider each of the channels of information perception.
How to understand what type a child belongs to?
I suggest taking a very useful test for children “CHANNELS OF INFORMATION PERCEPTION”
The test is intended for preschoolers and primary schoolchildren.
As you read the questions, note the traits that your child has. Then summarize and compare the results.
1. COMMUNICATION
If my child wants to say something, then...
Visual - speaks using the simplest figures of speech, pronounces some words and sounds incorrectly, and misses adverbs and prepositions.
Auditory - Uses the same figures of speech as adults, uses grammatically correct sentences, and tells carefully thought out stories.
Kinesthetic - speech is difficult to understand, speaks in short, grammatically incorrect sentences, strives to depict events instead of telling about them.
2. FAVORITE TOYS AND FREE TIME
While playing, my child...
Visual - prefers puzzles and board games, enjoys computer games or games with a calculator, learns about new things by observing.
Auditory - loves listening to audio recordings, loves books and fantasy play. learns new things by reading instructions.
Kinesthetic person - loves to play in the fresh air, enjoys being in the pool, skating rink or slide, and finds full use for almost every toy.
3. COMPLEX MOTOR SKILLS
When my child starts doing something with his hands, then...
Visual - he writes diligently, his works of art are very neat and beautiful, he can easily cut out, paint, and glue together.
Auditory - writes quite well; he talks to himself while working.
Kinesthetic - he writes with difficulty, many of his letters and numbers turn out ugly, his work is untidy.
4. SIMPLE MOTOR SKILLS
When my baby starts moving...
Visual - he considers board games better than outdoor games; he loves games with clearly established rules.
Auditory - talks more than plays; prefers games that require verbal communication; during any activity he talks to himself.
Kinesthetic - considers outdoor games better than board games, has good coordination, does not walk quietly, but rushes about.
5. SOCIAL SKILLS
When my child is surrounded by other children, then...
Visual - even in a crowd he remains alone; before taking part in the game, watches how others play; takes a long time to get used to new people.
Auditory - literally blossoms among friends; may interfere during classes because she talks a lot; often takes responsibility for others and behaves somewhat dismissively.
Kinesthetic - collectivist, but not very talkative; can cause anxiety because he interferes with his neighbors during class activities and likes to play pranks.
6. EMOTIONS
When a child is worried about something, he...
Visual - not very emotional, begins to get nervous, feeling the concern of others.
Auditory - freely talks about his feelings, can go into confrontation with others about his feelings.
Kinesthetic - emotionally dependent and easily offended; when called to order, he reacts angrily, without embarrassment or repentance.
7. MEMORY
When my child studies, he...
Visual - can reproduce letters and numbers from memory; remembers what was shown to him.
Auditory - learns best by memorizing; knows the sounds corresponding to the letters of the alphabet.
Kinesthetic person - does not remember well, is easily distracted.
8. SCHOOL SKILLS
When my child is in the classroom, he...
Visual - monitors the neatness of his clothes and the cleanliness of his workplace; in his free time he prefers construction sets, puzzles, various types of art and crafts; slowly gets used to the new situation.
Audial - his appearance is not very sloppy, but not very neat either; he has to be reminded to clean his work area; he is attentive and obedient.
Kinesthetic - does not care at all about his appearance and is often very unkempt; works in an environment of complete chaos; is able to turn over his workplace in a few minutes; is very active during games; forced to sit in one place, literally writhing and squirming.
One of the definitions - auditory (auditory perception), visual (visual perception) or kinesthetic (tactile perception) - most likely received the most marks. This channel of information perception means the way of cognition that is most characteristic of your child.
Characteristics of digitals
There are relatively few people who can with a high degree of confidence be classified as true digitalists.
Digital people are distinguished by their desire for systematization; it is important for them to understand what advantages and disadvantages a product or advertised service has. A person with a digital type of perception is extremely logical; for him, functionality is more important than design. In trade and business, pure digitals are almost never found
It is not surprising that people with this type of perception began to be talked about only with the advent of computers and the Internet.
In trade and business, pure digitals are almost never found. It is not surprising that people with this type of perception began to be talked about only with the advent of computers and the Internet.
Online, digital feels like a duck to water. Here there is everything he needs - structured information, comparative characteristics, the opportunity to freely choose.
How it can be used
You can only reach the digital with the help of logic. People with this type of thinking instantly recognize any manipulation.
Therefore, when communicating with digital consumers, you need to draw their attention to such aspects of the product as favorable price, functionality, outstanding characteristics, etc. The more reasonable and well-founded arguments a seller or entrepreneur gives, the higher the chances that digital will turn into a buyer or client
Audials
There are many music fans among audio audiences
These kids love to listen. There are many music fans among audiophiles; they prefer audio books. If you see that during a lesson a child repeats after you, pronounces a new rule, or mumbles, it means that you have a typical auditory learner.
Auditory learners are easy to recognize by their speech: they speak measuredly, rhythmically, often nodding in time with the tempo of their speech. If such a child retells the content of a film or book, get ready to listen to all the details with a verbatim reproduction of the characters’ lines. This flow cannot be stopped with the words: “Everything is clear, move on!” If you interrupt the auditory speaker, he will lose the thread of the conversation.
Visual child
Visual learners instantly remember faces, but often forget first and last names. They easily find their way even to places they have only been to once. The speech of visual children is filled with the words “look”, “have you seen”, “beautiful”, “bright”, “red”, “green”... They think in images. In the process of thinking, pictures from the past, ideas about the future, images appear in their heads, and imaginary situations are played out. Little visual learners have a wild and lively imagination.
Children with visual perception do not like hugs and kisses, but they will willingly talk to you about adult topics. They usually look older than their age because they keep themselves aloof and a little arrogant. They love to lecture their elders and quote phrases “from TV,” which they adore. They sense your mood and desires by your facial expressions, but do not always let you understand this (of course, in their own interests). Visual learners have excellent visual memory and fine motor skills are well developed, but they have difficulty understanding verbal instructions and often repeat tasks. Quickly remembers color, shape, size. They find it easy to tell stories based on pictures. Their eyes are always searching for information.
Visual children begin to write in block letters early and can read quite fluently by the time they reach school. In raising a visual student, it is necessary to pay attention to the development of speech (he is taciturn), sociability (the ability to communicate), and physical coordination. Visual students remember the teacher’s explanations more easily if they are duplicated on the school board or on diagram posters: it is easier for them to see and visually remember the word than to understand the rule why they should write it that way. Visual aids, illustrations, the use of colored pencils: sketch, reproduce, highlight - all this contributes to better assimilation of the material.
Allow your child to use colored pens to highlight important points in the book. As visual learners, it is vital for them to have a draft in which they can draw and draw.
Auditory child
These children remember in great detail who said what, where, when, and in what words. They instantly “grab” first names and patronymics, but easily forget faces. Their greatest pleasure is conversation; they will never be interested in a book if they have someone to talk to. All secrets and news immediately become known to them. No, they are not specifically trying to find out what you are talking about, it’s just that their hearing is much better developed than others. Auditory children have a large vocabulary, but may lag slightly behind their peers in the development of skills related to visual (finding differences in pictures) and motor (the ability to deftly climb a slide, run quickly and for a long time) perception.
In their speech, auditory learners often use the words “listen”, “hear”, “noisy”, “quiet”.
Such children think through internal speech, mentally pronouncing their own remarks and the interlocutor’s answers, assuming what kind of voice he will have, what intonation. They love the radio. They like television programs that are dominated by “words” rather than “pictures.” They are very attentive in conversations. In a conversation with an auditory speaker, it is useful to use vocal features: pauses, intonation, volume.
In primary school, auditory learners often study well; their strength is developed auditory memory and speech, but they often have difficulties with spelling and drawing. In middle school, auditory learners who are accustomed to using their memory usually demonstrate significantly less success. During this period, you should pay more attention to reading, pronouncing, and repeating the rules out loud. Auditory learners are musical and easily grasp foreign languages. They are recommended to use audio materials first. When doing homework, such children may move their lips and talk to themselves. Another feature of auditory learners that is associated with difficulties at school is the ability to tell only from the very beginning.
Channels of perception
Dividing people into visual, auditory, kinesthetic and digital in accordance with the basics of neuro-linguistic programming (NLP) allows us to identify their dominant sense organ. At the same time, one predominant sensory perception of the world in a person does not mean suppression of others. People typically have four channels through which they experience the world:
- Visual. With it, a person has a predominantly developed visual system for perceiving the surrounding reality. Color and shape matter to him.
- Auditory. The organ of hearing and the corresponding perception of the world through sounds, timbres, melodies, and volume dominate.
- Kinesthetic. The tactile function predominates. It is easier for a person to recognize this or that object by smell, taste, touch.
- Digital. The logical perception of the world dominates through the construction of an internal dialogue by a person.
The leading channel of a person’s worldview of information allows one to intensify mental activity. Thanks to it, other processes are launched in the form of memory and imagination.
There are several methods for identifying visual, auditory, kinesthetic and digital learners. The main thing is the diagnosis of the predominant modality through testing developed by S. Efremtsev. The test is available online for Internet users who want to find out their dominant type of perception.
Characteristics of auditory, visual, kinesthetic and digital learners include:
- the dominant organ involved in a person’s perception of the surrounding world;
- the influence of the leading channel of perception on character;
- correlation of the type of perception with a person’s personality type;
- a set of differences between one form of human assessment of the surrounding reality and others.
Visual (B). What we see. Images, pictures, movies. Auditory (A). What we hear. Like speech, so is the whistle of the wind, or the sound of dripping water. And, accordingly, intonation, timbre, pitch of the voice. Kinesthetic (K) (From “kines” - “movement”, in Greek). What we feel. This also includes Smell and Taste.
It is convenient to divide what we feel in the body into 3 parts: Tactile sensations - skin sensations, touch; Internal - muscle sensations, sensations in the stomach, warmth; meta-sensations - evaluative sensations that tell us about attitude, emotions: joy, love, happiness, grief and other meta-sensations are usually located in the chest area and sometimes involve the neck and head.
If we combine everything together, we get: Vision (visual system). Hearing (auditory system). Taste. Smell. Skin sensitivity (tactile sensations). Internal - muscular, sensation in the stomach, warmth. Meta-sensations - evaluative sensations.