| Place | Name | Characteristics in the rating |
| Top 10 best vitamins for the nervous system |
| 1 | Life Extension ComfortMax | Better efficiency. Correct dosage |
| 2 | Now Foods Sunflower Lecithin | High efficiency. Allowed from the first days of life |
| 3 | Doctor's Best Magnesium | Easy to digest. Allowed for pregnant women |
| 4 | UNIPHARM Inc. Vitrum Superstress | High concentration of active substance |
| 5 | Vitamax Taurine | The best ratio of price and quality |
| 6 | Herb Pharm Brain & Memory | Based on natural herbs |
| 7 | Doppelhertz Active Antistress | Cumulative effect |
| 8 | Multitabs B-complex | Complex action |
| 9 | Pharmstandard Complivit Antistress | Best price. Availability |
| 10 | Vneshtorg Pharma Alphabet Energy | Rich composition. Uniquely selected elements |
Stressful situations, overexertion, vanity - all these daily and familiar things lead to dysfunction of the nervous system and symptoms such as chronic fatigue, unstable emotional background, memory loss, poor sleep and absent-mindedness.
In order to combat existing problems and prevent the emergence of new ones, you need to lead an active lifestyle, play sports, give up bad habits and eat a properly balanced diet. Vitamins have an additional effect, helping to reduce stress levels, normalize brain function, replenish the deficiency of essential substances and equalize the balance of microelements in the body.
The most useful are vitamins of group B (B1, B2, B3, B9, B12), E or tocopherol, C or ascorbic acid. You can drink them either separately or in a specially selected complex that combines the necessary substances in ideal proportions. Below is the TOP 10 best remedies for the nervous system, which is based on user ratings and reviews, as well as comments from experts.
There are contraindications. Consult your doctor.
The best vitamins for nerves for adults
Vitamins for the nervous system are produced in 2 forms:
- pills;
- injections.
Vitamin complexes
Regular intake of vitamin complexes to strengthen the central nervous system has long become a necessary condition for ensuring the ability to live and work fully. This applies to both men and women. In order not to get confused in a large number of drugs designed to strengthen the central nervous system, when choosing, you need to focus on the daily need for each nutrient.
For women
For the normal functioning of the central nervous system, a woman needs to consume per day:
- retinol - 1 mg;
- thiamine - 1.1 mg;
- riboflavin - 1.1 mg;
- nicotinic acid - 14 mg;
- pantothenic acid - 5 mg;
- pyridoxine - 1.3 mg;
- cyanocobalamin - 2.4 mg;
- biotin - 30 mcg;
- ascorbic acid - from 75 to 150 mg;
- tocopherol - 10 mg;
- calciferol - 2.5 mg.
For pregnant and lactating women, dosages are increased.
For men
For the normal functioning of the male body, higher doses of vitamins are required:
- retinol - 1 mg;
- thiamine - 1.5 mg;
- riboflavin - 1.8 mg;
- nicotinic acid - 25 mg;
- pantothenic acid - 7 mg;
- pyridoxine - 1.3 mg;
- cyanocobalamin - 2.4 mg;
- biotin - 30 mcg;
- ascorbic acid - from 100 to 150 mg;
- tocopherol - 18 mg;
- calciferol - 2.5 mg.
In tablets
The best vitamins for strengthening the nervous system in tablets include:
- Milgamma. The main active ingredients are thiamine and pyridoxine, the natural supply of which in the body is too small. Therefore, their additional intake should be carried out daily.
- Doppelhertz-Active-Magnesium + B Vitamins. This dietary supplement is recommended for unbalanced nutrition and excessive mental and mental stress, causing nervousness, irritability, fatigue and chronic fatigue. Includes:
- thiamine;
- pyridoxine;
- cyanocobalamin;
- folic acid;
- magnesium;
- ascorbic acid.
- Magne B6. A powerful anti-stress agent that combines pyridoxine and an increased amount of magnesium - substances that effectively support the functioning of central nervous system cells during periods of severe mental and mental fatigue.
- Multi-Tabs-In-Complex. A powerful remedy intended for the prevention of group B hypovitaminosis, treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome and assistance in overcoming deep stress. It includes:
- thiamine;
- riboflavin;
- pyridoxine;
- cyanocobalamin;
- folic acid;
- nicotinamide;
- pantothenic acid.
- Folic acid. A drug that improves mood. It is often prescribed during pregnancy and for nervous disorders that threaten to develop into depression.
- Vitrum-Superstress. A powerful therapeutic and prophylactic multivitamin complex designed to support the body during periods of increased physical and mental stress. It includes:
- thiamine;
- riboflavin;
- pantothenic acid;
- pyridoxine;
- folic acid;
- cyanocobalamin;
- tocopherol;
- ascorbic acid;
- biotin;
- nicotinamide;
- iron.
- Neurobion. A vitamin complex containing increased dosages of thiamine, pyridoxine and cyanocobalamin, which is prescribed for a deficiency of these substances or diseases of the central nervous system such as neuritis, neuralgia, etc.
- Glycine. A metabolic drug that reduces psycho-emotional stress, activates protective inhibition processes in the central nervous system, and increases mental performance. It is prescribed for:
- reducing psycho-emotional stress, aggressiveness, conflict;
- mood improvement;
- making it easier to fall asleep and normalizing sleep.
- Vitabalance-Multivit. A highly effective vitamin and mineral complex aimed at increasing the adaptive capabilities and energy potential of the body, improving the functioning of the central nervous system. The complex includes:
- retinol;
- thiamine;
- riboflavin;
- pyridoxine;
- nicotinamide;
- folic acid;
- cyanocobalamin;
- biotin;
- ascorbic acid;
- tocopherol;
- succinic acid;
- calcium;
- magnesium.
- Neuromultivitis. B-vitamin complex, which includes thiamine, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin. The drug is used for neuritis and neuralgia of various origins.
- Relaxozan and Motherwort Forte. 2 types of biologically active supplements from Russian, which have a mild sedative effect on the central nervous system. Relaxozan contains extracts of mint, lemon balm and valerian. Motherwort Forte contains motherwort extract, pyridoxine and magnesium.
Preparations for parenteral administration (injections)
Parenteral administration of a drug means that the substance enters the body bypassing the gastrointestinal tract, for example, by injection.
Injections of B vitamins are painful, but their use is justified. They act much faster and more effectively than similar drugs in tablets or capsules. Injections are used to prevent nervous diseases, as well as in the treatment of diseases caused by impaired nervous activity and accompanied by severe pain. In addition, they are used in critical situations as stress vitamins.
The most popular B-complex drugs are:
- Milgamma compositum;
- Vitagamma;
- Trigamma;
- Combilipen;
- Neurobion;
- Neurorubin.
The first 4 drugs are distinguished by the presence of lidocaine in the composition, which makes taking injections less painful. All of these products have the same composition of active ingredients, including:
- thiamine;
- pyridoxine;
- cyanocobalamin.
Anti-stress vitamins should not be taken without consulting a doctor, especially for medications in ampoules.
Like any other medicines, vitamins have contraindications for use. In addition, hypervitaminosis is just as dangerous as vitamin deficiency. By acting faster and more powerfully, vitamin injections may be more likely to cause unwanted side effects.
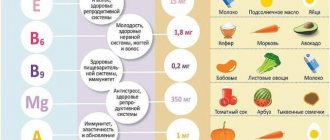
What foods contain B6?
| The product's name | Vitamin B6 content per 100g | Percent Daily Value |
| Pistachios | 1.7 mg | 85% |
| Sunflower seeds (seeds) | 1.34 mg | 67% |
| Wheat bran | 1.3 mg | 65% |
| Garlic | 1.23 mg | 62% |
| Beans (grain) | 0.9 mg | 45% |
| Soybean (grain) | 0.85 mg | 43% |
| Walnut | 0.8 mg | 40% |
| Atlantic salmon (salmon) | 0.8 mg | 40% |
| Mackerel | 0.8 mg | 40% |
| Sesame | 0.79 mg | 40% |
| Tuna | 0.77 mg | 39% |
| Hazelnut | 0.7 mg | 35% |
| Dried acorns | 0.69 mg | 35% |
| Pink salmon | 0.61 mg | 31% |
| Wheat (grain, durum) | 0.6 mg | 30% |
| Buckwheat flour | 0.58 mg | 29% |
| Wheat flour | 0.55 mg | 28% |
| Barley groats | 0.54 mg | 27% |
| Rice (grain) | 0.54 mg | 27% |
| Millet groats (polished) | 0.52 mg | 26% |
| Meat (chicken) | 0.52 mg | 26% |
| Sweet pepper (Bulgarian) | 0.52 mg | 26% |
| Meat (broiler chickens) | 0.51 mg | 26% |
| Chum salmon | 0.5 mg | 25% |
Vitamin b6 in which foods: complete list
Vitamins for the nervous system
Vitamins are biologically active substances that act as catalysts for most metabolic processes in the body. In conditions of vitamin deficiency, not a single organ or system can function normally.
Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system are felt much faster than failures in other systems, as they manifest themselves in increased irritability, worsening mood, decreased performance, the appearance of chronic fatigue, and stressful situations can completely deprive a person of the opportunity to live and work normally.
Various vitamins and minerals are important for maintaining a healthy nervous system. They are produced in the form of complex preparations. Vitamins for stress and vitamins for neurosis must be included in the list of therapeutic measures.
B vitamins
The most important nutrients for the cells of the central nervous system are B vitamins - they are involved in all processes associated with its normal activity, and during stress they help to recover faster:
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) prevents mental stress, relieves anxiety, and protects against nervous disorders. In addition, thiamine has antidepressant properties.
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) helps normalize sleep, increases energy reserves and overall tone of the body.
- Vitamin B3 (nicotinic acid) has every reason to be equated to a drug. It is involved in the production of proteins, fats and hormones. Nicotinic acid improves blood transportation to the brain, and this in turn leads to normalization of the functioning of all its parts and even alleviation of the condition of patients with schizophrenia.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) helps improve memory, increase mental activity, and is involved in the production of hemoglobin.
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid) is the most important substance that maintains the excitability of the central nervous system at an optimal level.
- Vitamin B11 (levocarnitine) restores and strengthens the central nervous system, activates the body's protective functions, improves the functioning of the brain, heart, muscles, and fills all organs and systems with energy.
- Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) is a powerful tool in the fight against depression, effectively calming the central nervous system and preventing the development of pathologies.
Vitamin A
A lack of Vitamin A (retinol) in the body leads to the following consequences:
- decreased vitality;
- sleep disturbance;
- chronic fatigue.
Timely intake of retinol into the body helps to effectively counteract the destructive activity of free radicals and provide reliable protection against damage to every cell of the central nervous system, as well as normalize sleep and brain function.
Vitamin E
A lack of Vitamin E (tocopherol) leads to increased fatigue, decreased ability to concentrate, nervousness and irritability.
Vitamin D
Symptoms of Vitamin D (calciferol) deficiency in adults are poor sleep and fatigue. For young children, a lack of calciferol is especially dangerous, as it can lead to slow growth, deformation of limbs, mental retardation and capricious behavior.
B12 (cyanocobalamin)
Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) has a pronounced lipotropic effect, preventing the development of obesity and fatty infiltration of the liver. If any vitamin enters the body insufficiently, then multiple neuropathies are formed. B12 is required for the formation of myelin, methionine, and regulates the formation of hematopoietic cells. If the amount of cyanocobalamin in the body is insufficient, irreversible changes in the central nervous system develop over a long period of time. And its normal functioning is necessary for humans. For many diseases, a more reasonable option would be to use not one specific drug, but a whole complex. Then all three vitamins act as synergists, and the combined use causes a more pronounced therapeutic effect. The use of this category of vitamin compounds is useful, since their participation in metabolic reactions in neurons can hardly be overestimated. Experts have discovered that when using fairly large dosages of this vitamin complex, therapeutic results appear that differ from the known effects.
Sources of vitamins for the nervous system
Natural sources of vitamins for the nervous system are products of plant origin, which, in addition to vitamins, contain a large number of other nutrients (biologically important elements) necessary for the health of the central nervous system.
Vegetable
The greatest amount of retinol is found in products:
- carrot,
- rose hip,
- green onions,
- tomatoes,
- zucchini,
- dried plum,
- dried apricots.
Thiamine is found in the following:
- buckwheat grain,
- nuts,
- beans,
- asparagus,
- wholemeal bread,
- potato.
Riboflavin is found in:
- white cabbage,
- spinach,
- broccoli.
Large amounts of niacin are found in nuts and green vegetables.
Rich in folic acid:
- mushrooms;
- cauliflower;
- carrot;
- parsley.
Soy contains a large amount of cyanocobalamin.
The list of foods rich in ascorbic acid is long. It includes:
- sea buckthorn;
- rose hip;
- black currant;
- cabbage (all types);
- bell pepper;
- orange;
- mandarin;
- lemon;
- grapefruit;
- kiwi;
- chanterelles;
- greens (onions, spinach, sorrel, celery, dill, etc.).
Rich sources of calciferol are:
- soy;
- soy milk;
- cereals;
- mushrooms.
They contain a lot of tocopherol:
- wheat germ;
- vegetable oils:
- linen;
- sunflower;
- cotton;
- olive;
- sea buckthorn;
- nuts:
- hazelnut;
- almond;
- peanut;
- walnut
Animals
According to recent studies, it has become known that animal products make a person more irritable and emotional. During periods of stress, it is recommended to eat only plant foods.
Anti-stress vitamins for children
Vitamin and mineral complexes for children can satisfy the needs of the nervous system 100%.
When choosing a drug for a child, you must follow some medical recommendations. The remedy should:
- appropriate for the child’s age;
- be hypoallergenic;
- contain not retinol, but beta-carotene;
- be designed for 2-3 doses per day.
Preparations for a child aged 1 to 3 years must contain:
- cyanocobalamin;
- folic acid;
- ascorbic acid;
- calciferol;
- iron;
- iodine;
- calcium;
- zinc.
Proven and effective children's drugs for strengthening the central nervous system include:
- domestic multivitamin complex Alphabet;
- Centrum (USA) - sweet tablets with raspberry flavor for children 2-4 years old;
- Vitrum Kids (USA) - chewable tablets for children aged 3 years and older;
- Vitrum Junior (USA) - chewable tablets for children from 7 to 14 years old;
- Multi-tabs (Denmark) is a powerful drug that has several options designed for different age categories (Multi-tabs Junior, Multi-tabs Baby, Multi-tabs Baby);
- Pikovit (Slovenia).