What is this pathology?
Let's start with the definition of dizziness. This condition is commonly called vertigo. The feeling of involuntary rotation or movement of one’s own body in space or objects relative to one’s body is considered dizziness. At the same time, a person loses stability, balance, and a feeling appears as if the earth is disappearing from under his feet.
Dizziness is classified into the following groups:
- Central. The cause is brain disease or injury.
- Peripheral. The cause is damage to the vestibular nerve or inner ear.
- Systemic. The cause is a malfunction in any of the systems: visual, vestibular, muscular.
- Not systemic. The causes are neurogenic.
Psychogenic dizziness should be classified in the fourth group. Appears as a result of mental and neurotic disorders. This is especially observed during periods of strong excitement or after it. A synonym in medicine is considered to be “Phobic postural dizziness,” that is, depending on the vertical position of the body.
Mechanism of development and manifestation
There are quite a few reasons why pathology develops. They can be divided into the following groups:
- background;
- unemotional;
- emotional.
Clinical features of psychogenic dizziness
The last item on the list should include all the reasons that deplete the anti-stress system of the brain. These same factors contribute to increased levels of anxiety and dizziness in depression. Among them are:
- Life situations that severely traumatize the psyche. These include the death of relatives or divorce.
- Chronic stress, for example, with frequent intense physical exertion. Increased workload, a long production process with the need for overtime, frequent night shifts, responsibility for people in hazardous production, or unsettled personal life leads to stress.
Consequences of stress
- Initially high emotionality. A person who perceives any information “personally” quickly experiences psycho-emotional exhaustion.
- Frequently finding yourself in any frustrating situations in which desires do not coincide with available capabilities. Such circumstances can be considered as a traumatic factor for the psyche.
In the thoughts of the patient himself, this reason does not have much significance, however, dissatisfaction of desires for a long time causes negative emotions. A person subconsciously considers himself a loser.
Non-emotional reasons:
- Recently treated benign positional vertigo or vestibular neuronitis.
- Severe pathologies suffered in the recent past. These could be oncological malignant tumors, surgical interventions involving a large “field”, heart attacks or strokes.
After a person is in such states, his “subconscious” remembers the episode during which dizziness occurred during neurosis (as an example). And then, under new stress, the brain “remembers” the acute situation it experienced.
It is also possible that at a subconscious level there is an expectation of some kind of ailment or the manifestation of negative symptoms. As soon as something like this happens, the “subconscious” immediately remembers the negative situation and psychogenic dizziness appears.
Background causes may be pathologies that occur in a compensated form:
- migraine attacks;
- damage to the blood vessels of the brain (dyscirculatory encephalopathy);
- residual encephalopathy (a brain disease manifested due to the death of cells in the central nervous system).
Encephalopathy
With these diseases, the level of anxiety increases significantly. Even the presence of such pathologies is chronic stress. With them, on a subconscious level, the idea is formed that dizziness will ever manifest itself anyway.
Certain reminders—stimuli—can provoke psychogenic dizziness. They can be, for example, empty spaces or overturned furniture, being in a situation that has already been encountered, and an unpleasant memory of it remains in the subconscious - a surrounding crowd of people, a stuffy room or being at a meeting. In this case, the disease has no objective signs of organic pathology.
Features of the pathology
Psychogenic dizziness has its own characteristics:
- It has no system.
- Random and abnormal deviations may occur within a few seconds.
- Feeling of instability for 2-3 seconds.
- It occurs unexpectedly, but provoking factors may be present.
- All complaints are related to dizziness that occurs while walking or standing.
- May be combined with other types of disorders. Psychogenic dizziness will be secondary.
- There are no clinical or paraclinical signs of organic pathology.
- Feelings of anxiety or anxiety-depressive conditions accompany dizziness, but these factors may be absent.
Classification of pathology
Patients can describe various sensations as dizziness, so in any case, the specialist needs to clarify their nature.
Based on the totality of their characteristics, they can be classified into one of the following groups:
- imbalance;
- lightheadedness and fainting;
- psychogenic dizziness;
- vestibular vertigo.
In addition to the clinical type of dizziness, concomitant symptoms, the presence of contributing factors and the clinical course are important for diagnosis. A single case of systemic vertigo is mainly caused by hemorrhage in the brainstem or cerebellum. The resumption of attacks can appear either without obvious reasons or can be provoked by certain contributing factors.
Causes of psychogenic dizziness
As a rule, a greater likelihood of psychogenic dizziness is observed in people predisposed to panic attacks. Women are most prone to this. Also, a feeling of fear, anxious fears can be attributed to the causes of such dizziness.
Let's highlight a few more reasons:
- Stressful situations.
- Overwork at work.
- Lack of sleep, insomnia.
- Excessive mental stress.
- Sudden change of position.
- Climate change.
- Hyperventilation syndrome.
- High blood pressure.
- Neuritis.
- Menopause in women.
- Motion sickness in transport, when riding on a swing.
- Altitude intolerance.
As a rule, all these situations are associated with worries or anxiety. There is also an obvious fear of losing control over the position of the body, falling and possibly getting injured.
Causes
A distinctive feature of psychogenic dizziness from other similar conditions is the origins and factors of development of this disorder. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that in its formation it does not depend on physiological reasons. For example, this type of dizziness does not occur against the background of neurological or somatic ailments. It becomes the result of the individual having internal stimuli, which can be:
- unresolved internal conflicts;
- psychological problems;
- tendency to excessive self-examination;
- total negativism of the individual towards the outside world, coupled with the indulgence of his ego.
This disorder often manifests itself in people who have a high level of anxiety and tend to react violently to any irritants. In addition to frequent worries for minor reasons, those suffering from this type of dizziness often feel stiffness and tension. Neuroses are their accompanying disorders. It seems to them a very difficult task to distract themselves from obsessive thoughts, and one polarity of their mood too often gives way to another: either they are oppressed by deep depression, or they are elevated to carefree euphoria.
Addiction to other disorders
Psychogenic dizziness is just a manifestation of one of the ailments. However, it almost never exists as an isolated, independent symptom. This feeling is adjacent to other characteristic signs of psychotic and neurotic conditions. Most patients have various phobias:
- Among the pathological fears that provoke dizziness, agoraphobia takes precedence - an irrational fear of open spaces. When a person is in open, deserted areas (fields and squares), he experiences episodes of dizziness. This is often characterized by a feeling of weightlessness of one’s body and a feeling of loss of one’s own “I”, while the surrounding environment and objects lose clarity and even realism.
- Panic fear of all kinds of vehicles is another disorder in which psychogenic dizziness is often observed. The main difference is that in this case, in those suffering from the disease, dizziness is combined with a feeling of suffocation and tightness in the chest.
- Episodes of dizziness sometimes indicate the presence of anthropophobia, in which the patient experiences a fear of crowds. When in crowded places, a person suffering from this disease may experience a sharp loss of strength, clouded consciousness and blurred vision.
- Fear of flying and irrational fear of heights in general is also one of the factors that can provoke dizziness.
Sometimes the causes of attacks of lightheadedness lie in various social phenomena. For some people, a school exam or divorce may be a trigger. In another category, attacks begin when interacting with certain people.
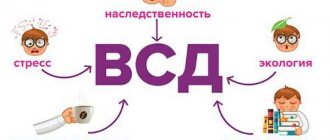
Dizziness, coupled with a feeling of impending fainting, sometimes occurs in people suffering from weakened vascular tone and patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD). In the case of VSD, the causes of dizziness can be not only psychogenic , but also physiological factors.
Asthenic disease
Asthenic status is one of the causes of dizziness. Asthenia itself is characterized by neuropsychic weakness, which is expressed in a decrease in tolerance to any physical and mental stress, as well as to stress. Fatigue in a person suffering from asthenia does not go away even after rest, against which various disorders develop.
Asthenia itself accompanies various disorders in the body. It is not surprising that one of its manifestations can be dizziness, the causes of which are not physiological. Lack of vitality and low mental performance aggravate and increase the frequency of manifestations of this symptom.
Especially often, an unhealthy condition occurs in asthenics during a sharp change in weather conditions. This is often caused by squeezing headaches and a feeling of staleness in the head.
Affective states
In many cases, the causes of lightheadedness are deeply emotional. Often, anticipation of loss of consciousness manifests itself during the depression of hypochondriacal syndrome, in which a person is convinced that he has a life-threatening illness. Even encouraging tests and assurances from doctors cannot convince him otherwise. The subject’s confidence in the futility of treatment and the hopelessness of his situation is imposed on him by other fears. Usually, anxious fears begin to provoke psychogenic dizziness from the very moment these unfounded fears appear.
Signs and symptoms of pathology
Dizziness of a psychogenic nature at the developmental stage has several signs:
- Performance decreases and fatigue increases.
- Mood worsens, irritability increases.
- Appetite either disappears or increases sharply.
- Sexual activity may decrease or increase sharply.
For those who have experienced psychogenic dizziness, patients describe the symptoms as follows:
- Tinnitus appears, but hearing is not lost.
- Fog in the head.
- There is a feeling of instability, but this does not affect the gait.
- Attention is completely focused on the noise and dizziness.
- There is increased anxiety.
- There is a feeling of lack of air.
- Cold sweat.
- Thinking is unclear, confused.
These symptoms are also typical for panic attacks. You can also add a few characteristic symptoms:
- Cardiopalmus.
- Possible trembling of limbs, chills.
- "Formication.
- Irrational fear of impending disaster.
- "Cotton" legs.
This condition can also be caused by memories of a traumatic situation.
Psychogenic dizziness is not caused by a disorder of the vestibular system, although the symptoms are very similar.
It is worth noting that manifestations of these disorders can be called psychogenic only if the patient recognizes the connection with the cause.
Symptoms
Psychogenic dizziness includes a wide and varied spectrum of symptoms and signs. The symptoms of the phenomenon are not tied to time, any human action, blood pressure or other manifestations. The disease does not have a specific time frame for the duration of symptoms.
Specific signs of psychogenic dizziness:
- sensations arise or intensify against the background of emotional excitement, increasing anxiety, tension or constriction;
- no systematicity was recorded;
- absence of noise in the head and ears.
Associated symptoms that may appear when the disease manifests itself:
- increased sweating;
- nystagmus - involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyes of high frequency;
- rapid breathing due to a feeling of lack of oxygen;
- panic attacks;
- sleep disorders - insomnia, nightmares, intermittent sleep, difficulty falling asleep;
- feeling of a “lump in the throat” - inability to swallow;
- increased heart rate;
- irritable bowel;
- "restless" bladder;
- general weakness;
- increased fatigue.
The onset of psychogenic dizziness is often preceded by a vasomotor disorder, which manifests itself in unpleasant sensations in the head - pulsation, hot flashes, heaviness, etc.
False symptoms of psychogenic dizziness
There are symptoms that patients mistakenly confuse with dizziness.
Here are some of them:
- Flickering of objects in the eyes.
- Double vision.
- The appearance of a “mesh” before the eyes.
- The appearance of nausea.
- Pre-fainting state.
- Feeling unsteady.
- Feeling of "emptiness" in the head.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you have a question about how to treat psychogenic dizziness, you need to contact a therapist, who will then refer you to specialized specialists:
- Otorhinolaryngologist.
- Neuropathologist.
- Cardiologist.
- To a psychiatrist.
To find out the reasons, specialists may prescribe the following types of examination:
- Computed tomography of the brain. Allows you to recognize abnormalities in the structure of the brain.
- Ultrasound of large arteries and vessels that supply blood to the brain.
- X-ray examination of the skull and cervical spine.
- General and biochemical blood test. Determination of blood glucose levels.
- Balance tests are required.
- Audiography.
- Definition of nystagmus.
At the initial stage of diagnosing psychogenic dizziness, the doctor must exclude all possible causes that are associated with loss of balance.
These include:
- Damage to the vestibular apparatus.
- Diseases in which one of the symptoms is loss of consciousness, fainting.
- Diseases of a neurological nature, which are accompanied by impaired walking and balance.
The above examinations will help find the true cause.
At the second stage, neurotic disorders that arise as a result of stress are diagnosed. As we found out earlier, the most common cause is panic attacks and anxiety-depressive disorder. Let's look at how to get rid of psychogenic dizziness below.
Diagnostic methods
In order to clearly and accurately identify this disorder in a patient, a diagnosis is carried out, consisting of two mandatory stages. It is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination, for which in some cases specialists such as a neurologist, cardiologist, hematologist and some others are involved.
First stage
First, a negative diagnosis is carried out, the task of which is to exclude any other causes of dizziness. Among them may be:
- diseases of somatic and neuralgic origin accompanied by lipothymia;
- disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular system at any level;
- neurological diseases accompanied by walking disorders.
Thus, at the first stage of the examination, the causes of his illness are identified. In many ways, this is based on the method of exclusion. The patient is asked in detail about what exactly he means by dizziness. If it is of a psychogenic nature, it is always non-systemic in nature.
In order to exclude any “organic” causes of non-systemic dizziness, balance tests, nystagmus studies, computed tomography, audiographic examination and a number of other medical measures are performed. General tests are also taken.
Second phase
The study of stress-related neurotic disorders is the second stage, called positive diagnosis. The most common causes of dizziness, the frequency of increased tension, stiffness and anxiety, as well as other indicators of mental abnormalities are established. The most common symptoms that lead to a pre-fainting state are also to be identified. Only after all these examinations is it determined how to deal with dizziness.
It often happens that when turning to a doctor, the patient reports only somatic, and not mental symptoms. For many, they worry more than the feeling of anxiety, stiffness and depression. Some patients confuse cause with effect, believing that their fears originate from bodily ailments. Because of this, for a specialist to draw up an overall picture, and sometimes the psychogenic nature of the disorder remains unidentified. The psychogenic nature of dizziness is dangerous because its disorders represent a vicious circle, which can be depicted as follows:
- The patient is depressed;
- Depression leads to dizziness;
- The psychogenic nature of dizziness leads to depression.
Such a seemingly hopeless situation should be identified by a specialist first. If the patient himself notices such a closed chain, then when going to the doctor with complaints of headaches, he should not ignore the symptoms of non-physiological manifestations.
Treatment methods for psychogenic dizziness
For a disease such as psychogenic dizziness, treatment includes non-drug and medicinal methods.
Non-drug treatment is a priority. It includes:
- Psychotherapy.
- Gymnastic exercises to improve the vestibular apparatus.
- Breathing exercises. Helps cope with increased vascular tone.
Treatment of psychogenic dizziness consists of changing the internal attitude towards traumatic situations so that dizziness and other disturbing symptoms do not occur. This is very difficult psychologically, although it costs nothing financially. The most difficult thing is to work on yourself, on your fears and beliefs. Treatment comes down to normalizing the psycho-emotional state.
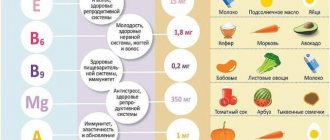
It is also necessary to reconsider the patient's diet. Vitamins of groups A and C are necessary. They are found in the following foods, fruits and vegetables:
- Lemon.
- Orange.
- Beef liver.
- Fatty dairy products.
- Fish fat.
- Carrot.
- Persimmon.
- Strawberry.
- Sprouted grain crops.
- Rose hip.
- Black currant.
It is necessary to follow the correct diet, which should contain all the necessary microelements and vitamins for the body. It is advisable to eat at the same time, smaller portions are better, but more often.
Treatment and prognosis
Depending on what the additional symptoms are, the treatment may be adjusted in a certain way. When treating such an illness, consultations with a psychotherapist and a neurologist, who will tell you how to get rid of the disease, are of particular importance.
Treatment of psychogenic dizziness at the present stage of medical development is carried out comprehensively. Both medications and non-drug methods are used. It is the latter that are the priority.
Drug therapy for psychogenic dizziness
At the initial stage of drug therapy, it is considered sufficient to prescribe mild sedatives. Adaptogens help relieve stress. Vitamin therapy is also prescribed. The complexes should predominantly contain vitamins C and A. They are a source of adaptogens that increase the body's resistance to harmful influences.
Nootropic (positively affecting higher brain functions) drugs (Piracetam, Glycine) also help to get rid of psychogenic dizziness. They help supply brain cells not only with oxygen, but also with glucose.
The basis of therapy is the normalization of the patient’s mental and emotional state, which makes it possible to successfully combat dizziness. For this purpose, vestibular and breathing exercises are used, as well as psychotherapy.
Vestibular gymnastics
Since dizziness most often occurs after we are nervous, the patient needs to know the rules to avoid such situations. It is of no small importance to explain to the patient that the “culprit” for the manifestation of signs of the disease is the subconscious of the person himself.
In general, the prognosis for treatment of the disease is favorable. Psychogenic dizziness does not pose a threat to the patient’s life. But you should understand that such a disease requires increased attention. Incomplete diagnosis and inadequate treatment lead to a decrease in the quality of life of the patient.
The process can become chronic. If you feel dizzy just once, then there is no reason to urgently visit a doctor. However, if the symptom constantly appears, this must be done. Psychological health is no less important than physiological health.
Drug treatment
Medicines used to treat psychogenic dizziness:
- Antidepressants: Fevarin, Paxil.
- Anxiolytics: Phenazepam, Clonazepam, Atarax.
- Neuroleptics: Tiapride, Sulpirida.
- Nootropic drugs.
The drug "Betaserc" has proven itself to be excellent in the treatment of a disease such as psychogenic dizziness. Reviews about this drug are only good. Patients note an improvement in their condition. The dizziness goes away and there is no tinnitus. But the drug is recommended to be taken in long courses for a lasting effect and as an additional therapy.
Folk remedies
As we know, the priority is therapy without the use of drugs, including such diseases as psychogenic dizziness. Treatment with folk remedies in such cases has always been popular. Let's name some of them.
- Aromatherapy. Juniper and orange oils are useful.
- Oregano infusion. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water into 2 tablespoons of herbs. Let it brew.
- Lavender infusion. 1 tablespoon per glass of boiling water.
- Ginger tea.
- Eat pomegranate more often.
It is recommended to drink infusions half an hour before meals and throughout the day. Folk remedies do not give quick results, so therapy must be long-term.
How to help
If an attack of dizziness occurs at home, you must:
- Lie down so that your head, neck and shoulders are on the pillow.
- Avoid turning your head.
- Release clothing pressure.
- It is necessary to ensure good air access.
- You can apply a cold towel moistened with a light vinegar solution to your forehead.
If you feel dizzy on the street:
- You need to calm down and not panic.
- Sit down and focus your gaze, but do not close your eyes.
- Do not move or turn your head.
- If at the same time there is severe pain in the chest, abdomen, or numbness in the arms and legs, or speech impairment, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance.
Prevention of psychogenic dizziness
In order to reduce the amount of dizziness, you must not only try to remain calm in all situations and learn to control yourself, but also follow some recommendations:
- Move more and do exercises, especially when working sedentarily.
- Observe the work and rest schedule.
- Don't overwork, get enough sleep.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Do not make sudden movements of the head and neck, and do not suddenly change the position of the body.
- Relax more in the fresh air.
- Limit the consumption of salt, strong tea and coffee.
- Learn relaxation techniques.
If you experience frequent attacks of dizziness, you should consult a doctor. If serious pathologies are detected in the early stages, therapy will be more effective. Much more often, dizziness is associated with overwork and improper work and rest schedule, but it is still better to play it safe and visit a specialist.
Manifestations of psychosomatics
Let's consider the relationship between the body and the psyche in one of the diseases - asthma. To put it in simple words, during an exacerbation, under the influence of allergens, an attack occurs and the person cannot breathe fully because he cannot exhale. What is the body trying to tell a person so harshly? The fact that a person does not want to live a full life, does not want to “breathe deeply”, does not want or believes that he does not have the right to breathe and live independently (especially in the case of constant use of an inhaler), that a person takes a lot, and gives with great difficulty (difficulty in exhaling).
Plus, the presence of the allergen itself, which triggers an asthma attack, indicates that a person cannot stand something, protests against some events or actions, but cannot or does not allow himself to express this protest due to upbringing, stereotypes, fear opinions of others. And it was the constant ignoring of all these psychological factors that became the cause of the disease, and these same factors are the reason for its transition to the chronic stage. And this is how you can analyze each disease.
Let's consider what pathologies can lead to attacks of psychogenic dizziness.
On the way to getting rid of psychogenic dizziness, you will definitely need to undergo diagnostic measures. The first step is to contact your general practitioner. He will prescribe the necessary research methods and, if necessary, refer the patient to another specialist. Most often, with psychogenic dizziness, you need to undergo:
- X-ray.
- Ultrasound of blood supply organs.
- MRI, CT of central nervous system structures.
- Laboratory research of biomaterials.
- Measurement of blood pressure at rest and in motion.