Panic attack syndrome is a fairly common modern psychoneurological disease, which is the result of subconscious fears, as well as various phobias, manifesting itself in the form of unexpected, often completely groundless, uncontrollable panic attacks that seriously complicate the patient’s life, accompanied by some somatic symptoms with physical consequences.
To understand the principle of treating panic attacks, you first need to understand the symptoms and causes.
Causes and symptoms
During attacks, a person feels simple anxiety or extreme fear, which can even completely subjugate the victim. Panic most often begins suddenly, but sometimes patients note some anxiety or excitement before it begins. Sometimes the patient manages to cope with the surging feelings, however, often during acute attacks, it is very difficult for him to control himself, which is fraught with accidents if the person is driving at the time or is engaged in dangerous work that requires attention and concentration. The duration of the condition varies depending on the severity of the syndrome, and can range from a minute to ten. If the duration lasts more than ten minutes, the patient requires immediate examination and treatment, as this becomes dangerous to his health, and sometimes life.
The attacks of panic attacks themselves are relatively safe, however, they can cause serious somatic symptoms, for example, there is the concept of a muscle panic attack, when attacks are accompanied by muscle hypertonicity. Numbness or failure of the limbs, epileptic seizures, nervous tics of various locations, symptoms of urticaria, severe headaches or neuralgic pain may also be present. If a person suffers from this disease for a long time, then he may develop more dangerous psychosomatic symptoms, fraught with real health problems: cardioneurosis and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Cardioneurosis is a neurosis of the heart caused by stressful reactions or experiences, which is characterized by disruption, depletion of the heart muscle under the influence of uncoordinated signals from the autonomic nervous system (responsible for the functioning of internal organs), knocked down by a large number of stress hormones.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a polysymptomatic syndrome, accompanied by more serious than with cardioneurosis, all kinds of deviations in the functioning of the entire cardiovascular system, even accompanied by fainting and dizziness.
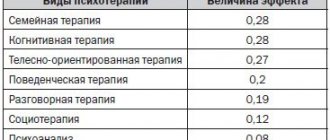
Cognitive behavioral therapy
This therapy combines 2 approaches: cognitive and behavioral therapy.
Cognitive psychotherapy is aimed at searching for “thinking errors”: identifying automatic thoughts and attitudes, replacing them with more rational ones. The client also learns to be aware of the influence of thoughts on emotions and behavior.
The behavioral approach to psychotherapy is aimed at eliminating unwanted behaviors and developing new useful skills.
Those. the main goal is not to identify the causes of the problem, but to change behavior. For panic attacks, cognitive behavioral therapy is good because the client learns not to avoid the places and events in which the attack occurred.
Etiology of panic attacks
At this point in time, the causes of panic attack syndrome are not known for certain. In medicine, there are four equal versions of the origin: hormonal-reflex, hereditary, psychological and cognitive.
According to the first, the syndrome begins with hormonal imbalances. If during severe stressful situations and feelings of fear the body reacts in a standard way: certain substances are released into the blood, breathing and pulse quicken, then the combination of these manifestations can play on the principle of a conditioned reflex and cause a panic attack.
According to the theory of genetic inheritance, a tendency to all kinds of phobias and their exacerbations can be transmitted along a family line, however, it is very difficult to verify it, since no special gene has been identified, and the prevalence of the syndrome is too wide to talk about specific patterns.
The psychological background of the illness can be all sorts of intrapersonal conflicts, pent-up emotions, subconscious experiences, as well as accumulated discontent that breaks out in this form.
Cognitive reasons are a kind of mentality or nervous system of the patient, forcing him to react too violently subconsciously not only to external factors, but even to minor deviations in the functioning of internal organs. For example, a person may not even notice an increased heart rate, but his brain will perceive this as a threat to the vital functions of the body and send a signal to consciousness in the form of strong fear.
It has also been noted that frequent attacks are typical for people from a certain risk group:
- Cores,
- Patients with neurological disorders, including those due to trauma, endocrine diseases,
- Those who are prone to bad habits, especially those associated with taking alcohol and psychotropic substances,
- Patients with psychological illnesses,
- Workers in hazardous industries, as well as people often exposed to stress,
- Chronically sleep deprived, leading a sedentary lifestyle,
- Lonely or socially disadvantaged, without a strong stable financial foundation,
- People in certain physiological periods: pregnancy, childbirth, puberty, first sexual experience, the onset of the menstrual cycle, etc.
After conducting a statistical study, it was revealed that people begin to experience panic attack syndrome from the moment of final consciousness at about the age of three, and most often women are exposed to it, since they have a more developed instinct of self-preservation, a more sensitive nervous system, they are more often in certain physiological conditions that provoke attacks. However, the proportion of adult, young, strong, healthy men among patients is also not small.
An interesting feature of the syndrome is its ability to worsen itself, since attacks of the disease, most often caused by stress, provoke a new strong release of stress hormones and already cause fear about the next repetition of the attack with its possible consequences, say, at work. New fears add to the causes of phobias and intensify the syndrome.
Psychoanalysis
The basis of the method is that our subconscious has a huge influence on us.
The client speaks out his thoughts, fantasies, dreams, including free associations. The therapist helps to find the unconscious conflicts that are causing the symptoms.
This method may not be entirely suitable for treating panic attacks. Because it takes a long time. On average, at least 2 years. Other methods will cope with the task much faster.
Possible consequences of chronic panic attack syndrome
As noted above, chronic syndrome can cause psychosomatic diseases of the cardiovascular system, which can develop into truly life-threatening diseases, including the following consequences: cardiac arrest, stroke, heart attack, endocrine overload, blood pressure disorders and others.
The actively involved nervous system begins to be depressed, lose neurons, provoke nervous tics and disruptions in the functioning of internal organs.
In addition to the physiological consequences, psychological consequences can also be just as dangerous, consisting in the appearance of phobias, personality changes, up to the development of schizophrenia and other ailments.
The patient also feels social discomfort, begins to fear social attacks, and avoids communicating with other people and meeting new people.
In addition to the above, there is a risk of potential accidents due to sudden attacks during dangerous or attention-demanding activities.
Body-oriented psychotherapy
Muscular armor
The essence of the method implies a connection between physical stress and psychological problems.
Muscle clamps (muscle armor) hide certain emotions. And if the clamp is relaxed, then the emotion will be released.
And, conversely, if emotional tension is removed (released emotion), then physical tension will disappear.
This therapy combines massage, exercise and analytical work.
During panic attacks, the client learns to understand the cause of unpleasant sensations in the body. Trains in various relaxation techniques (Jacobson relaxation, breathing exercises).
How to cure panic attacks
Many people who experience systematic panic attacks are embarrassed by their illness and do not know whether they are being treated or not. In addition, in Russian social culture, the presence of any psychological or neurological diseases is considered something shameful, unlike developed countries, where health problems are not a reason for social discrimination. There, they prefer not to hush up problems, but to eliminate them, restoring personal comfort for both the patient and his environment.
To cure panic attacks, first of all, even before treatment begins, the patient and his loved ones need to learn to calculate the approach of the next panic attack, and also stop it. This vital skill will allow you to minimize or completely eliminate the social consequences of the disease, the likelihood of accidents, and at the same time slow down the psychological changes in personality provoked by the syndrome.
Patients with a similar problem often note increasing agitation, mild anxiety, nervousness, or worry about a real issue before an exacerbation.
In order to independently stop the onset of symptoms, the patient must have a sober mind with a certain willpower capable of suppressing panic and maintaining a normal mind. Most often, people who succeed in this quickly and soberly assess the current life situation, ignoring dangerous or unpleasant moments, and concentrating on the pleasant aspects or, in general, calming down by force, switching to something good. However, self-help requires developed self-control skills, which not every patient suffering from panic attacks possesses.
Those who are unable to independently cope with the onset of attacks can be effectively helped by loved ones or simply people nearby.
First of all, the patient needs to provide urgent emotional support and create a feeling of security using simple psychological techniques:
- Take your hand
- Hug tight
- Cover or take into a closed room isolated from other strangers,
- Warm up
- Say words such as: don’t be afraid, I’m with you; Everything is fine; you can handle it, I will help; are you strong or are you good,
- Distract with something very sharp, unexpected, very important or pleasant.
In no case should you talk to people susceptible to the disease based on shame or what people will say, since they already experience increased anxiety, including about this, which does not need to be aggravated instead of help. Also, only orders that irritate even a healthy person to calm down and statements in the style of “you’re not a man” or “if you don’t stop, I’ll leave” or “fire you” won’t help. In this case, attempts to reach logical thinking also do not help much, because during attacks a person is not only illogical, but may even be inadequate. The algorithm of actions should be somewhat reminiscent of the principle of calming a small frightened child by a large, strong adult or mother.
It is also an effective way to combat using the basic animal instincts inherent in nature that subconsciously control human actions: self-preservation, nutrition and reproduction. If self-preservation failed in this case, then the other two pillars of the life activity of all biological objects have not gone away. It is known for certain that during the procedure of satisfying the other two needs, the human brain completely switches all the body’s resources, which can be used very effectively.
Sex and food are very powerful antidepressants, with the former being stronger and the latter being more accessible, which causes some of the societal problems associated with obesity. High-quality sex will help to very effectively stop an attack and delay its recurrence for a long time, however, it is not always available and appropriate. The process of absorbing food, especially your favorite one, switches the nervous system and internal resources to absorption and digestion, distracting from other stimuli, and creates a feeling of security of vital activity, which is necessary in this case.
Proper management and recovery from attacks will help to avoid many unpleasant consequences, however, it will not help to completely get rid of the disease with its side effects.
For any serious problem, including those not related to such a serious thing as health, a person usually turns to a specialist in this field, which one should not hesitate to do in this case. Few people know which doctor deals with the problem of panic attacks, treatment and elimination of consequences.
Who to contact
First of all, such specialists are a psychotherapist and a psychiatrist, and secondly, a neurologist and other highly qualified medical specialists.
The task of the psychotherapist is to find and bring to light the subconscious cause of the syndrome, to coordinate the patient’s attitude to the problem. Typically, psychological therapy is accompanied by the use of sedatives and drugs that suppress the production of stress hormones of varying degrees of strength. They are necessary to normalize the nervous system and increase the influence of consciousness on the treatment process. Drug therapy is selected purely individually and exclusively by a doctor, since improper use can radically aggravate the situation.
A psychiatrist examines a person and gets involved if panic attacks occur against the background of some detected mental disorder. Many people still retain the memory of the times of tsarist, Soviet medicine and psychiatry of the nineties, and therefore fear this specialist like fire. However, modern psychiatry is as close as possible to the European standard and is far from the terrible images of madhouses, firmly imprinted in people’s minds, and also deals with completely different things.
The modern standard of living has given rise to a completely different type of mental illness, caused by banal chronic overwork, overexertion and stress, which are not shameful or signs of a low level of rational activity, so this specialist should not be afraid or embarrassed. In the Western world, psychiatrists and psychotherapists, especially children’s therapists, rival even therapists in the popularity of their visits.
A neurologist is a specialist who is already struggling with the consequences of panic attack syndrome, working on how to cure nervous system disorders caused by psychosomatics. It is the neurologist who deals with such side effects as VSD, cardioneurosis, neuralgia and muscle panic attacks. Treatment occurs according to standard methods using medication and physiotherapy.
Other specialized specialists treat the consequences of the disease that affect other organs, for example, a heart attack.
For panic attack syndrome, treatment should be comprehensive, containing methods to combat attacks, eradicate the psychological cause and completely physiological consequences. How to treat and what exactly should be determined directly by specialists, and the patient should strictly follow the instructions.
However, traditional medicine methods, coordinated with a doctor, always come to the aid of official methods and are no less effective than officially registered ones. In this case, all kinds of soothing, relaxing, nourishing, restoring and strengthening recipes and procedures, both physically and mentally, are appropriate, of which there are a great many in the experience of our ancestors, the main thing is to find one that suits your taste and budget.