Many people have heard about epilepsy, but not everyone understands what kind of disease it is, why it occurs and how it progresses. In most cases, we imagine an epileptic attack when a person convulses and foam comes out of his mouth. However, such phenomena are only a small part of the possible options for the development of the disease, because there are many manifestations of such a pathological condition. Many patients can live without seizures at all, as long as they take their epilepsy medication promptly and undergo regular testing.
This disease has been known for a long time. Epilepsy is perhaps one of the oldest forms of brain diseases, which was recognized and tried to be treated with traditional methods hundreds of years ago. For a long time, people suffering from this pathology preferred to hide their diagnosis. This often happens today.
What it is
People have been familiar with epilepsy for a long time: even the ancient Greek healers associated epileptic seizures with the world of the gods and believed that this illness was sent to them because of the unworthy way of their existence. In 400 BC, the outstanding ancient Greek physician and philosopher Hippocrates described this phenomenon. He believed that the cause of epileptic seizures was natural conditions that could provoke liquefaction of the brain.
In the Middle Ages, this disease was feared, believing that it was transmitted from a patient during an epileptic seizure. Meanwhile, they were in awe of her, since many saints and prophets suffered from such an illness.
Modern medicine has proven that epilepsy is a chronic brain disease, characterized by regularly recurring seizures. This is a very common disease, affecting about 50 million people worldwide, which is approximately 1% of the total population of the planet.
How does the disease appear?
Many patients wonder what caused the onset of the disease, because this is a dangerous condition and requires mandatory medical supervision. Medicine identifies three main groups of factors that can lead to the development of the disease:
- Idiopathic (genetic predisposition). Even after tens of generations, the disease can be transmitted. In this case, there are no organic defects or damage in the brain, but there is a certain reaction of neurons. With this form of pathology, an epileptic attack can begin without a reason.
- Symptomatic. The disease can appear after injury, intoxication or tumor processes in the brain. This form of epilepsy occurs spontaneously, and a seizure can occur unpredictably.
- Cryptogenic. A little-studied factor, the exact cause of which has not yet been established. A seizure can occur due to any psycho-emotional stimulus.
The disease can appear at any age, however, according to statistics, epilepsy is more common in young children, adolescents and adults over 60 years of age. To date, medicine has identified about 40 different types of epilepsy. Therefore, the treating doctor must carry out an accurate diagnosis to establish the form of the disease and determine the nature of the seizures. The effectiveness of the results in certain cases depends entirely on the adequacy of the choice of antiepileptic drug and the prescription of the treatment regimen. If treatment is untimely or inadequate, the patient may die. Therefore, a full examination of the patient and an accurate diagnosis of the disease are necessary.
A spontaneous attack can occur due to hormonal changes in the body, alcohol intoxication, or the appearance of flickering and flashing images while driving a car.
Examinations and treatment
If epilepsy is suspected, the patient is thoroughly examined. First of all, the patient is examined by a neurologist and studies the history of the disease, including family history. The patient is prescribed the following tests:
- blood;
- fundus;
- X-ray of the skull;
- Dopplerographic study of cerebral arteries.
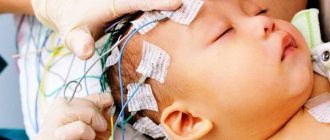
It is mandatory to visualize the structure, functions and biochemical characteristics of the brain using X-ray, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Hours of electroencephalography (EEG) are of great importance in diagnosing the disease.
Such laboratory studies are aimed at determining the true causes of the disease and excluding pathologies that can cause seizures, but are not associated with brain diseases.
The main effect on epilepsy is medications. The result of medical care in the treatment of pathology depends both on the correct selection of medications and on the patient’s compliance with all doctor’s recommendations. The principle of medical intervention is an individual approach to each patient, continuity and duration of treatment. Antiepileptic therapy will be effective if:
- early onset of exposure to the manifestation of characteristic symptoms with antiepileptic drugs;
- desire for monotherapy;
- the correct choice of medication for epilepsy, depending on the type of attacks of a particular patient;
- if necessary, introduction of a rational combination of polytherapy (if there is no effect from the use of one drug);
- prescribing appropriate medications in dosages that provide complete therapy;
- taking into account the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of prescribed drugs;
- monitoring the presence of antiepileptic drugs in the patient’s body.
Epilepsy medications cannot be stopped at once. They should be taken until complete relief from pathological manifestations is obtained. Only in cases of individual intolerance to the components of the drug, allergies, or in the event of side effects, gradual withdrawal of the drug is necessary. Doses of drugs for the treatment of epilepsy are gradually reduced. If the doctor decides that the therapy does not bring the desired result, then new medications are also gradually introduced.
It has been proven that almost all patients newly diagnosed with epilepsy can completely control the occurrence of seizures with the help of antiepileptic drugs. After 2-5 years of full treatment, most patients can stop treatment without the risk of relapse.
Removal of status epilepticus
If the patient has epistatus, it is removed with Diazepam and Seduxen. Sibazon is indicated for slow intravenous administration. After 15 minutes it can be administered again. If there is no effect, then the drug is replaced with Phenytoin, Hexenal or sodium Thiopental. To avoid depression of respiratory function, a one-minute break will be required after administering 10 ml of the drug.
When intravenous administration of drugs does not help relieve status epilepticus, inhalation anesthesia is used. To do this, nitrous oxide and oxygen are used in a 2:1 ratio. However, a contraindication to this method of treatment is the patient’s comatose state, impaired respiratory function and collapse.
Drug groups
Achieving optimal results in the treatment of epilepsy is largely determined by the correct calculation of the dose and duration of treatment. Depending on the symptomatic manifestations, the names of recommended drugs may belong to different groups of drugs:
- Anticonvulsants. Drugs belonging to this group of drugs help relax muscle tissue. They are often recommended for the treatment of various forms of epilepsy. Such drugs can be prescribed to both adults and children in the presence of tonic-clonic and myoclonic seizures.
- Tranquilizers. The purpose of drugs in this group is to relieve or suppress nervous excitability. They help in the fight against the manifestations of minor seizures. However, such drugs are used with caution, since at the beginning of use they can aggravate the severity of the disease.
- Sedatives. Not all epileptic seizures end well. Often, immediately before or after a seizure, the patient falls into severe depressive states, becomes irritable or aggressive. Sedatives in combination with a visit to a psychotherapist can calm and relieve such symptoms.
- Injections. Used for twilight states and affective disorders. Injections of nootropic drugs (Actovegin, Cerebrolysin, etc.) have proven themselves well as a means to alleviate and localize some symptoms of neurological disorders.
Medicines for epilepsy: the best anticonvulsants – Izvilina
There are different pills for epilepsy. This is a chronic brain disorder, the main symptom of which is considered to be sudden seizures, expressed by convulsions and loss of consciousness. This is one of the most common neurological disorders.
Causes of epilepsy
Epilepsy is divided into 2 main types: idiopathic and symptomatic.
The idiopathic form is most often generalized. Symptomatic is characterized by partial manifestation. This is due to various factors that provoke the appearance of pathology. In the central nervous system, signals between neurons are transmitted under the influence of electrical impulses generated on the surface of cells.
Unnecessary excess vibrations often appear. If the nervous system works stably, such impulses are neutralized by natural anti-epileptic structures.
The idiopathic form of the disorder occurs when there are genetic disorders of such structures. In such a situation, the nervous system does not cope well with the excessive electrical saturation of neurons, convulsive readiness arises, due to which an attack occurs.
In the partial form of the disease, a focus is formed with epileptic seizures, nerve cells in one hemisphere. They produce electrical impulses.
In this case, a protective reaction of antiepileptic structures around such foci is carried out.
Up to a certain point, convulsions do not appear, but epileptic discharges can break through the natural defenses and a convulsive attack begins. It will take a little time until the next attack.
Such foci with epileptic structures are often created against the background of certain pathologies. Let's list the main ones: defects in the development of brain structures, neoplasms, stroke, constant alcohol consumption, infectious processes in the central nervous system, skull injuries, drug addiction, medication use, hereditary predisposition, antiphospholipid syndrome, multiple sclerosis.
Situations arise when a genetic disorder does not manifest itself as idiopathic epilepsy, so the patient exists without the disease. If any of the above disorders appear, symptomatic epilepsy begins. In young patients, epilepsy appears after a head injury, alcohol intoxication, in old people - against the background of neoplasms or post-stroke conditions.
Therapy
Taking medications helps prevent and relieve pain from new attacks. When it is not possible to prevent seizures, the frequency of dosage is reduced. When another attack develops, breathing problems may occur. In such a situation, medications help reduce the duration of convulsions and prevent the resumption of seizures.
When a patient poses a danger to himself or the environment, involuntary inpatient treatment is used . Thanks to therapy, it is possible to get rid of the condition that leads to attacks. For successful treatment you need to follow simple instructions. The norms of medications for epilepsy in children and adults differ depending on body weight.
The minimum norm is prescribed from the very beginning of the course, the sizes are gradually increased to the desired effect. You should not stop taking medications right away. The dosage should be reduced gradually, reducing the dose to transfer to another drug. All medications for the treatment of epilepsy can only be prescribed by a therapist.
Anticonvulsants
Anticonvulsants or anticonvulsants have a pharmacological effect, reducing convulsions, the frequency and duration of seizures. The work of inhibitory neurons is stimulated, excitatory nerve fibers inhibit signals.
The list of main antispasmodic drugs includes the use of barbiturates. Phenobarbital has a non-selective effect on the central nervous system. Derivatives of this drug also stimulate the activity of inhibitory neurons.
How are anticonvulsants used?
Polytherapy is prescribed in rare cases due to the risks of several side effects. Toxic effects can affect health in different ways, so before procedures you need to be regularly examined by a specialist.
Correctly selected treatment does not cause side effects and makes the quality of life noticeably better. The main condition for achieving a lasting therapeutic effect is long-term and regular use of drugs. In some situations, therapy should never be stopped.
The effectiveness of therapy should be judged several years after the start of use. If you want to replace the product, you will have to consult a specialist.
The peculiarities of the effects of medications on the body necessitate a gradual reduction in dosage when stopping use.
Anticonvulsants are allowed to be used by children; the dose and pattern of use are determined by a specialist.
It is not advisable to take pills during the first trimester of pregnancy. As an exception, we can consider a situation where the health condition worsens.
Neuroleptics
Neuroleptics include psychotropic drugs with extracts of various plants. For medical purposes, only ephedrine, opiate, and morphine are used. They affect the peripheral and central nervous systems by reducing or stimulating impulses in several areas of the brain. Habituation in adults inhibits their use.
Racetams
Racetams are modern nootropic substances that excite nerve cells . Doctors rely on these medications to treat partial generalized convulsions.
Sedatives
Sedatives are used for overexcited sick patients and during depression. This group of drugs is used in combination with antispasmodic drugs, improves sleep quality, calms, and eliminates anxiety. Injections are used to relieve twilight states and affective disorders.
Such medications are determined only by doctors due to possible addiction. Drugs from this category should be used according to indications. You should inform your doctor about the following changes in your condition: affective disorder, depression, panic.
Tranquilizers inhibit the activity of certain parts of the brain. This determines their effectiveness against epileptic seizures. They are endowed with some side effects and undesirable consequences appear, so they must be used carefully.
Sedatives help to achieve the following effect:
- Elimination of hyperexcitability of nerve cells.
- Stabilization of performance.
- The patient sleeps better.
- The symptoms of some neurological disorders are reduced.
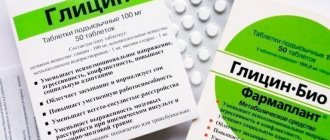
Sedatives have advantages over tranquilizers. They are not addictive. The most popular remedies are peony tincture or glycine.
The active components of the drugs are easily tolerated by the body. The drugs are safe and can be prescribed even to children .
If you make a list of the most popular sedatives, the medicine will take first place in the ranking.
Medicines for minor seizures
Suxilep is used for mild convulsions during meals 3 times a day. First, drink ¼ tablet or 20 drops, gradually increase the dosage. The doctor determines the amount of medications used individually. It should not be used by women during pregnancy or with complex disorders of the kidneys, liver, blood vessels, or blood.
Trimethine is often used for seizures and should be taken with meals 3 times a day. The medicine has side effects: vomiting, dizziness, decreased appetite, drowsiness.
Do not use during pregnancy or complex disorders of the kidneys, liver, blood.
Glycine is an excellent safe remedy, has a calming effect, stimulates brain function, and is prescribed for children under 3 years of age.
Efficacy of therapy
The results of treatment depend on the patient himself. Medicines selected by doctors should be used for a long time without delays, failures or violations of the regime. Anticonvulsants can be taken every day.
Only the doctor chooses the drugs. When the patient is not satisfied with the remedy, you need to consult and choose a suitable replacement. Regardless of the fact that expensive drugs cause fewer side effects, not everyone can buy them.
If the patient is prescribed a drug that is too expensive, you need to consult a specialist. It is not difficult to select a suitable medicine from analogues.
Hexamine
Antiepileptic drugs containing primidone. This chemical modification of deoxybarbiturate has a characteristic anticonvulsant effect, does not have a depressant effect on the central nervous system, and is considered the basis for the first stages of therapy. Eliminates the excitability of nerve cells in the epileptic focus.
Doctors prescribe it for various forms of epilepsy, and it has little effect on myoclonic seizures. Not used for hysteroid epilepsy. Analogs: Misodin, Primaclon, Milepsin.
The amount of medications taken for adults is determined by a specialist; tablets can be taken after meals. If the drug is well tolerated, the dosage is gradually increased to 250 mg per day. Adults and 1 g for children should not consume more than 1.5 g per day .
Side effects include slight drowsiness and lethargy after the first doses. Such symptoms disappear on their own after a few days with regular use. If side effects occur, you should contact a specialist, who will most likely cancel such therapy.
Fenacon
The medicine is presented as a white powder; its pharmacological properties resemble chloracone. A good therapeutic effect is expressed in cases of severe convulsions, mental disorders, and paroxysms.
The difference between the drug is the possibility of its use for non-convulsive seizures. The medicine blocks excessive electrical activity in certain areas of the brain. Deterioration in neuronal excitability causes stabilization of membrane potentials, and convulsive readiness decreases. Analogues: Alepsin, Phenytoin, Dipantin.
If the patient has a complex disorder, phenacone is combined with drugs from other groups. Changes made to therapy are made gradually. The daily dosage for adults starts with 1 g after meals, a maximum of 5 g per day can be consumed.
Fenacon should be taken in the morning and at night to avoid side effects such as sleep disturbances, dizziness, and gastrointestinal disorders.
Sodium valproate
These are drugs for epilepsy that inhibit enzymes in the central nervous system responsible for the appearance of agitation. Sodium valproate is endowed with tranquilizing properties and eliminates the excitability of certain areas of the brain .
This medicine is suitable for monotherapy of various forms of the disease, and is effective in generalized forms. There is a list of analogues: Delakin, Konvulex, Enkorat. The tablets are quickly absorbed and have increased bioavailability. This determines a certain effect of therapy.
Toxic effects on the body limit the use of valproate in patients with hepatocellular diseases and alcohol abusers. In addition to liver damage, the following side effects are identified: constant weight gain, thrombocytopenia, dyspepsia, dizziness, trembling arms and legs, hair loss.
We need constant blood donation for analysis that reflects the functionality of the kidneys. If deviations occur, therapy with this drug should be discontinued.
Source: https://fiz-disp.ru/prochee/lekarstva-ot-epilepsii-luchshie-protivosudorozhnye-preparaty.html
Effect of medications
It is known that if you regularly and promptly take anticonvulsant drugs for epilepsy, you can completely control the occurrence of epileptic seizures. Modern medications allow:
- block the excitability system of neurons of the epileptic focus;
- stimulate the activity of the inhibitory complex of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors;
- influence ion channels and stabilize neuronal membranes.
Prescribed tablets for epilepsy may have either one of these mechanisms of action or a complex of them. Modern antiepileptic drugs are conventionally divided into drugs of the 1st line (basic category) and 2nd line (drugs of the latest generations). Depending on the symptoms, the doctor recommends taking certain medications.
Anticonvulsants
Their main task is to block seizures and relieve tension in the affected area of the brain.
The mechanism of action of such drugs for epilepsy in humans is as follows:
- GABA receptors are stimulated, which sharply reduce the activity of neurons.
- The amount of glutamate decreases; it is a neurotransmitter that has a stimulating effect on the nervous system.
- The source of excitation is activated in the brain due to an incorrect ratio of ions in the cell membrane; these drugs normalize this process by blocking ion channels.
As a rule, the doctor selects one drug, carefully examining possible side effects.
These funds are divided into 2 groups. Class 1 includes medications that have been used for a long time: Carbamazepine, Benzobarbital, etc. The second includes those containing Phenobarbital and other potent drugs.
Basic category of antiepileptic drugs
In our country, basic therapy drugs are used as the main treatment for signs of epilepsy. The list of these drugs includes drugs that have been tested over many years of use and have good results in treatment. These include:
- Phenobarbital (Luminal);
- Primidone (Hexamidine);
- Benzobarbital (Benzene);
- Lamotrigine;
- Phenytoin (Difenin, Epanutin);
- Carbamazepine (Tegretol, Finlepsin);
- Valproic acid and its salts (Konvulex, Depakine);
- Ethosuximide (Petnidan, Suxilep, Zarontin);
- Levetiracetam (Keppra, Levetinol, etc.).
This is not the entire list of medications that are recommended for epileptics to take. The choice of a particular medication depends on the form of the disease, the nature of the attacks, the age and gender of the patient.
2nd line drugs
Drugs belonging to the second category of antiepileptic drugs do not have the same spectrum of action or have a larger list of contraindications than the basic ones. Luminal, Diacarb, Lamictal, Sabril, Frisium or Seduxen have a good therapeutic effect and are also often recommended as effective pills for epilepsy, but for a short time.
The list of drugs for the treatment of epilepsy is very long. Epilepsy must be treated by a doctor. Self-selection of medications and inadequate self-medication can lead to death.
Constant companions of epilepsy are migraine and depression. It has been proven that in patients suffering from migraines, manifestations of epilepsy occur much more often. It was found that depressive states in people with controlled seizures occur 20% less often than in people with uncontrolled seizures.
Treatment of epilepsy with folk remedies
- Stone oil for epilepsy. Stone oil is recommended to be taken for epilepsy, as it contains up to 70 elements beneficial to humans. It has antispasmodic and immunomodulatory properties. There is a “Siberian” recipe for a solution based on stone oil, used for epilepsy. To prepare the medicine, you need to dilute 3 grams of stone oil in 2 liters of water and take a glass orally three times a day. This must be done before meals. The course of treatment is 1 month. It is best to conduct such a course once a year;
- Treatment of epilepsy with herbal powder. Take in equal parts: peony, duckweed, licorice. In order to obtain the powder, you can use a coffee grinder or, for example, a small mortar. One dose will be half a teaspoon. You should also add a diphenine tablet. Take this remedy for epilepsy 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 14 days, after which you need to take a break for a week and repeat the course. In total, you need to complete 3 courses, significant improvement should occur by the end of the first course;
- Maryin root for the treatment of epilepsy. In folk medicine, marin root is used for epilepsy, neurasthenia, paralysis and other neurological diseases. Alcohol tincture of petals (3 tablespoons per half liter of vodka, infuse for 20-30 days) take a teaspoon 2-3 times a day;
- The smell of myrrh for epilepsy. You just need to make sure that the smell of myrrh is constantly present in the room of a person who suffers from epilepsy for a month and a half. You can ask for this fragrant resin in church. Take a couple of pieces of myrrh, set it on fire in a bowl and before the patient goes to bed, spread its smell throughout the room. This method has been known for a very long time; this is how priests treated epilepsy in ancient times. The smell of myrrh will help not only with epilepsy, but also with chronic fatigue, insomnia and neuroses.
Read more: List of all medicinal herbs used for epilepsy
Polytherapy: combined treatment regimen
When treating this pathology, the doctor strives to achieve monotherapy. This allows you to select the appropriate drug, optimal dosage and appropriate treatment regimen, as well as achieve high clinical effectiveness. In addition, monotherapy minimizes the side effects of treatment.
However, in some situations it is more advisable to choose a combined drug regimen. This is what they do:
- In the form of the pathological process, which combines several types of attacks and there is no possibility of complete monotherapy;
- For conditions accompanied by the same type of epileptic seizures, but not treatable with any medication.
In these cases, medications with different mechanisms of action are used in treatment regimens. However, the chosen treatment tactics must be rational and combine drugs that do not interfere with each other. For example, a prohibited combination is the simultaneous use of phenobarbital with primidone and benzobarbital or phenytoin with lamotrigine.
When using a combined treatment technique, a slight decrease in the therapeutic effect is possible. Often, patients experience signs of intoxication when using one of the drugs that was previously well tolerated. Therefore, at the initial stages of polytherapy, monitoring the level of drugs used in the blood plasma is necessary.
Interaction with antiepileptic drugs
There are many drugs whose combined use with anticonvulsants is contraindicated.
Some antiepileptics (Carbamazepine, Diphenin, Benzonal) cannot be taken together with any antidepressants and antipsychotics. This leads to depression of the nervous system and a decrease in the effectiveness of anticonvulsants.
It is important to know that drugs against seizures cannot be taken together with Levomycetin, Butadion, Suxilep, Teturam, or anesthesia.
A particularly severe reaction is caused by the combination with the anti-tuberculosis drug Isoniazid. If co-administration cannot be avoided, the dosage of anticonvulsants is significantly reduced.
Duration of treatment
The cessation or reduction of epileptic seizures, reducing their duration, alleviating and improving the psycho-emotional state of the patient is already considered a positive trend in treatment. The use of the latest pharmacotherapy techniques makes it possible to achieve complete relief or significant minimization of seizures.
The duration of drug therapy is determined by the type of attacks and form of the disease, age and individual characteristics of the patient. Practical recovery can occur with idiopathic forms of epilepsy. A small percentage of relapses occur in idiopathic forms with absence seizures that occur in childhood or adolescence. Cancellation of treatment for low-recurrence epilepsy is possible after two years of remission. In other cases, the question of stopping therapy can be raised only after five years of remission. In this case, the EEG should show a complete absence of pathological activity.
Termination of therapeutic treatment is carried out gradually, with a reduction in dosage to 1/8 daily over 6-12 months. Antiepileptic therapy should not be discontinued in patients with severe symptoms.
Alternative Treatments
Among the variety of alternative treatment methods, homeopathic treatments occupy a special place. Although epilepsy cannot be completely cured, this treatment method has its advantages. For example, the use of homeopathic recipes brings a tangible therapeutic effect, affecting the entire body. Homeopathic procedures are non-addictive and easy to use. In addition, they have a low cost.
It is worth taking into account that such therapy is safe and gentle on the body. The obvious advantages of such methods include the fact that this is the only method that does not have a toxic effect on tissues and organs.